Unleashing the Power of Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Review on R&D Breakthroughs
Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride's R&D Progress
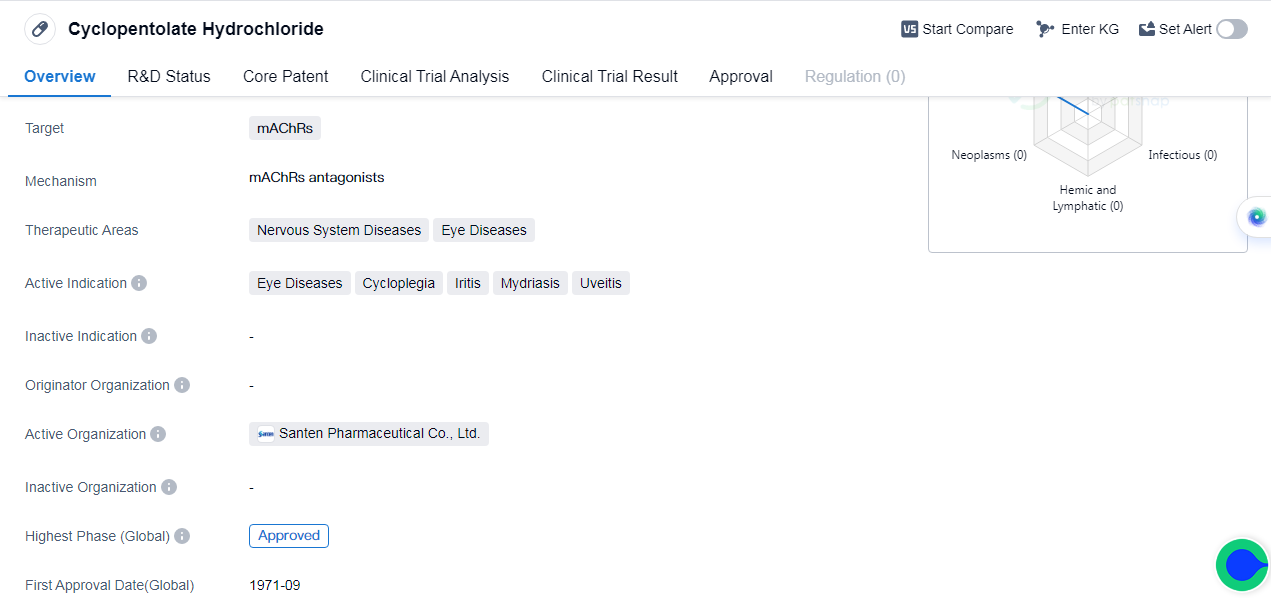
Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). The drug has been approved for use in multiple countries, including Japan, since September 1971.
It is used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases and eye diseases. The latter includes cycloplegia, iritis, mydriasis, and uveitis. These conditions involve inflammation or dysfunction of the eye, and Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride helps to alleviate symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride is classified as a small molecule drug, the type of drug is typically orally administered and can easily penetrate cell membranes, allowing for efficient absorption and distribution throughout the body.
The highest phase of development for Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride is approved globally, and the first approval of Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride occurred in September 1971 in Japan. This suggests that the drug has a long history of use and has been available to patients for several decades.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride: mAChRs antagonists
mAChRs antagonists refers to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists. These are a class of drugs that block the action of acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors in the body. Muscarinic receptors are a type of acetylcholine receptor existed in various tissues and organs, including the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and smooth muscle cells.
By antagonizing or inhibiting the activity of muscarinic receptors, mAChRs antagonists can have various effects depending on the specific receptor subtype being targeted. These effects may include relaxation of smooth muscles, decreased secretion of certain glands, and inhibition of certain nerve signals.
In a biomedical perspective, mAChRs antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of various medical conditions. For example, they can be used to treat overactive bladder by reducing bladder muscle contractions. They are also used in the management of certain gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome, to alleviate symptoms like abdominal pain and cramping.
Additionally, mAChRs antagonists can be used in the field of anesthesia to prevent or reverse the effects of excessive acetylcholine activity during surgery. They can help reduce excessive secretions and prevent bradycardia caused by excessive stimulation of muscarinic receptors.
Overall, mAChRs antagonists play a crucial role in modulating the effects of acetylcholine in the body and have therapeutic applications in various medical conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride
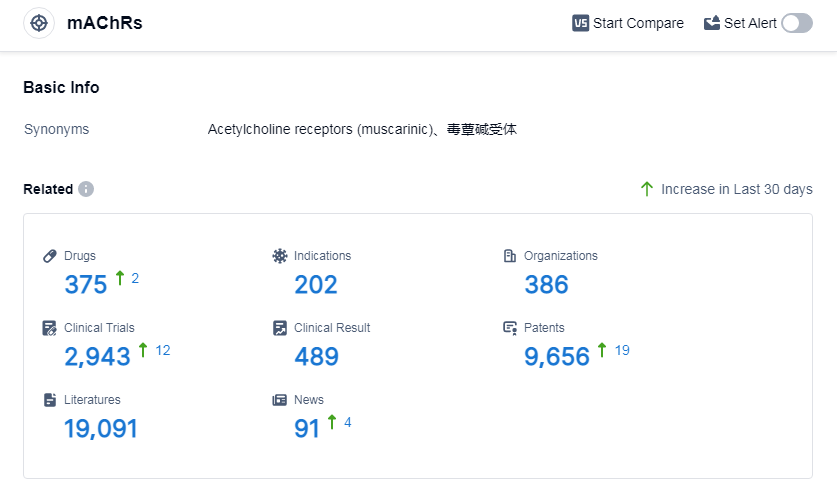
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 5 Sep 2023, there are a total of 375 mAChRs drugs worldwide, from 386 organizations, covering 202 indications, and conducting 2943 clinical trials.
Overall, the analysis suggests a competitive and dynamic landscape for target mAChRs, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on addressing various indications. And the future development of mAChR-targeted therapies holds promise.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets mAChRs and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and eye diseases. It has been approved for use globally, with its first approval occurring in Japan in September 1971. The drug has a long history of use and has proven to be effective in alleviating symptoms associated with various eye conditions.