Unleashing the Power of Naphazoline Hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Review on R&D Breakthroughs
Naphazoline Hydrochloride's R&D Progress
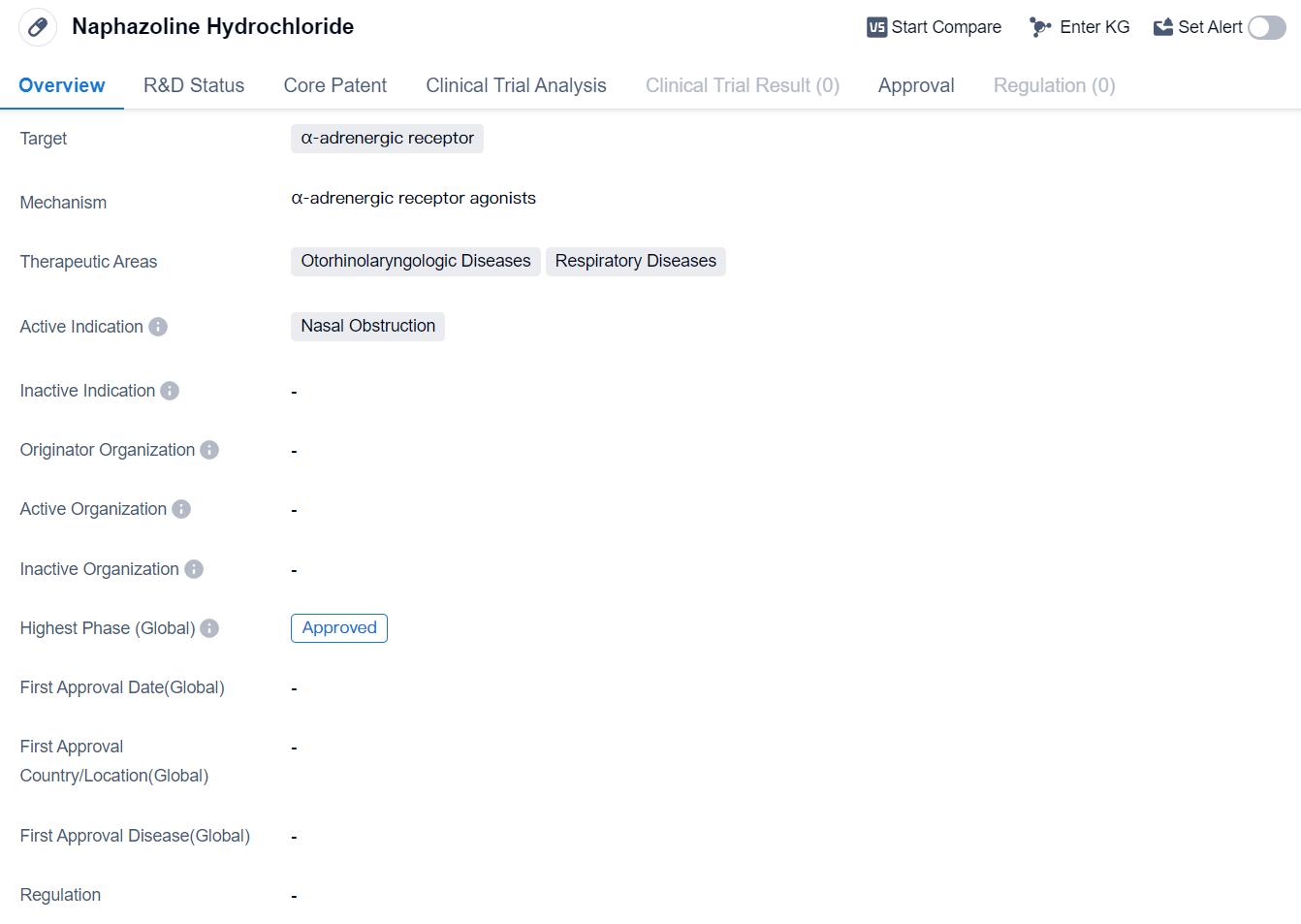
Naphazoline Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the α-adrenergic receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of otorhinolaryngologic diseases and respiratory diseases, specifically for nasal obstruction.
In terms of its development, Naphazoline Hydrochloride has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
Nasal obstruction is a common symptom associated with various conditions such as allergies, sinusitis, and the common cold. It is characterized by the blockage or congestion of the nasal passages, leading to difficulty in breathing through the nose. Naphazoline Hydrochloride works by stimulating the α-adrenergic receptor, which helps to constrict the blood vessels in the nasal mucosa. This constriction reduces swelling and congestion, thereby relieving nasal obstruction and improving airflow.
The approval of Naphazoline Hydrochloride in the global markets highlights its effectiveness and safety profile. This indicates that it has undergone rigorous clinical trials and regulatory processes to ensure its quality and efficacy. As a result, healthcare professionals can confidently prescribe this drug to patients suffering from nasal obstruction, providing them with relief and improved quality of life.
The therapeutic areas of otorhinolaryngologic diseases and respiratory diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, including allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, and nasal congestion. These conditions can significantly impact an individual's daily life, causing discomfort and impairing their ability to breathe properly. Naphazoline Hydrochloride offers a targeted solution for nasal obstruction, addressing a key symptom of these diseases and providing relief to patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Naphazoline Hydrochloride: α-adrenergic receptor agonist
From a biomedical perspective, α-adrenergic receptor agonists are a class of drugs that bind to and activate α-adrenergic receptors in the body. These receptors are part of the adrenergic system, which is involved in regulating various physiological processes such as blood pressure, heart rate, and smooth muscle contraction.
By binding to α-adrenergic receptors, agonists can mimic the effects of the natural neurotransmitter norepinephrine, which is released by the sympathetic nervous system. This activation leads to vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), increased blood pressure, and other responses depending on the specific subtype of α-adrenergic receptor targeted.
α-adrenergic receptor agonists are used in medicine for various purposes. For example, they can be used as nasal decongestants to relieve congestion by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages. They can also be used to treat conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure), by causing vasoconstriction and reducing blood flow.
It's important to note that there are different subtypes of α-adrenergic receptors (α1 and α2), and agonists can selectively target one or both subtypes. This selectivity allows for specific therapeutic effects and can help minimize side effects. Examples of α-adrenergic receptor agonists include phenylephrine, oxymetazoline, and clonidine.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Naphazoline Hydrochloride
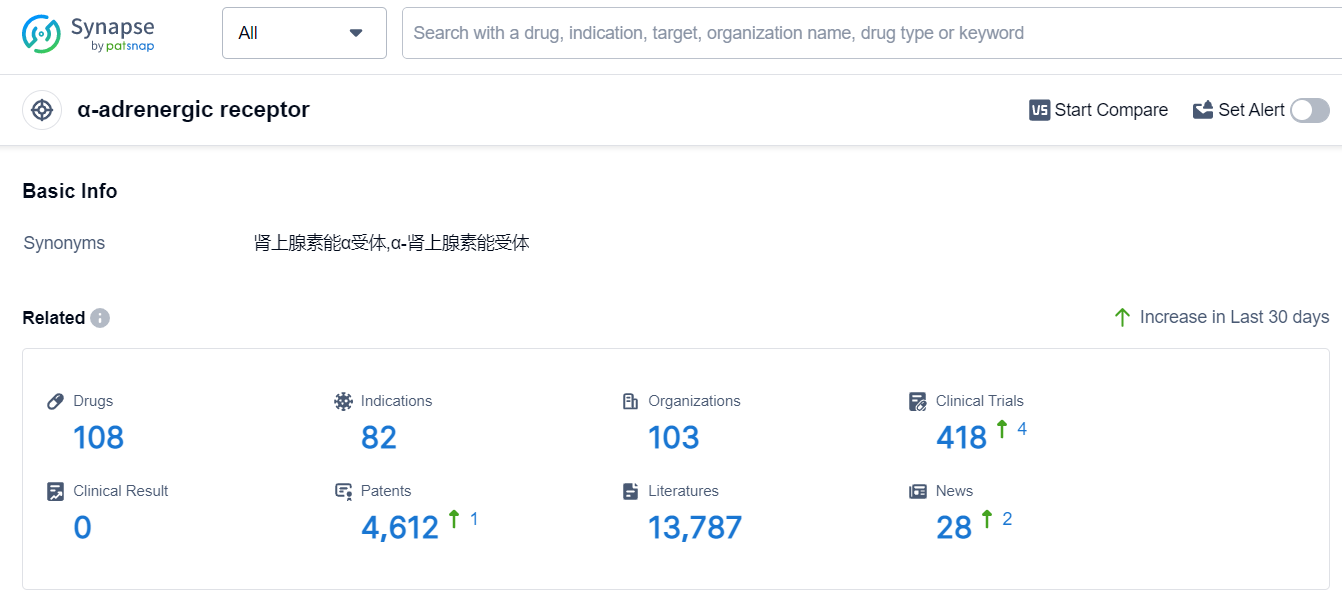
Based on the analysis of the data provided, the current competitive landscape of the target α-adrenergic receptor in the pharmaceutical industry is characterized by the dominance of companies like GSK Plc, Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson Consumer, Inc., Advanz Pharma Corp. Ltd., and Novartis AG. The target is primarily being explored for indications such as common cold, nasal obstruction, rhinitis, allergic, hypertension, and arrhythmias, cardiac. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly under this target, indicating intense competition. China is the country developing fastest under this target, followed by the United States, the European Union, and Japan. The future development of the target α-adrenergic receptor is expected to continue with a focus on respiratory and cardiovascular indications, with small molecule drugs leading the way.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 108 α-adrenergic receptor drugs worldwide, from 103 organizations, covering 82 indications, and conducting 418 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Naphazoline Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the α-adrenergic receptor and is approved for the treatment of nasal obstruction. Its approval in the global markets signifies its efficacy and safety in relieving nasal congestion associated with otorhinolaryngologic and respiratory diseases. This drug offers a valuable solution for patients suffering from nasal obstruction, improving their ability to breathe and enhancing their overall well-being.