Deep Scientific Insights on Metreleptin's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action
Metreleptin's R&D Progress
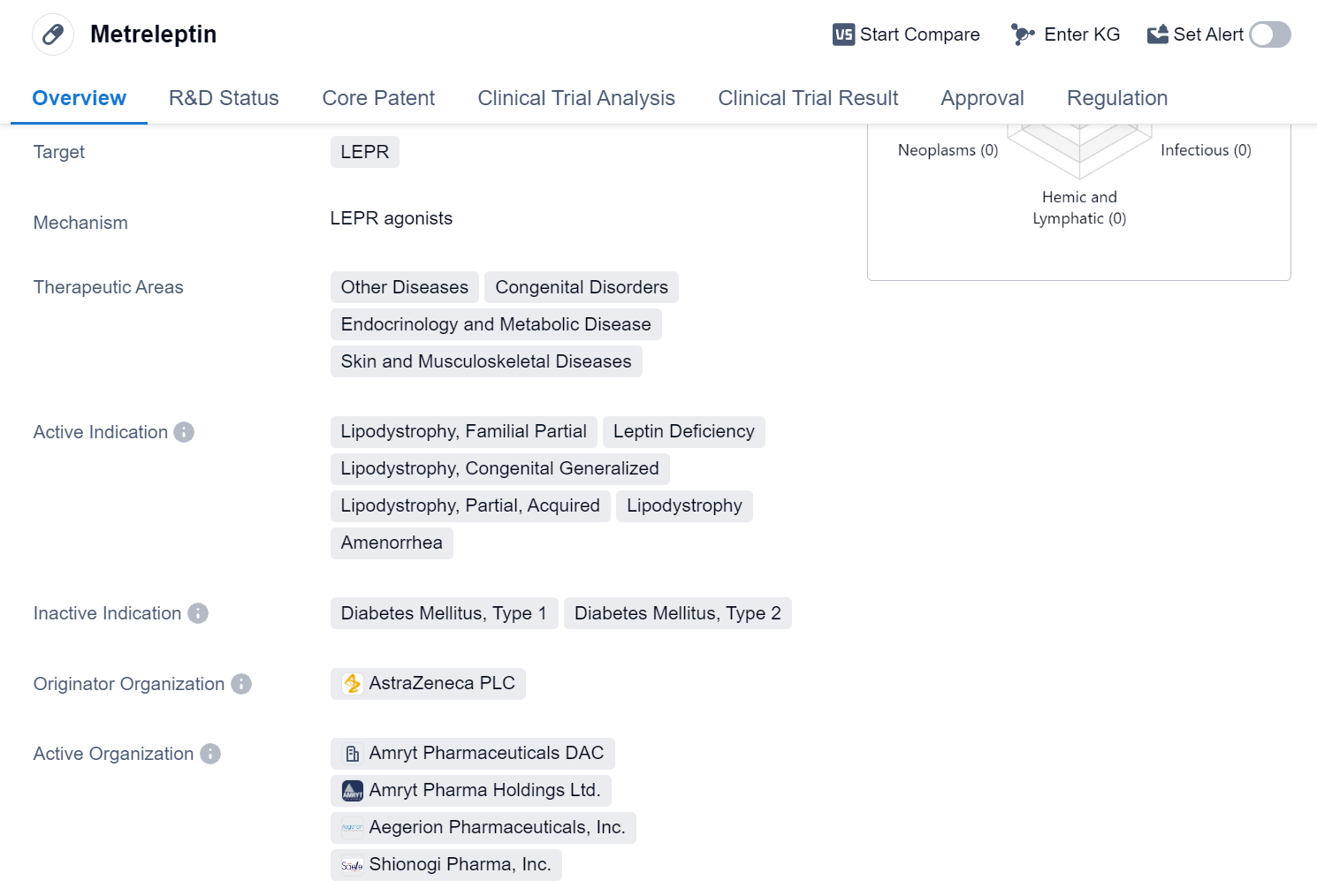
Metreleptin is a hormone drug that targets the LEPR (leptin receptor) and is used in the treatment of various diseases and disorders. It falls under the therapeutic areas of Other Diseases, Congenital Disorders, Endocrinology and Metabolic Disease, as well as Skin and Musculoskeletal Diseases.
The active indications for Metreleptin include Lipodystrophy, Familial Partial, Leptin Deficiency, Lipodystrophy, Congenital Generalized, Lipodystrophy, Partial, Acquired, and Amenorrhea. These conditions are characterized by abnormalities in fat distribution, leading to metabolic and hormonal imbalances.
Metreleptin was first approved globally in March 2013, with Japan being the first country to grant approval. The drug is developed by AstraZeneca PLC, a prominent pharmaceutical organization.
In terms of regulatory status, Metreleptin has been designated as a Fast Track and Orphan Drug. Fast Track designation is granted to drugs that address unmet medical needs and have the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. Orphan Drug designation is given to drugs intended for the treatment of rare diseases, providing incentives for their development.
As a hormone drug targeting the LEPR, Metreleptin aims to restore hormonal balance and improve metabolic function in patients with lipodystrophy and related disorders.
The therapeutic areas covered by Metreleptin indicate its potential to address a wide range of diseases and disorders beyond lipodystrophy. This suggests that the drug may have broader applications in the field of endocrinology and metabolic diseases, as well as in the treatment of skin and musculoskeletal conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Metreleptin: LEPR agonists
LEPR agonists are a type of drug that act on the leptin receptor (LEPR). Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that plays a crucial role in regulating energy balance and body weight. The LEPR agonists bind to and activate the LEPR, mimicking the effects of leptin.
From a biomedical perspective, LEPR agonists can be used to treat conditions associated with leptin deficiency or resistance, such as obesity. By activating the LEPR, these agonists can help regulate appetite, increase energy expenditure, and promote weight loss.
It's worth noting that LEPR agonists are still under development and not yet widely available as approved medications. However, research in this area holds promise for potential therapeutic interventions in the future.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Metreleptin
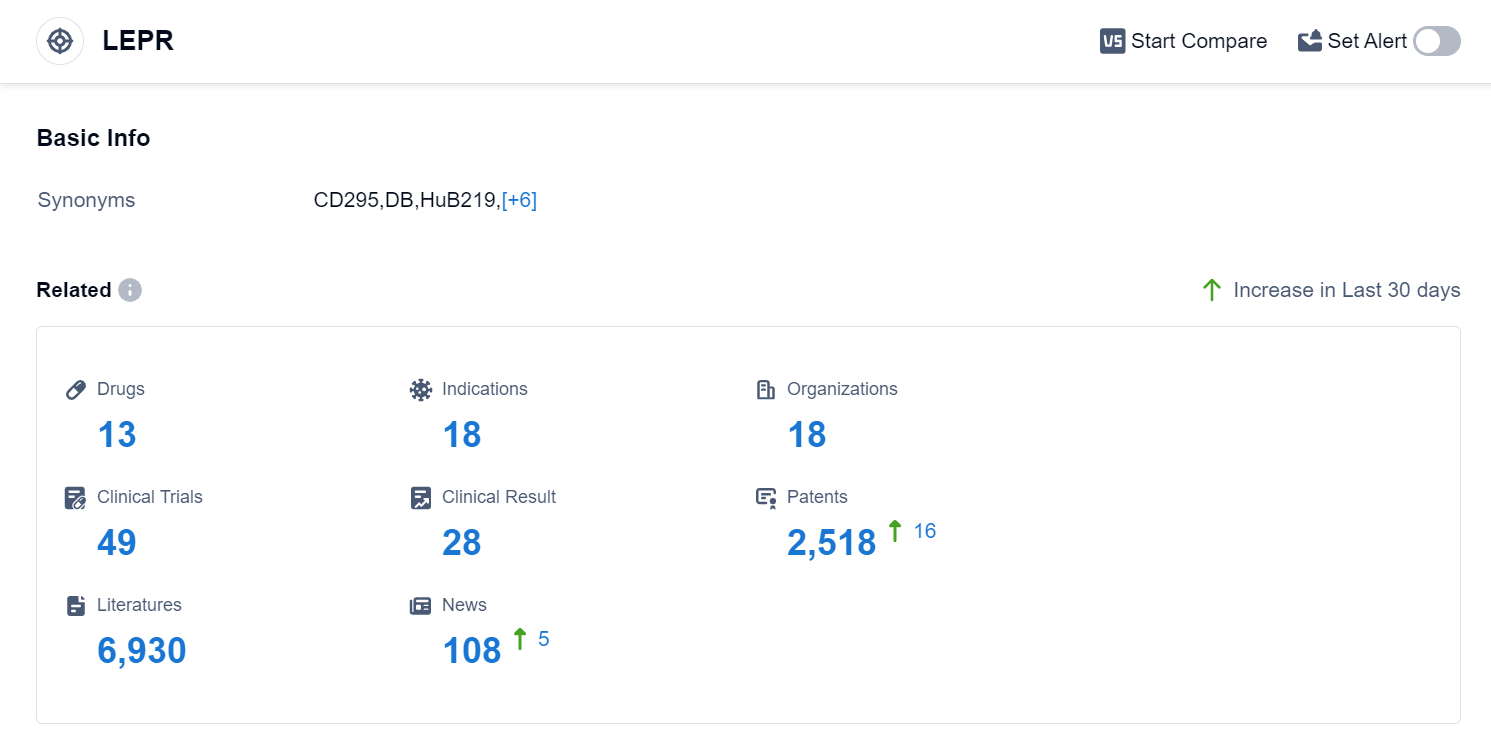
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 13 LEPR drugs worldwide, from 18 organizations, covering 18 indications, and conducting 49 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the target LEPR, it can be concluded that Amryt Pharma Plc, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. are the companies growing fastest under this target. The highest stage of development for drugs targeting LEPR is the Approved phase, with indications such as Lipodystrophy, Leptin Deficiency, and Lipodystrophy, Congenital Generalized. Hormone and Monoclonal antibody-based drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating potential competition around innovative drugs. The United States is leading in terms of development, followed by other countries like the European Union, Liechtenstein, United Kingdom, and Japan. Further research is needed to assess the progress in China. Overall, the target LEPR presents opportunities for further development and competition in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Metreleptin's approval and regulatory designations position it as a promising drug in the field of biomedicine. Its ability to target the LEPR and address various indications related to lipodystrophy and hormonal imbalances make it a valuable addition to the pharmaceutical industry's arsenal in combating these diseases.