Ixabepilone: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Ixabepilone's R&D Progress
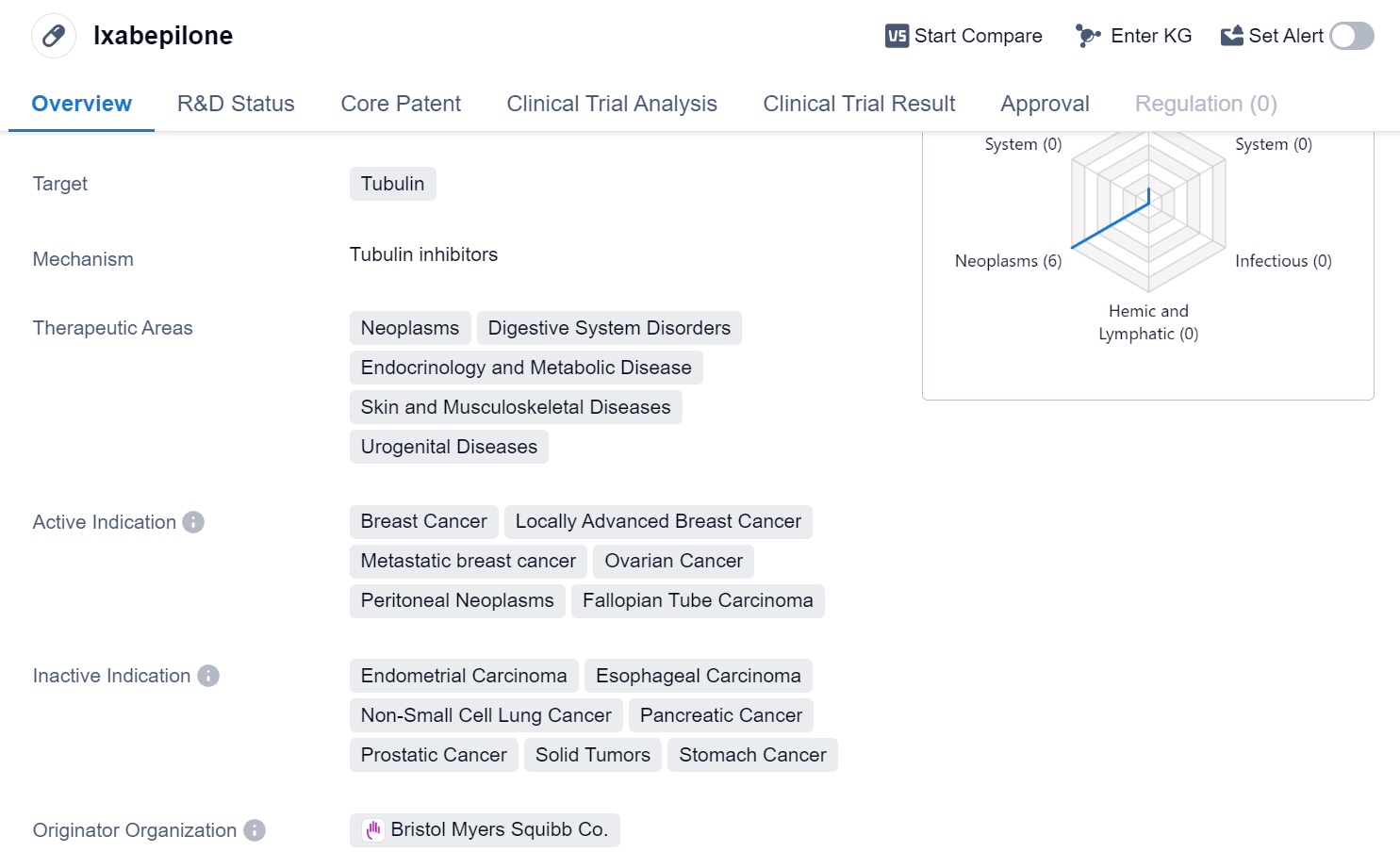
Ixabepilone is a small molecule drug that targets tubulin, a protein involved in cell division. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, digestive system disorders, endocrinology and metabolic disease, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, and urogenital diseases. The drug is primarily indicated for the treatment of breast cancer, including locally advanced breast cancer and metastatic breast cancer. It is also approved for the treatment of ovarian cancer, peritoneal neoplasms, and fallopian tube carcinoma.
The originator organization of Ixabepilone is Bristol Myers Squibb Co., a renowned pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development and has been approved for use globally. Its first approval date in the global market was in October 2007, with the United States being the first country to approve its use.
Ixabepilone's mechanism of action involves targeting tubulin, which plays a crucial role in cell division. By interfering with tubulin, the drug disrupts the formation of microtubules, which are essential for cell division and growth. This disruption ultimately leads to the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
The approval of Ixabepilone for various indications, particularly breast cancer, provides healthcare professionals with an additional treatment option for patients. Breast cancer is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening disease, and the availability of effective drugs like Ixabepilone is crucial in improving patient outcomes.
As a small molecule drug, Ixabepilone offers advantages such as oral administration and potential for formulation into different dosage forms. These characteristics contribute to its convenience and ease of use for patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Ixabepilone: Tubulin inhibitors
Tubulin inhibitors are a type of drugs that target tubulin, a protein involved in the formation of microtubules. Microtubules play a crucial role in various cellular processes, including cell division, intracellular transport, and maintenance of cell shape. By inhibiting tubulin, these drugs disrupt the normal function of microtubules, leading to impaired cell division and growth.
From a biomedical perspective, tubulin inhibitors are commonly used in cancer treatment. Cancer cells often have a higher rate of cell division compared to normal cells, and microtubules are essential for cell division. Tubulin inhibitors can selectively target rapidly dividing cancer cells and prevent them from dividing further, thereby inhibiting tumor growth.
There are different classes of tubulin inhibitors, including taxanes and vinca alkaloids. Taxanes, such as paclitaxel and docetaxel, stabilize microtubules and prevent their disassembly, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells. Vinca alkaloids, such as vincristine and vinblastine, bind to tubulin and prevent the formation of microtubules, disrupting cell division.
Overall, tubulin inhibitors are important therapeutic agents in the field of biomedicine, particularly in the treatment of cancer. They offer a targeted approach to inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Ixabepilone
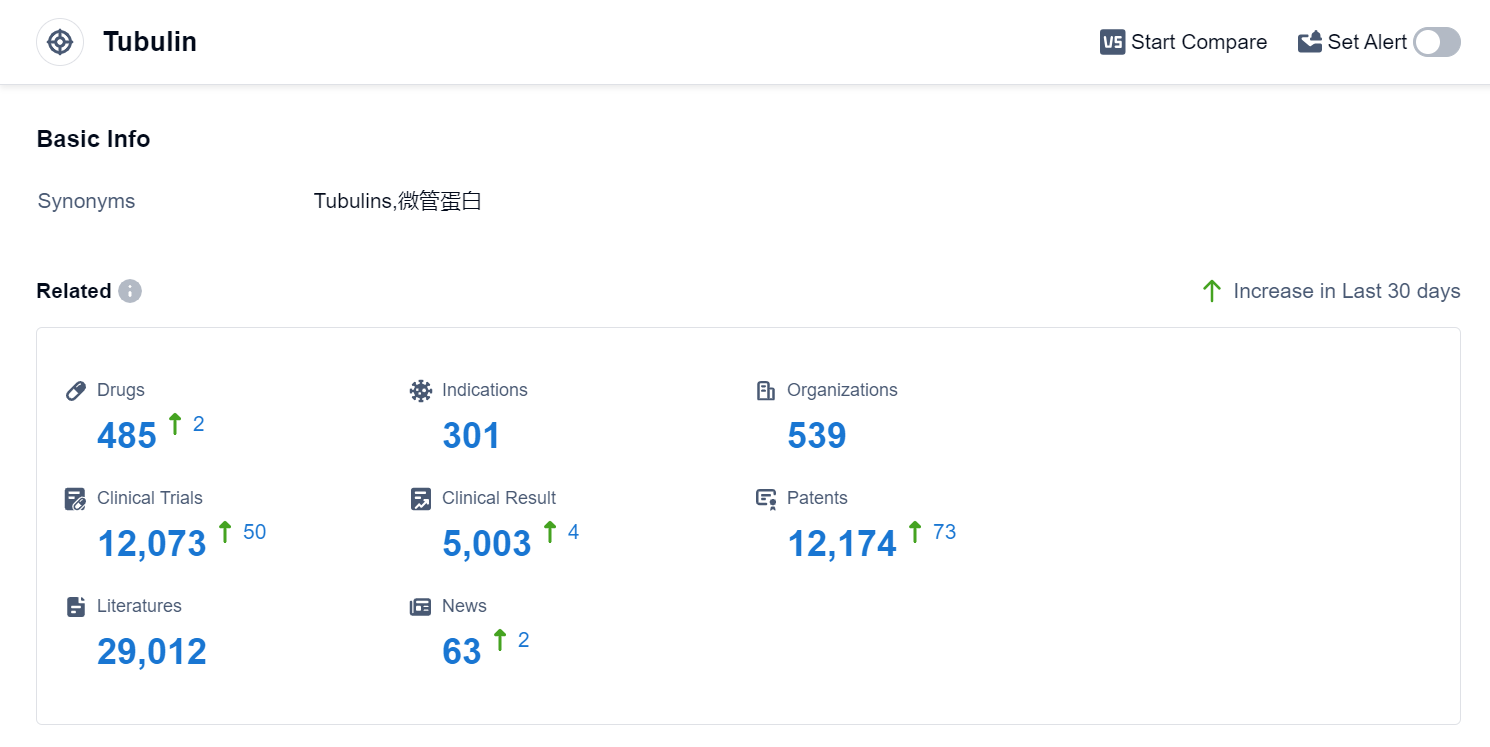
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 485 Tubulin drugs worldwide, from 539 organizations, covering 301 indications, and conducting 12073 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target Tubulin in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with several companies actively developing drugs for various indications. Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Roche Holding AG, Seagen Inc., Sanofi, and Novartis AG are the companies growing fastest under this target, with a high number of drugs in different stages of development. The most common indications for Tubulin-targeting drugs include breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and metastatic breast cancer. Small molecule drugs, monoclonal antibodies, and ADCs are the drug types progressing most rapidly. China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under this target, with China showing significant progress in terms of approved and preclinical drugs. The future development of Tubulin-targeting therapies holds promise for the treatment of various types of cancer.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Ixabepilone is a small molecule drug developed by Bristol Myers Squibb Co. that targets tubulin. It has been approved for use in various therapeutic areas, with its primary indication being breast cancer. The drug has reached the highest phase of development and has been approved globally, including in China. Its approval provides healthcare professionals with an additional treatment option for patients with breast cancer and other related indications.