Doxofylline: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Doxofylline's R&D Progress
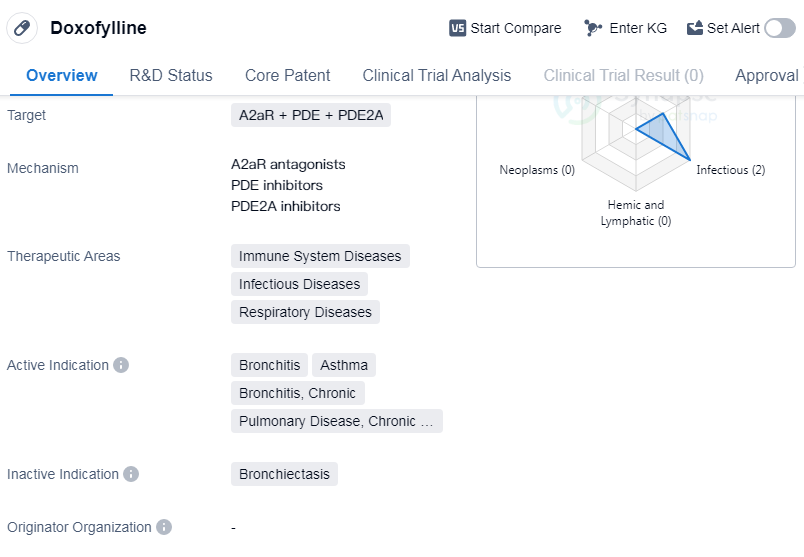
Doxofylline is a small molecule drug that targets A2aR, PDE, and PDE2A. It is primarily used in the treatment of immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and respiratory diseases. The active indications for Doxofylline include bronchitis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Doxofylline has reached the highest phase of approval globally. It was first approved in Italy in October 1988. The drug is regulated as an orphan drug, indicating that it is used to treat rare diseases or conditions.
As a small molecule drug, Doxofylline is designed to interact with specific targets in the body, namely A2aR, PDE, and PDE2A. These targets are involved in various physiological processes, particularly those related to the immune system, infectious diseases, and respiratory diseases. By modulating the activity of these targets, Doxofylline aims to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall health of patients with conditions such as bronchitis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and COPD.
The approval of Doxofylline in multiple countries, including Italy, suggests that it has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure its safety and efficacy. Its orphan drug status further highlights its potential in addressing unmet medical needs for rare diseases or conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Doxofylline: A2aR antagonists, PDE inhibitors and PDE2A inhibitors
A2aR antagonists are compounds that specifically block the adenosine A2a receptor. Adenosine A2a receptors are a type of G protein-coupled receptor found in various tissues, including the brain, heart, and immune cells. By blocking these receptors, A2aR antagonists can modulate the effects of adenosine, a signaling molecule involved in various physiological processes.
PDE inhibitors refer to a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of phosphodiesterase enzymes. Phosphodiesterases are enzymes that break down cyclic nucleotides, such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). By inhibiting phosphodiesterase activity, PDE inhibitors increase the levels of cAMP and/or cGMP, leading to various physiological effects depending on the specific phosphodiesterase targeted.
PDE2A inhibitors specifically inhibit the activity of phosphodiesterase 2A, which is a subtype of the phosphodiesterase enzyme family. PDE2A is primarily found in the brain and plays a role in regulating the levels of cAMP and cGMP. By inhibiting PDE2A, these inhibitors can modulate the levels of these cyclic nucleotides, potentially influencing neuronal signaling and other processes in the brain.
In summary, A2aR antagonists block a specific receptor involved in adenosine signaling, PDE inhibitors inhibit phosphodiesterase enzymes to increase levels of cyclic nucleotides, and PDE2A inhibitors specifically target the subtype of phosphodiesterase 2A.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Doxofylline
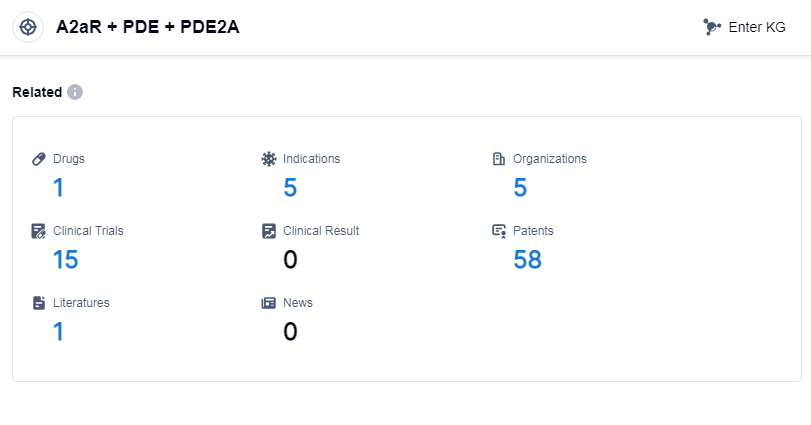
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 15 Sep 2023, there are a total of 1 A2aR, PDE and PDE2A drugs worldwide, from 5 organizations, covering 5 indications, and conducting 15 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target A2aR, PDE and PDE2A reveals a competitive landscape with companies like Heilongjiang Fuhe Huaxing Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd. and ABC leading in terms of R&D progress and drug approval. The approved drugs under this target have shown effectiveness in treating respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and pulmonary disease.
The development of small molecule drugs indicates a focus on innovative drug development, with potential competition from biosimilars. Further analysis of the research and development institutions involved in the development of these drugs is necessary to understand the competitive dynamics.
Countries/locations such as the European Union, China, and the Philippines have shown progress in the development of drugs under this target. China's progress in particular highlights its potential as a key player in the pharmaceutical industry.
Overall, the target A2aR, PDE and PDE2A presents opportunities for further research and development, with potential for innovative drug development and collaborations between companies and countries/locations.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Doxofylline is a small molecule drug that targets A2aR, PDE, and PDE2A. It is approved for use in the treatment of immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and respiratory diseases, including bronchitis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and COPD. Its approval in Italy in 1988 and its orphan drug status indicate its potential in addressing unmet medical needs. However, further information is needed to fully understand its clinical profile and potential benefits.