Exploring Methylergonovine Maleate's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Methylergonovine Maleate's R&D Progress
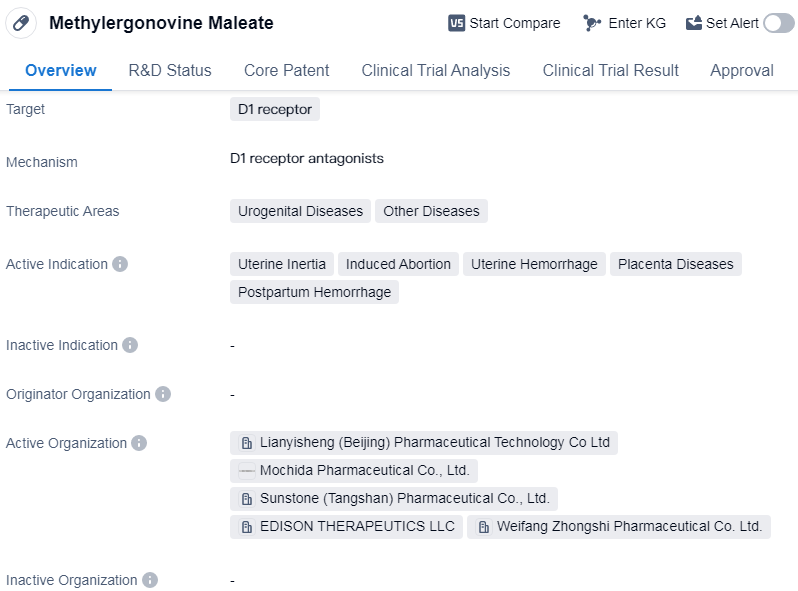
Methylergonovine Maleate is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the D1 receptor. It is used in the treatment of various urogenital diseases and other diseases. The drug has been approved for use globally and has reached phase 3 of clinical trials in China.
The active indications for Methylergonovine Maleate include uterine inertia, induced abortion, uterine hemorrhage, placenta diseases, and postpartum hemorrhage. These conditions are often associated with complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Methylergonovine Maleate was first approved for use in the United States in November 1946. It has since gained global recognition and has been widely used in the medical field for several decades.
As a small molecule drug, Methylergonovine Maleate is designed to interact with the D1 receptor, which plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. By targeting this receptor, the drug aims to regulate and improve the symptoms associated with urogenital diseases and other related conditions.
Methylergonovine Maleate 's highest phase of development is approved globally, indicating that it has successfully completed all necessary clinical trials and has been deemed safe and effective for use. In China, the drug has reached phase 3, suggesting that it is in the advanced stages of clinical testing.
Methylergonovine Maleate's first approval in the United States highlights its long-standing presence in the pharmaceutical market. Over the years, it has gained recognition for its therapeutic benefits and has become a trusted option for healthcare professionals in managing urogenital diseases and related complications.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Methylergonovine Maleate: D1 receptor antagonists
D1 receptor antagonists are a type of medication that block or inhibit the activity of D1 receptors in the body. D1 receptors are a subtype of dopamine receptors, which are proteins existed on the surface of cells in various tissues and organs. These receptors are involved in the transmission of signals mediated by the neurotransmitter dopamine.
From a biomedical perspective, D1 receptor antagonists are commonly used in the field of psychiatry to treat conditions such as schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. By blocking the D1 receptors, these medications can help to reduce the excessive dopamine activity in certain areas of the brain, which is believed to contribute to the symptoms of psychosis.
By inhibiting the D1 receptors, D1 receptor antagonists can help to alleviate symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking that are characteristic of psychotic disorders. These medications are typically prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may also include other antipsychotic medications and psychosocial interventions.
It is important to note that D1 receptor antagonists may have side effects, including sedation, movement disorders, and metabolic changes. The specific side effects and effectiveness of these medications can vary depending on the individual and the specific medication used. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Methylergonovine Maleate
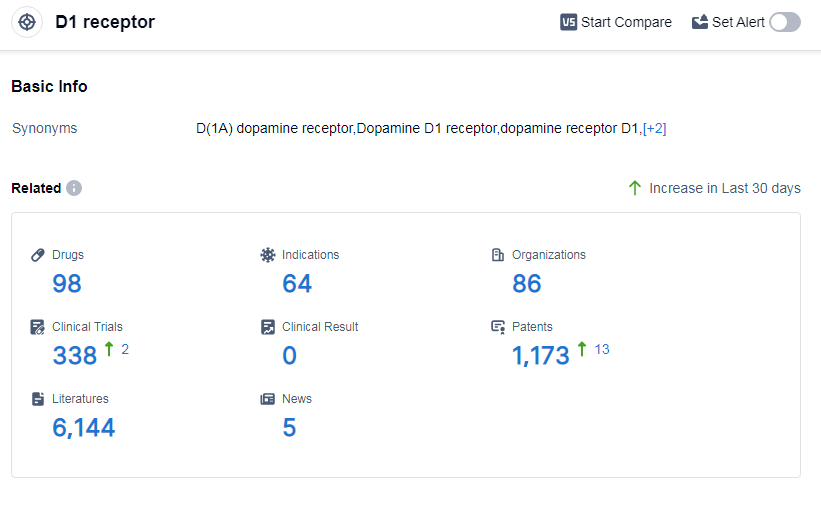
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 9 Sep 2023, there are a total of 98 D1 receptor drugs worldwide, from 86 organizations, covering 64 indications, and conducting 338 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target D1 receptor in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Pfizer Inc., Eli Lilly & Co., and Alkermes Plc are among the companies growing fastest under this target, with a diverse portfolio of drugs in various stages of development. The highest stage of development is the approved phase, with drugs targeting indications such as Parkinson disease, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and hypertension. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition around the innovative drugs. The United States, European Union, China, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest under this target, with progress also observed in other countries. Overall, the target D1 receptor shows promise for future development in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Methylergonovine Maleate is a small molecule drug that targets the D1 receptor. It is used in the treatment of urogenital diseases and other related conditions. The drug has been approved globally and has reached phase 3 of clinical trials in China. Methylergonovine Maleate was first approved in the United States in 1946 and has since become a widely recognized and trusted option in the pharmaceutical industry.