Decoding Methoxsalen: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Methoxsalen's R&D Progress
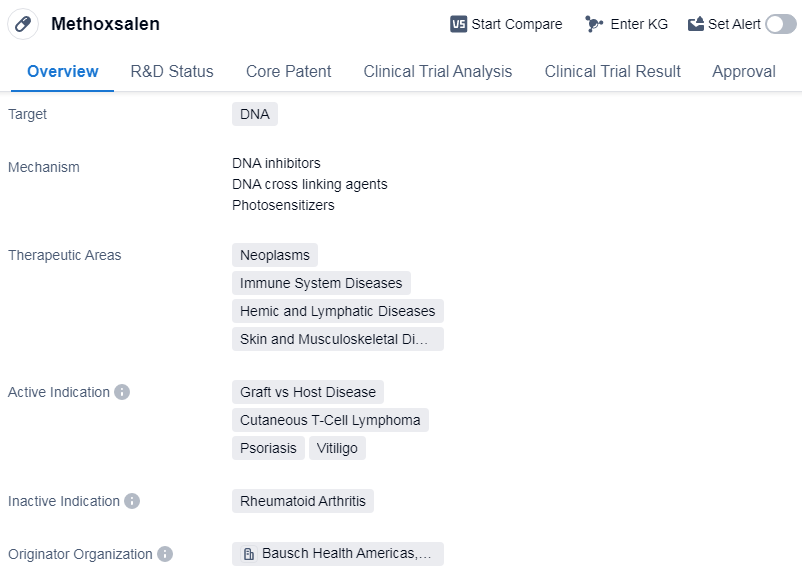
Methoxsalen is a small molecule drug that targets DNA and is used in the treatment of various therapeutic areas including neoplasms, immune system diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. It has been approved for the treatment of graft vs host disease, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psoriasis, and vitiligo.
The drug was first approved in the United States in December 1954 and is currently marketed by Bausch Health Americas, Inc. It is classified as an orphan drug, indicating that it is used to treat rare diseases or conditions that affect a small number of patients.
Methoxsalen works by binding to DNA and forming covalent bonds, which can lead to the inhibition of DNA synthesis and cell division. This mechanism of action makes it particularly effective in the treatment of diseases that involve abnormal cell growth, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Methoxsalen has undergone extensive clinical trials and has reached the highest phase of approval globally. This indicates that it has been thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy and has met the necessary regulatory requirements for market authorization.
Methoxsalen has been shown to be effective in managing the symptoms of graft vs host disease. It is also used in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects the skin. Additionally, it has been found to be beneficial in the management of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition, and vitiligo, a disorder characterized by the loss of skin color.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Methoxsalen: DNA inhibitors, DNA cross linking agents and Photosensitizers
DNA inhibitors are substances that interfere with the replication or transcription of DNA, thus inhibiting the growth and division of cells. From a biomedical perspective, DNA inhibitors can be used as chemotherapeutic agents to target rapidly dividing cancer cells. They work by disrupting the DNA synthesis process, preventing cancer cells from proliferating.
DNA cross-linking agents are compounds that form covalent bonds between two strands of DNA, leading to the formation of cross-links. These cross-links can prevent DNA replication and transcription, ultimately inhibiting cell division. Biomedical applications of DNA cross-linking agents include cancer treatment, where they can induce DNA damage and cell death in cancer cells.
Photosensitizers are substances that become activated upon exposure to light of a specific wavelength. When activated, they generate reactive oxygen species that can cause damage to cellular components, including DNA. In biomedicine, photosensitizers are used in photodynamic therapy (PDT) for the treatment of cancer and other diseases. During PDT, a photosensitizer is administered to the patient and then activated by light, leading to the destruction of targeted cells. Examples of photosensitizers include porphyrins and phthalocyanines.
In summary, DNA inhibitors, DNA cross-linking agents, and photosensitizers are all compounds with different mechanisms of action that can be used in biomedical applications such as cancer treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Methoxsalen
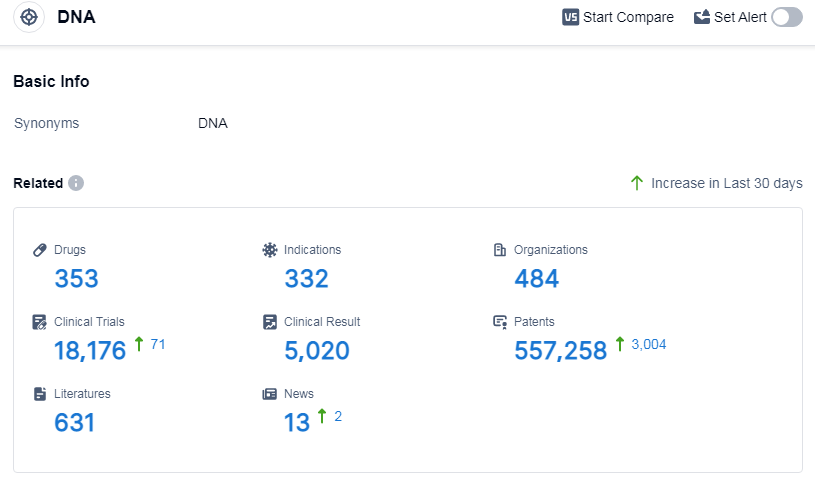
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 353 DNA drugs worldwide, from 484 organizations, covering 332 indications, and conducting 18176 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target DNA reveals that Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Baxter International, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Johnson & Johnson are the companies growing fastest under the current target. The most common indications for drugs targeting the DNA include lymphoma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, neoplasms, and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Small molecule drugs, monoclonal antibodies, and ADCs are the drug types progressing most rapidly. China, the United States, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current target DNA.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Methoxsalen is a well-established drug with a long history of use in the treatment of various diseases. Its approval as an orphan drug highlights its importance in addressing unmet medical needs for patients with rare conditions.