Exploring Camptothecin's Revolutionary R&D Successes and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Camptothecin's R&D Progress
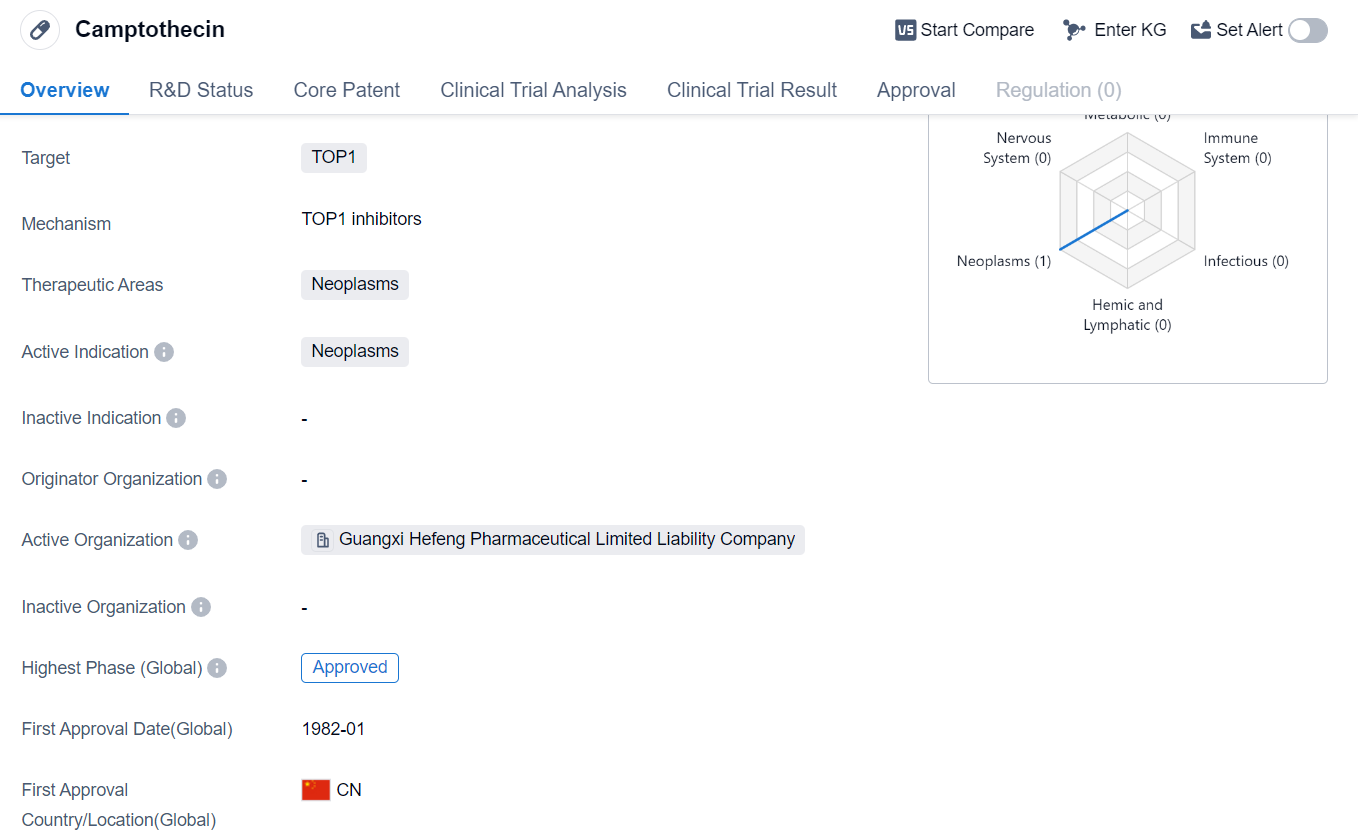
Camptothecin is a small molecule drug that is primarily used in the treatment of neoplasms, which are abnormal growths or tumors. It specifically targets the TOP1 enzyme, which plays a crucial role in DNA replication and repair. By inhibiting this enzyme, camptothecin prevents cancer cells from dividing and multiplying, ultimately leading to their death.
The drug has been approved for use in the global market. Its first approval date was in January 1982, with China being the first country to approve its use. This suggests that camptothecin has a long history of use and has been well-established in the field of oncology.
Camptothecin's approval for neoplasms highlights its potential as a treatment option for various types of cancer. Neoplasms encompass a wide range of malignancies, including solid tumors and hematological malignancies. The drug's mechanism of action, targeting the TOP1 enzyme, makes it particularly effective against rapidly dividing cancer cells.
As a small molecule drug, camptothecin is likely to have advantages such as ease of synthesis, oral bioavailability, and potential for formulation into different dosage forms. These characteristics make it a versatile drug that can be administered through various routes, including oral, intravenous, or intramuscular.
Given its long history of approval and use, camptothecin may have established itself as a standard treatment option for certain types of neoplasms. Its efficacy and safety profile have likely been extensively studied and documented, providing healthcare professionals with confidence in its use.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Camptothecin: TOP1 inhibitor
TOP1 inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme topoisomerase I (TOP1). Topoisomerases are enzymes that play a crucial role in DNA replication and repair by helping to unwind and untangle the DNA strands. TOP1 is a specific type of topoisomerase that is involved in the relaxation of supercoiled DNA during transcription.
In the context of biomedicine, TOP1 inhibitors are primarily used as anticancer drugs. By inhibiting the activity of TOP1, these inhibitors prevent the enzyme from repairing DNA damage caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This leads to the accumulation of DNA strand breaks, ultimately causing cell death and inhibiting tumor growth.
TOP1 inhibitors have shown effectiveness in treating various types of cancer, including colorectal, ovarian, and lung cancer. Examples of TOP1 inhibitors commonly used in clinical practice include irinotecan and topotecan. These drugs are typically administered intravenously and may be used alone or in combination with other chemotherapy agents.
It is important to note that TOP1 inhibitors can have side effects, including gastrointestinal issues, myelosuppression (reduced production of blood cells), and increased susceptibility to infections. Therefore, their use requires careful monitoring and management by healthcare professionals.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Camptothecin
The current competitive landscape of target TOP1 is characterized by the involvement of multiple companies from various countries/locations. Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Les Laboratoires Servier SAS, Gilead Sciences, Inc., Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd., AstraZeneca PLC, Ipsen SA, GSK Plc, Everest Medicines II (HK) Limited, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corp., Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., Novartis AG, Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Nihon Servier Co., Ltd., Alfresa Holdings Corp., Guangxi Hefeng Pharmaceutical Limited Liability Company, Grand Pharmaceutical Group Ltd., MOH Holdings Pte Ltd., and Baxter International, Inc. are among the companies that are growing fastest under this target.
The R&D progress of these companies varies, with some having drugs in advanced stages of development such as Phase 3, Phase 2, and Phase 1.
Several drugs under the current target TOP1 have been approved for relevant indications, including various types of cancers. The drug types that are progressing most rapidly include Small molecule drug, Antibody drug conjugate (ADC), and Monoclonal antibody.
China, United States, European Union, Japan, and other countries/locations are actively involved in the development of drugs under this target. China, in particular, has made significant progress in terms of drug development.
Overall, the current competitive landscape of target TOP1 is dynamic and promising, with multiple companies and countries/locations actively engaged in the development of innovative drugs. The future development of this target holds great potential for advancements in the pharmaceutical industry.
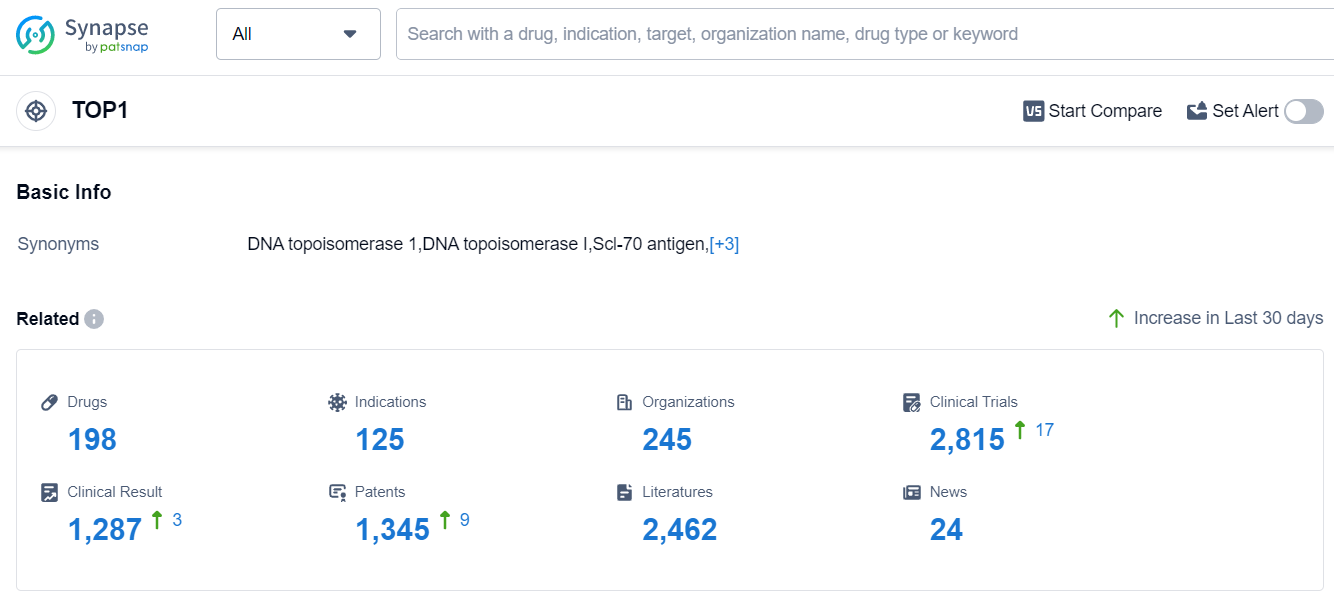
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 198 TOP1 drugs worldwide, from 245 organizations, covering 125 indications, and conducting 2815 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, camptothecin is a small molecule drug that targets the TOP1 enzyme and is approved for the treatment of neoplasms. Its first approval was in China in 1982, and it has since gained global approval. With its established efficacy and safety profile, camptothecin is a valuable treatment option for various types of cancer.