FDA Approves Lilly’s Kisunla™ (donanemab-azbt) for Early Alzheimer’s Treatment
The U.S. FDA has granted approval for Kisunla™ (donanemab-azbt, 350 mg/20 mL once-monthly injection for IV infusion), developed by Eli Lilly and Company, as a treatment for adults exhibiting early symptomatic stages of Alzheimer’s disease. This includes individuals with mild cognitive impairment and those in the mild dementia stage of AD, confirmed by amyloid pathology.
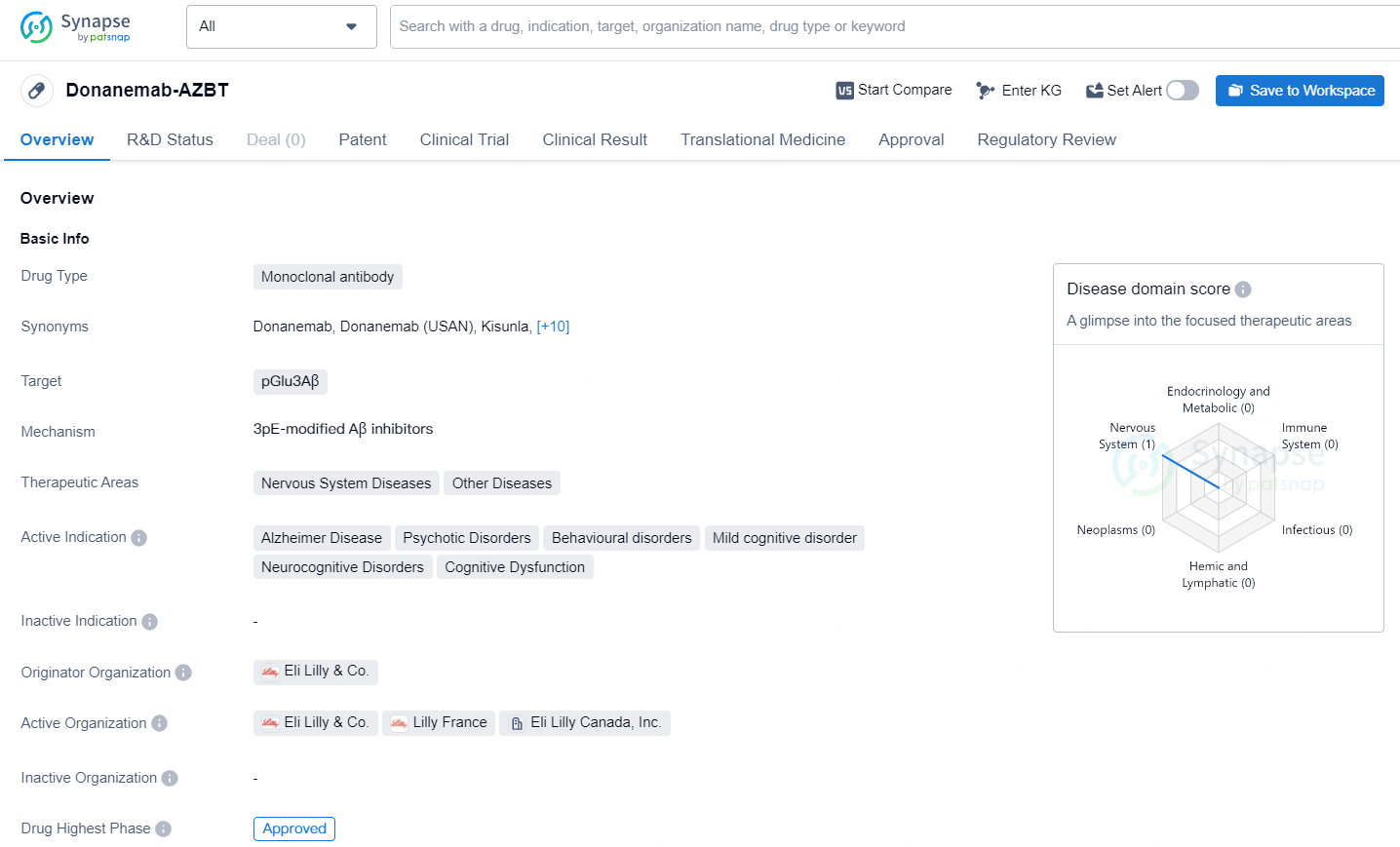
👇Explore more about this drug by clicking the image below. Gain detailed insights into its R&D Status, Core Patent, Clinical Trials and Global Approval Status. Stay informed and updated.
The once-monthly therapy Kisunla stands as the inaugural and exclusive amyloid plaque-targeting treatment demonstrating evidence that cessation of therapy is feasible once amyloid plaques are eradicated. This could lead to reduced treatment expenses and fewer infusions.
"Kisunla has shown highly significant results for individuals with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease, who are in dire need of effective treatment options. We understand that these medications offer the most significant benefits when administered earlier in the disease progression, and we are diligently collaborating with others to enhance detection and diagnosis," stated Anne White, Executive Vice President and President of Lilly Neuroscience at Eli Lilly and Company.
Anne White further expressed gratitude by saying, "Our profound thanks go to the patients and their families for engaging in our clinical trials, and to Lilly scientists and their collaborators, who have persisted through decades of research. With each passing year, an increasing number of people face the risk of this disease, and we are resolute in our mission to improve their lives."
Amyloid is a naturally occurring protein in the body that can aggregate to form amyloid plaques. Excessive amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain is linked to memory and cognitive issues associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Kisunla aids the body in removing this excessive amyloid buildup, thereby slowing the cognitive decline that can impair abilities such as recalling new information, important dates, and appointments; planning and organizing; preparing meals; using household appliances; managing finances; and independently functioning.
"This approval signifies another advancement in evolving the standard of care for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease, which will eventually encompass a range of innovative treatments, offering much-needed hope to the Alzheimer’s community. As a physician, I find the potential to stop treatment encouraging, as it may decrease the out-of-pocket costs and the burden of infusions for eligible patients," commented Howard Fillit, M.D., Co-Founder and Chief Science Officer at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
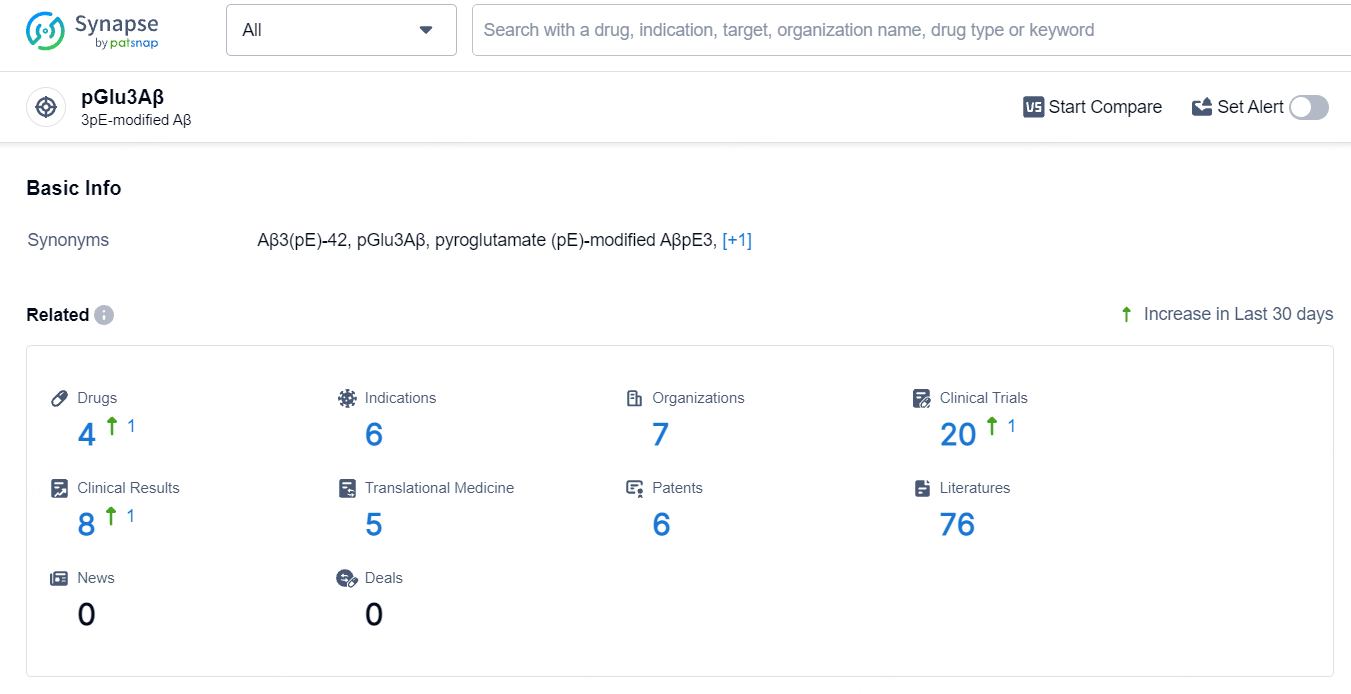
👇Explore the most recent advancements in drug research, indications, organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents related to this target by clicking the image link below. Dive in to gain deeper insights!
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of July 8, 2024, there are 4 investigational drugs for the pGlu3Aβ target, including 6 indications, 7 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 20, and as many as 6 patents.
Donanemab-AZBT is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets pGlu3Aβ and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and other related disorders. Donanemab-AZBT's approval and regulatory designations highlight its potential as a promising treatment option for patients with Alzheimer's disease and related cognitive disorders, and its development represents a significant advancement in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to address these challenging therapeutic areas.