How to find the structure and classification of Infliximab?
Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Developed by Centocor, now part of Johnson & Johnson, Infliximab is classified as a therapeutic protein and is primarily indicated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. It is used to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms in these autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.
Summary of Research Progress:
The research progress of Infliximab has been extensive and impactful. Its mechanism of action involves binding to TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a central role in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. By neutralizing TNF-α, Infliximab prevents the cytokine from binding to its receptors, thereby inhibiting the downstream signaling pathways that lead to inflammation, tissue damage, and immune cell activation. This inhibition results in reduced symptoms and improved quality of life for patients.
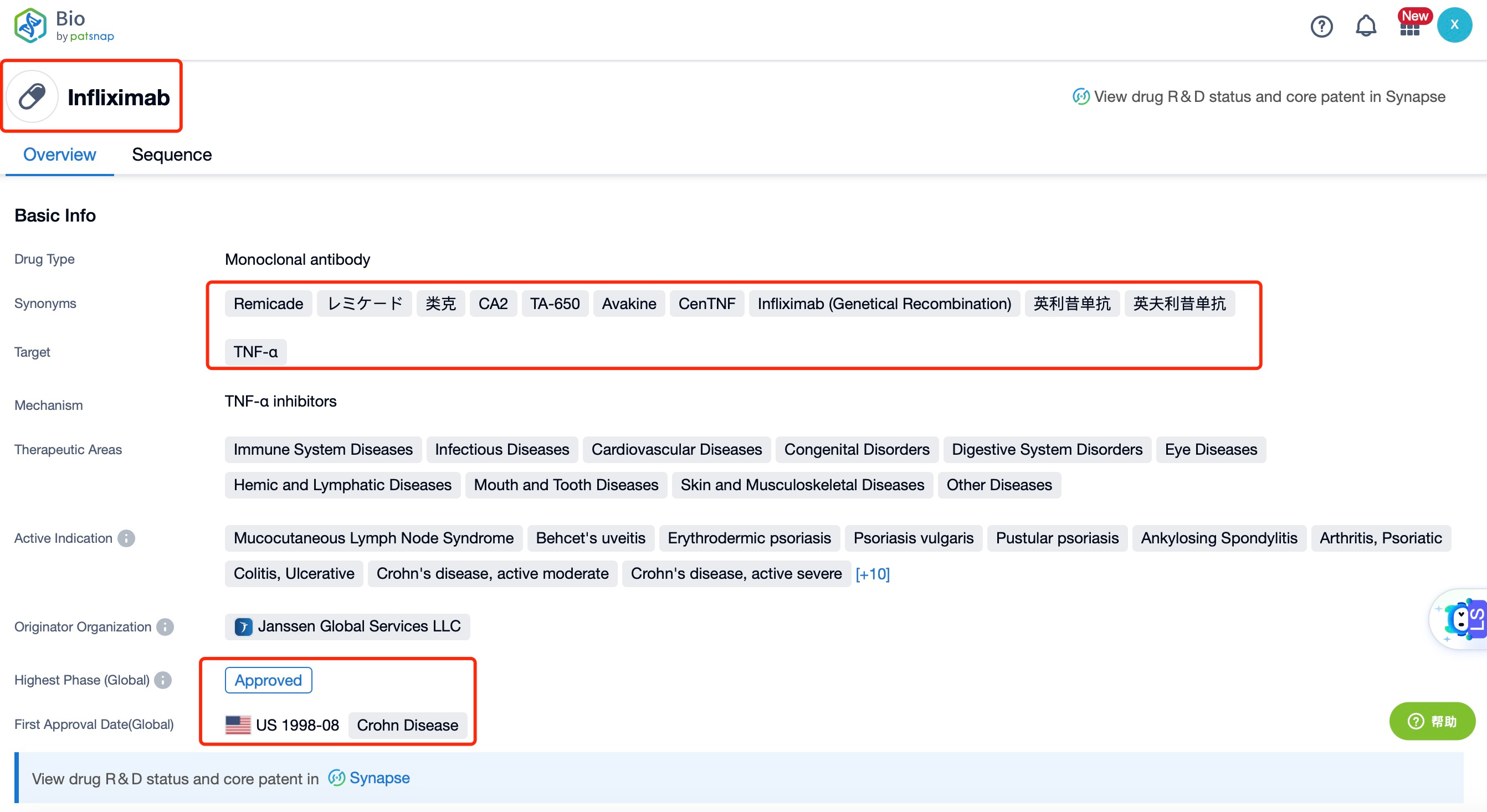
Globally, Infliximab has been approved in numerous countries, including the United States, Europe, and Japan. It received FDA approval in 1998 for the treatment of Crohn's disease and has since been approved for RA, ulcerative colitis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. Infliximab is available in both originator and biosimilar forms, with several biosimilars approved in recent years, including Remsima, Inflectra, and Avsola. These biosimilars have expanded access to the drug, making it more affordable and widely available.
The competitive landscape for Infliximab is dynamic, with several other biologics and small molecules targeting similar pathways. In RA, key competitors include adalimumab (Humira), etanercept (Enbrel), and tocilizumab (Actemra). For Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, competitors include vedolizumab (Entyvio), ustekinumab (Stelara), and golimumab (Simponi). In ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis, competitors include secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz). Despite this competition, Infliximab has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing disease activity and improving patient outcomes.
Type of Immunoglobulin of Infliximab
Infliximab is a chimeric IgG1κ immunoglobulin. Chimeric antibodies are engineered to combine the antigen-binding variable regions from a mouse antibody with the constant regions from a human antibody. This design reduces the immunogenicity of the antibody while maintaining its therapeutic efficacy. The κ light chain is one of the two types of light chains found in immunoglobulins, the other being λ. The κ light chain is more common and provides stability and specificity to the antibody structure.
Light and Heavy Chains and Structural Characteristics of Infliximab
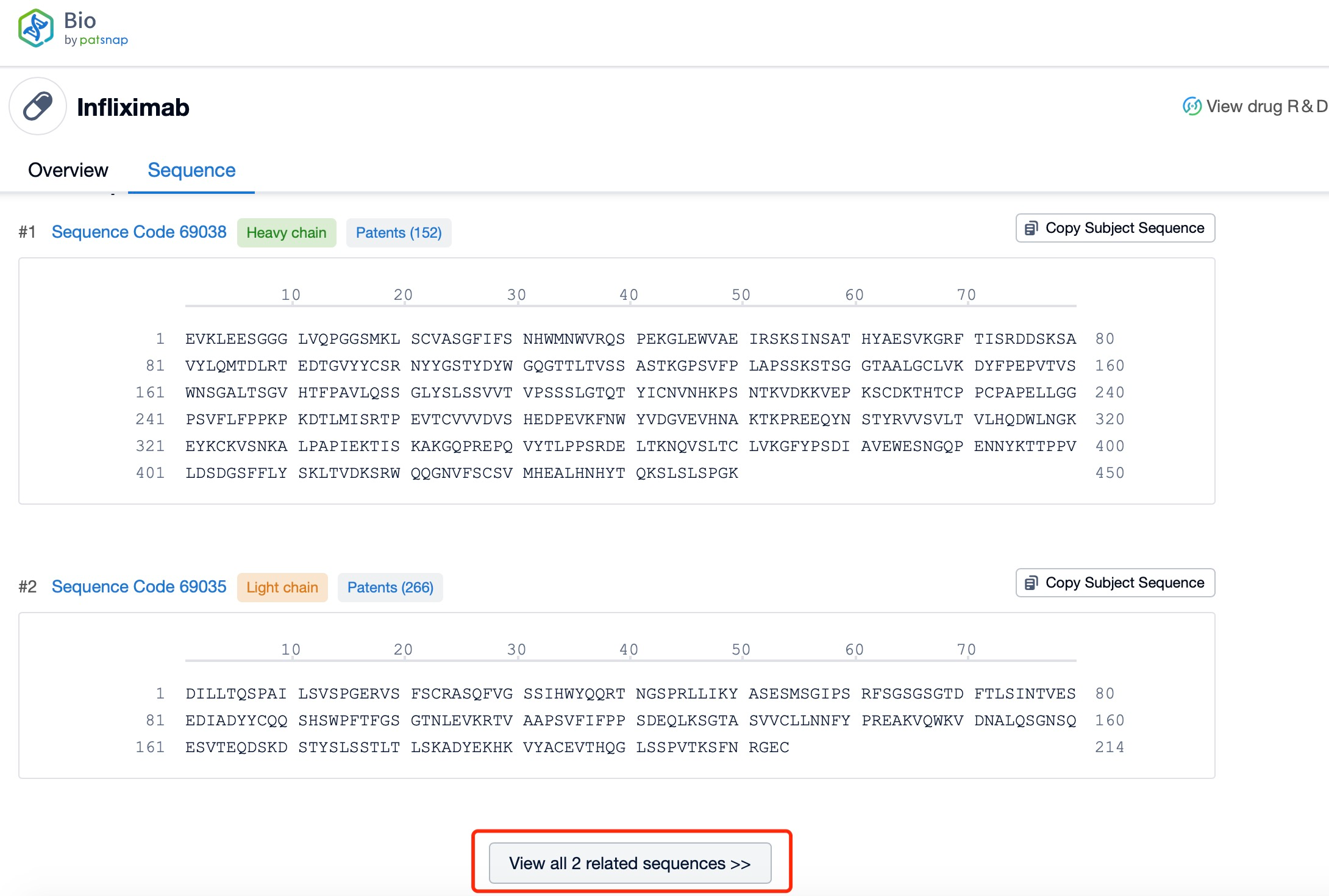
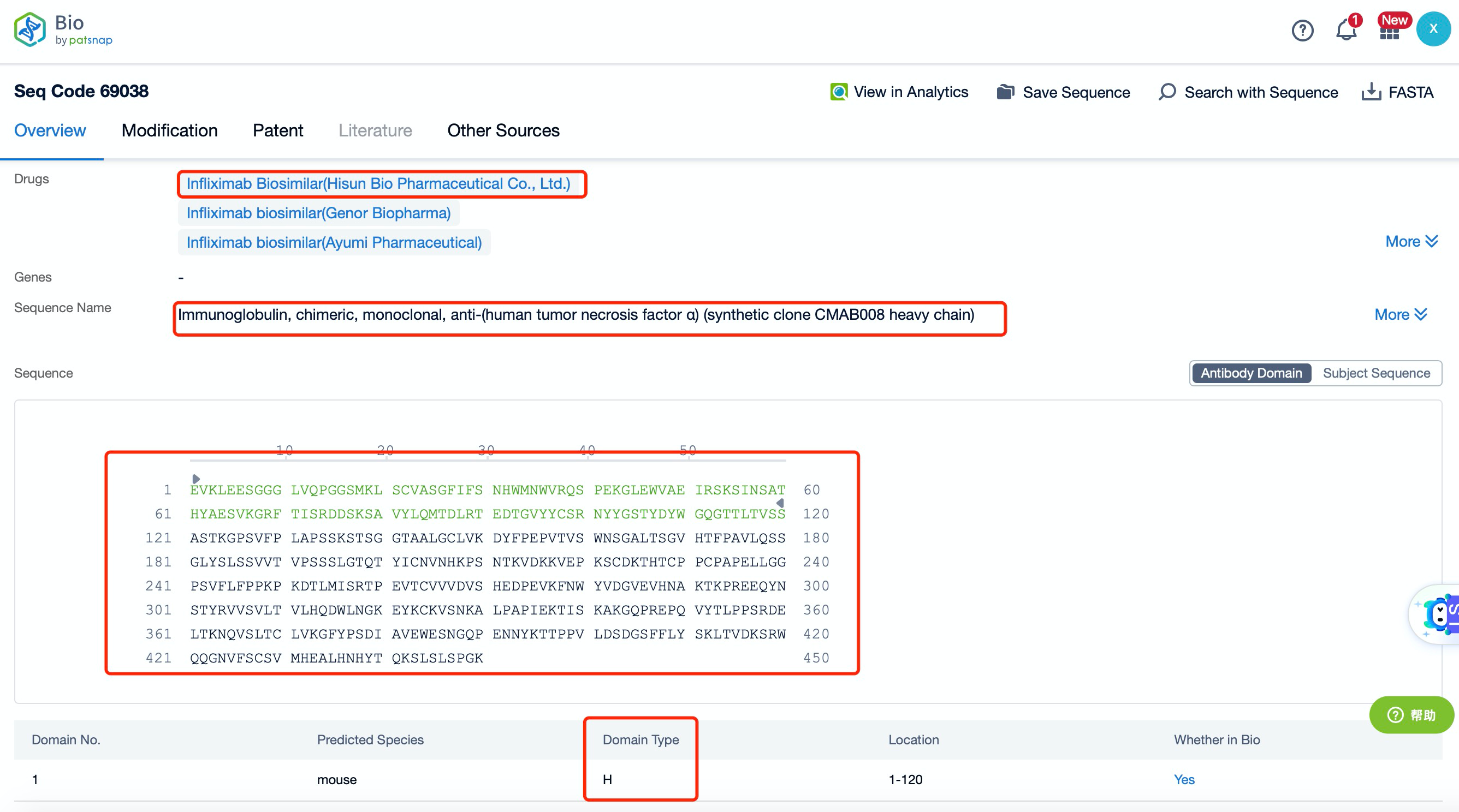
The heavy chain of Infliximab is a chimeric IgG1 molecule, which consists of four domains: variable (VH), constant 1 (CH1), constant 2 (CH2), and constant 3 (CH3). The VH domain is responsible for antigen binding, while the CH1 domain forms part of the Fc region, which is crucial for the antibody's effector functions. The CH2 and CH3 domains are involved in the interaction with Fc receptors and complement proteins, respectively. The Fc region is capable of engaging Fc receptors on immune cells, leading to various effector functions such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
The light chain of Infliximab is a κ chain, which also consists of two domains: variable (VL) and constant (CL). The VL domain pairs with the VH domain to form the antigen-binding site, ensuring high specificity and affinity for the target antigen. The CL domain, like the CH1 domain, contributes to the stability and function of the antibody.
Structurally, Infliximab is a well-characterized and highly specific monoclonal antibody. The variable regions of both the heavy and light chains are designed to recognize and bind to TNF-α with high affinity. This binding prevents TNF-α from binding to its receptors, effectively blocking the downstream signaling pathways that lead to inflammation and tissue damage. The constant regions of the heavy and light chains provide additional functional properties to Infliximab. The Fc region, composed of the CH2 and CH3 domains, is capable of engaging Fc receptors on immune cells, leading to various effector functions such as ADCC and CDC. These functions enhance the therapeutic potential of Infliximab by facilitating the clearance of targeted cells and modulating the immune response.
Summary and Prospect
In summary, Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), making it a valuable therapeutic option for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. Its mechanism of action involves binding to TNF-α and preventing the cytokine from binding to its receptors, thereby inhibiting the downstream signaling pathways that lead to inflammation and tissue damage. Infliximab has been approved globally for multiple indications and has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. As a chimeric IgG1κ immunoglobulin, Infliximab exhibits well-defined structural characteristics that contribute to its high specificity and efficacy. The heavy and light chains, with their respective variable and constant domains, ensure precise antigen binding and robust effector functions, making Infliximab a valuable and effective treatment for a range of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Future research and development efforts will likely focus on optimizing its delivery methods, exploring new indications, and enhancing its therapeutic benefits for patients.
How to find the structure and classification of antibody drugs?
In Patsnap Bio, you can find the sequence and latest research and development advances of all antibody drugs.
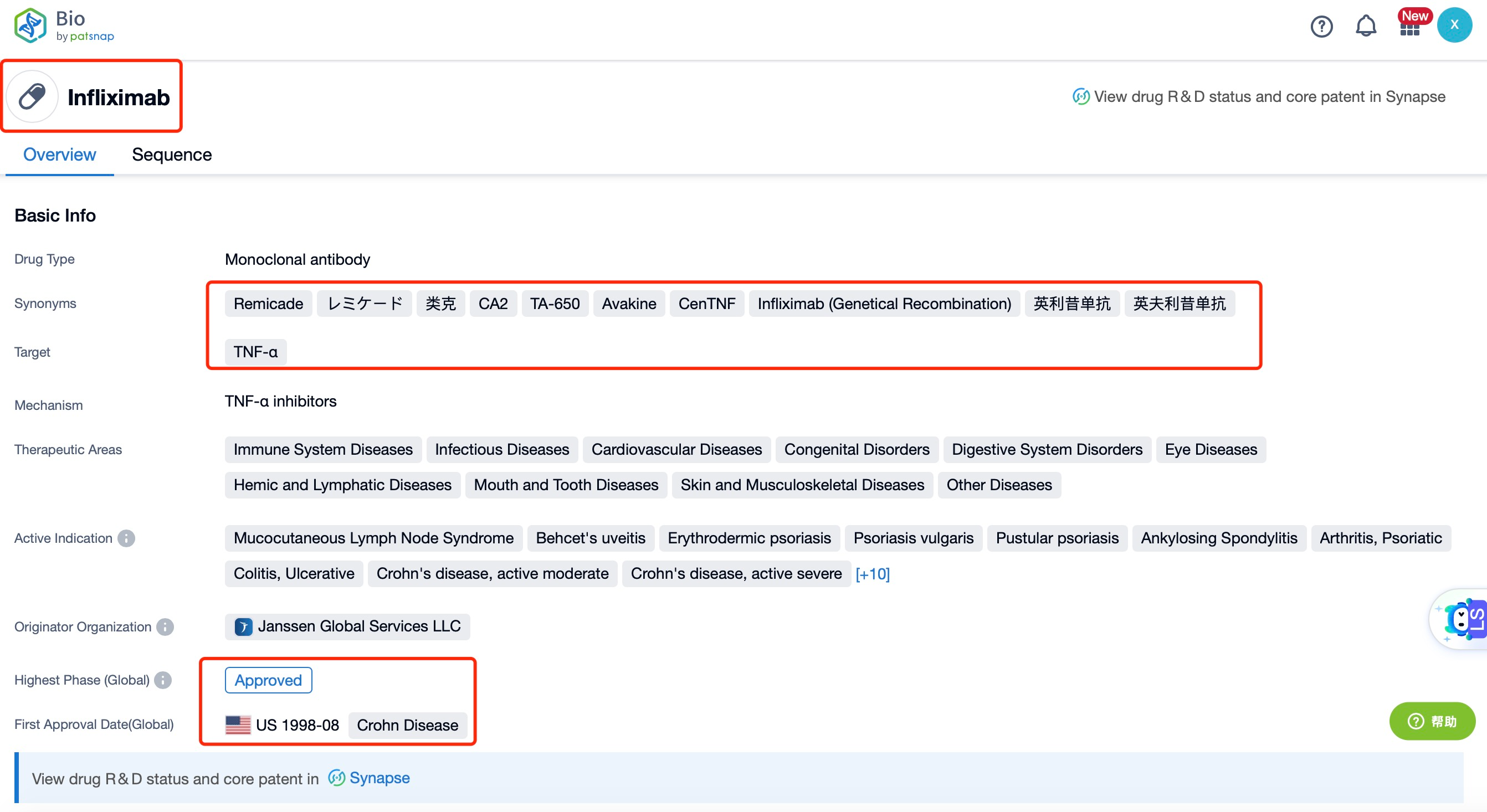
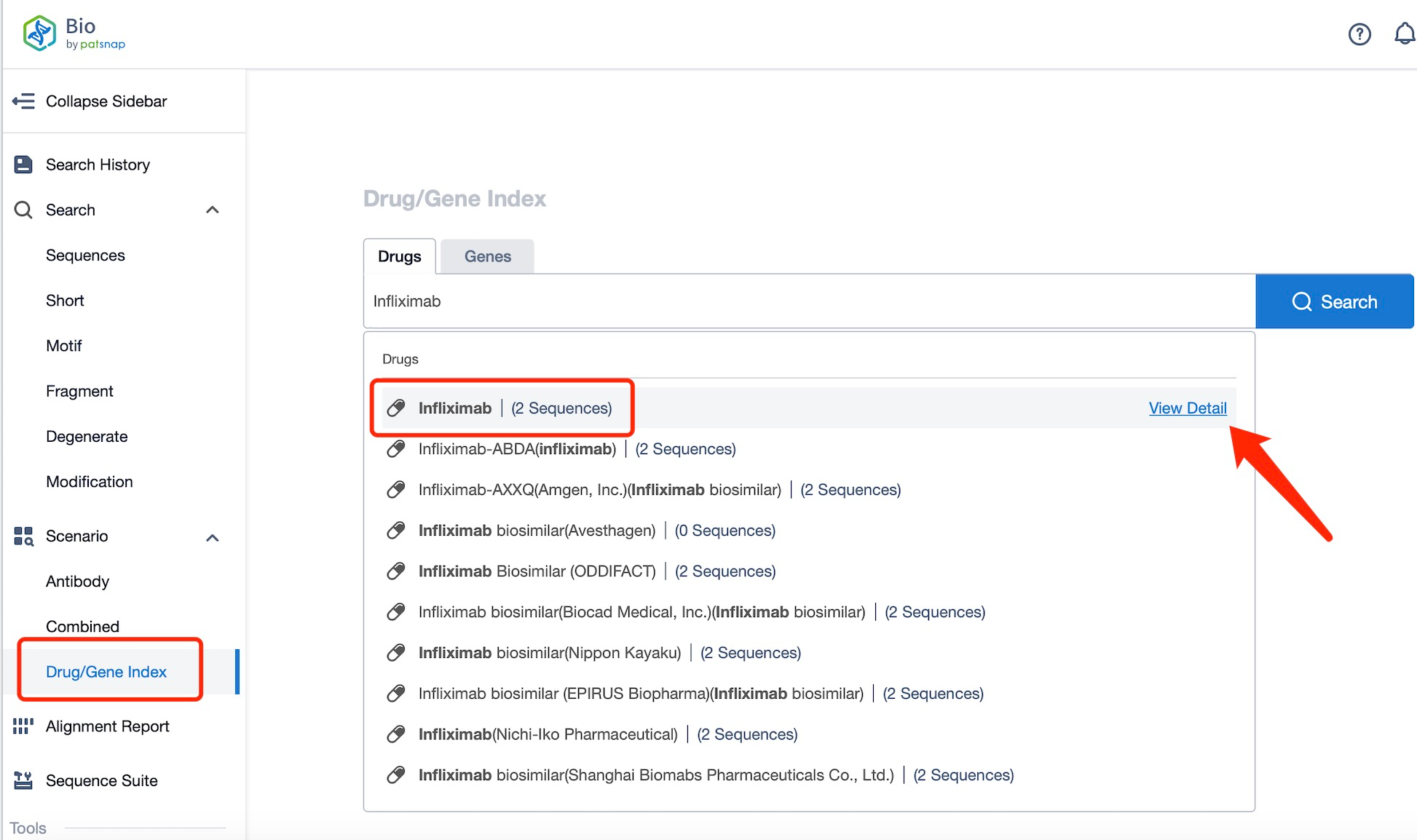
Taking Infliximab as an example, first click on the Drug/Gene Index on the Patsnap Bio homepage. Here you can search for sequence information by drug and gene names. Enter ' Infliximab ' in the search box and click to view the details. On the details page, you can find the basic information and research progress of Infliximab.
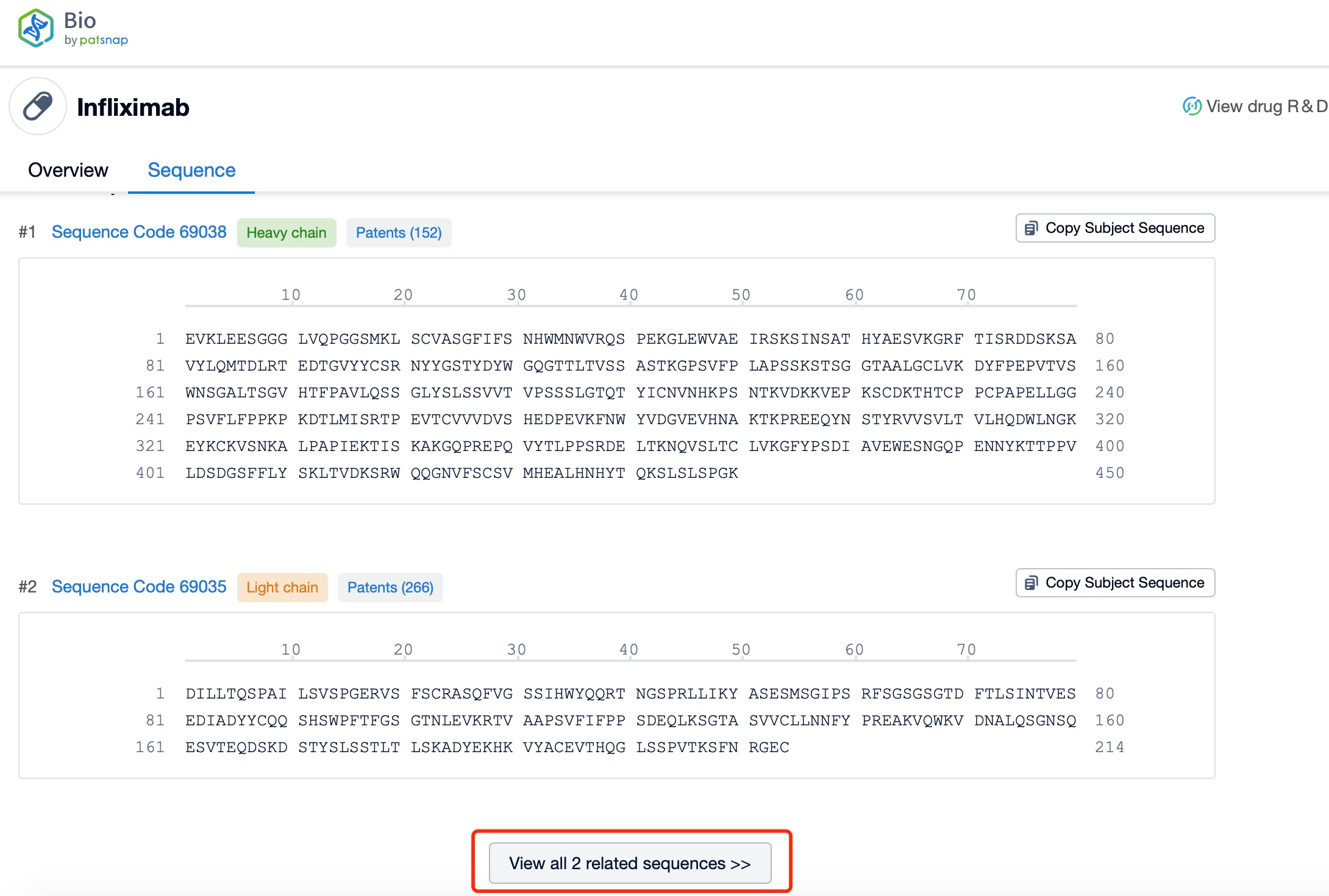
Click "View all related sequences" below the sequence information to search for and retrieve all biological sequences similar to this information.
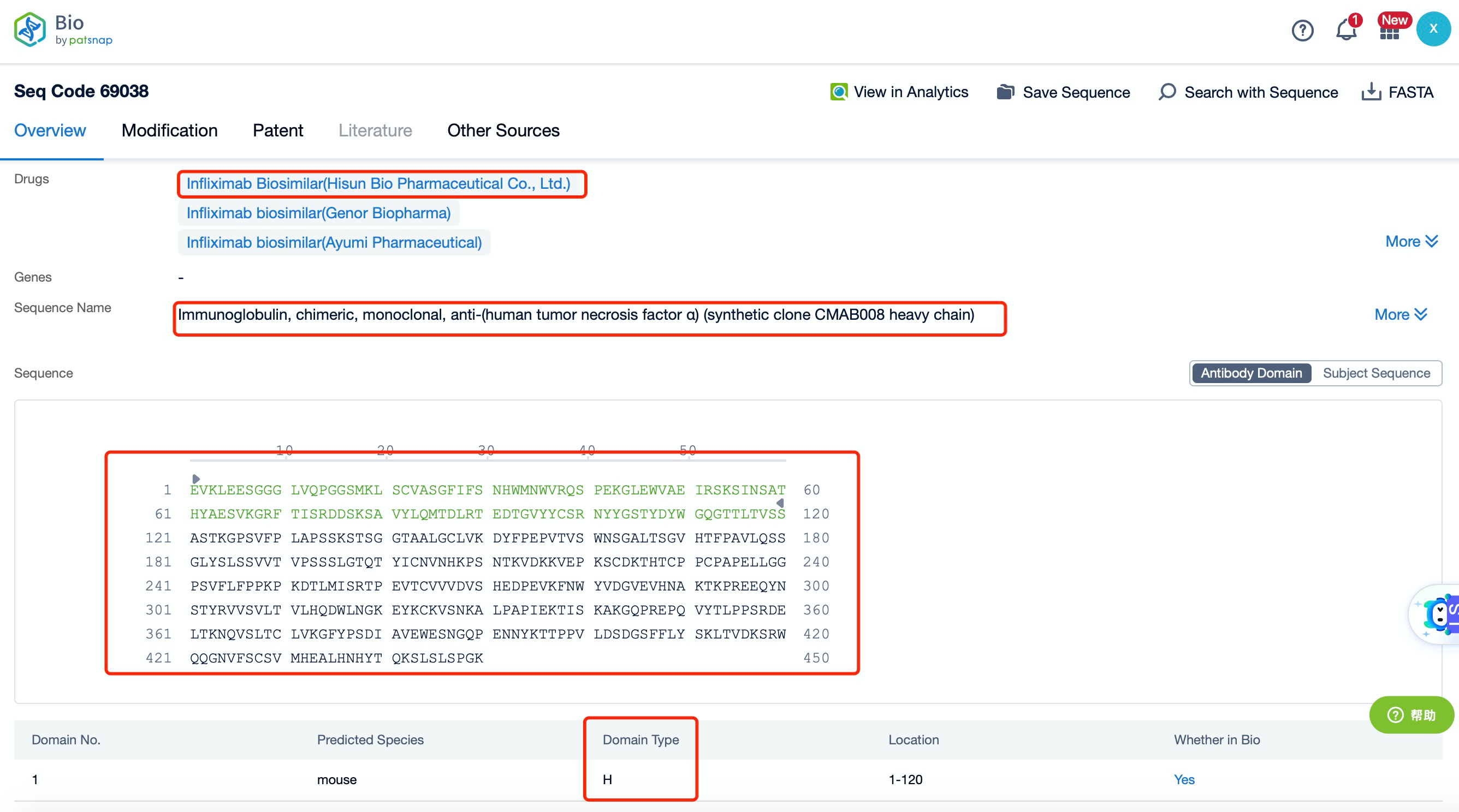
Clicking on the sequence name will provide you with all the basic information of that sequence. Here, you can easily query the sequence and action of the light and light chains of antibodies.
Patsnap Bio helps you turn weeks into minutes with cutting-edge AI-enabled tools built to master the complexities of sequence retrieval and automate IP analysis with precision and ease.