Eisai Gets Favorable CHMP Review for Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease in the EU
Eisai Co., Ltd. and Biogen Inc. have announced that they received a favorable opinion from the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) at the European Medicines Agency (EMA). This opinion endorses the approval of the amyloid-beta (Aβ) monoclonal antibody lecanemab for adult patients diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease (referred to as Early Alzheimer’s disease) who are non-carriers or heterozygotes of apolipoprotein E ε4 (ApoE ε4)* and have confirmed amyloid pathology. Eisai has sought a review of the previous unfavorable opinion issued by the CHMP in July 2024. Following the regulatory procedures of the European Medicines Agency, it is anticipated that the European Commission will reach a final decision regarding the marketing authorization application (MAA) for lecanemab within 67 days after receiving the CHMP’s opinion.
👇Explore more about this drug by clicking the image below. Gain detailed insights into its R&D Status, Core Patent, Clinical Trials and Global Approval Status. Stay informed and updated.
Lecanemab is designed to specifically target both soluble Aβ aggregates (protofibrils**) and insoluble Aβ aggregates (fibrils), which play a critical role in the formation of Aβ plaques associated with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). By binding to these aggregates, lecanemab helps to diminish the presence of both Aβ protofibrils and plaques within the brain.
Currently, around 6.9 million individuals in Europe are living with AD, a number projected to nearly double by 2050 due to the rising aging population. The disease advances through stages of increasing severity, presenting various challenges for affected individuals and their caregivers. There is a pressing need for innovative treatment solutions that can decelerate the progression of early AD and alleviate the burden on both individuals and society.
Eisai leads the global development and regulatory processes for lecanemab, while both Eisai and Biogen are involved in commercializing and promoting the therapeutic, with Eisai holding ultimate decision-making power.
Apolipoprotein E is a protein that plays a significant role in lipid metabolism in humans and has been linked to AD.
Protofibrils are thought to contribute to the neuronal damage associated with AD and are considered the most harmful form of Aβ, significantly influencing cognitive decline in this progressive condition. They inflict damage on brain neurons, causing cognitive impairment through various mechanisms, including promoting the formation of insoluble Aβ plaques and harming brain cell membranes, as well as disrupting signaling connections between nerve cells and other cells. It is believed that reducing protofibrils may mitigate the progression of AD by lessening neuronal damage and cognitive dysfunction.
👇Explore the most recent advancements in drug research, indications, organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents related to this target by clicking the image link below. Dive in to gain deeper insights!
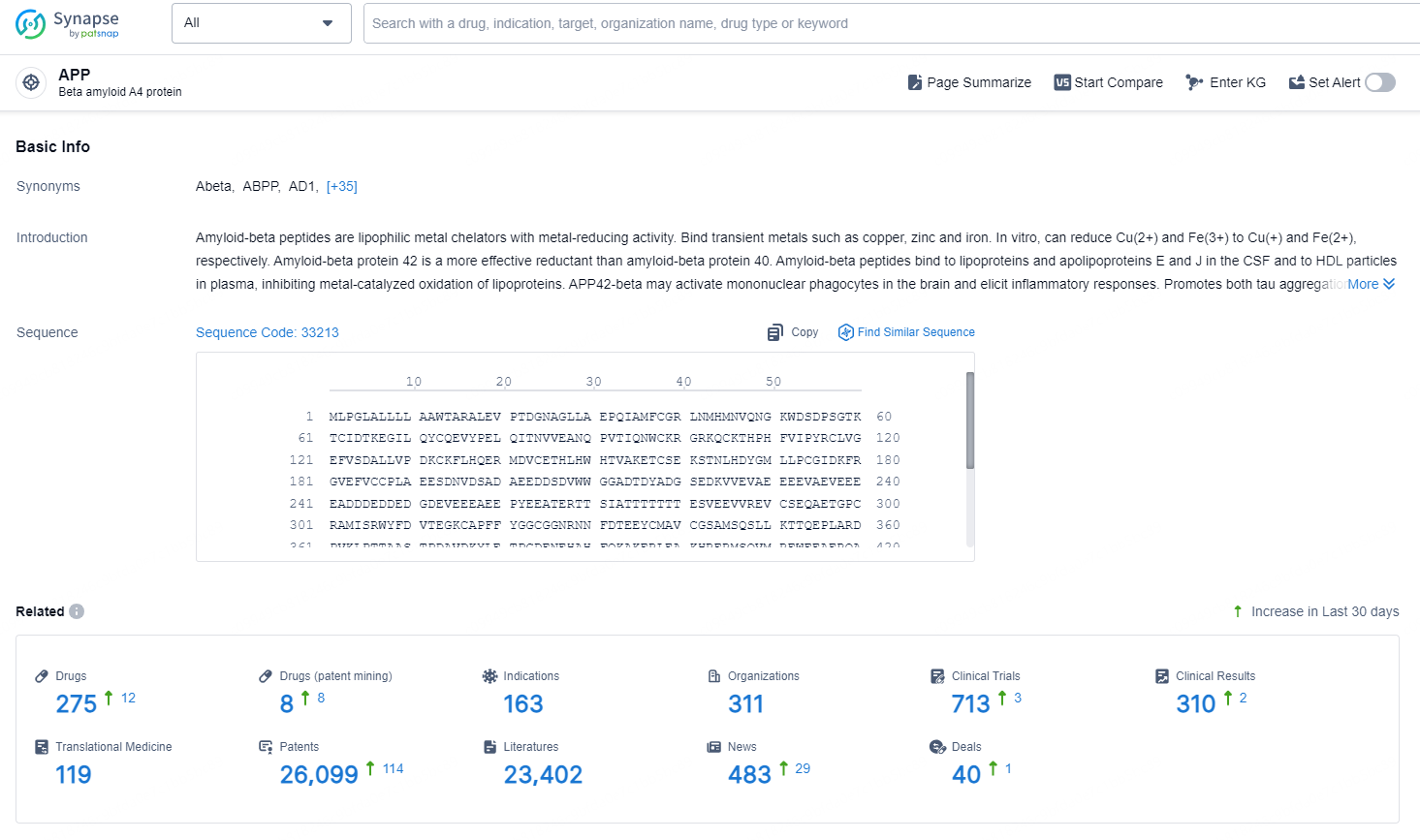
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of November 18, 2024, there are 275 investigational drugs for the APP target, including 163 indications, 311 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 713, and as many as 26099 patents.
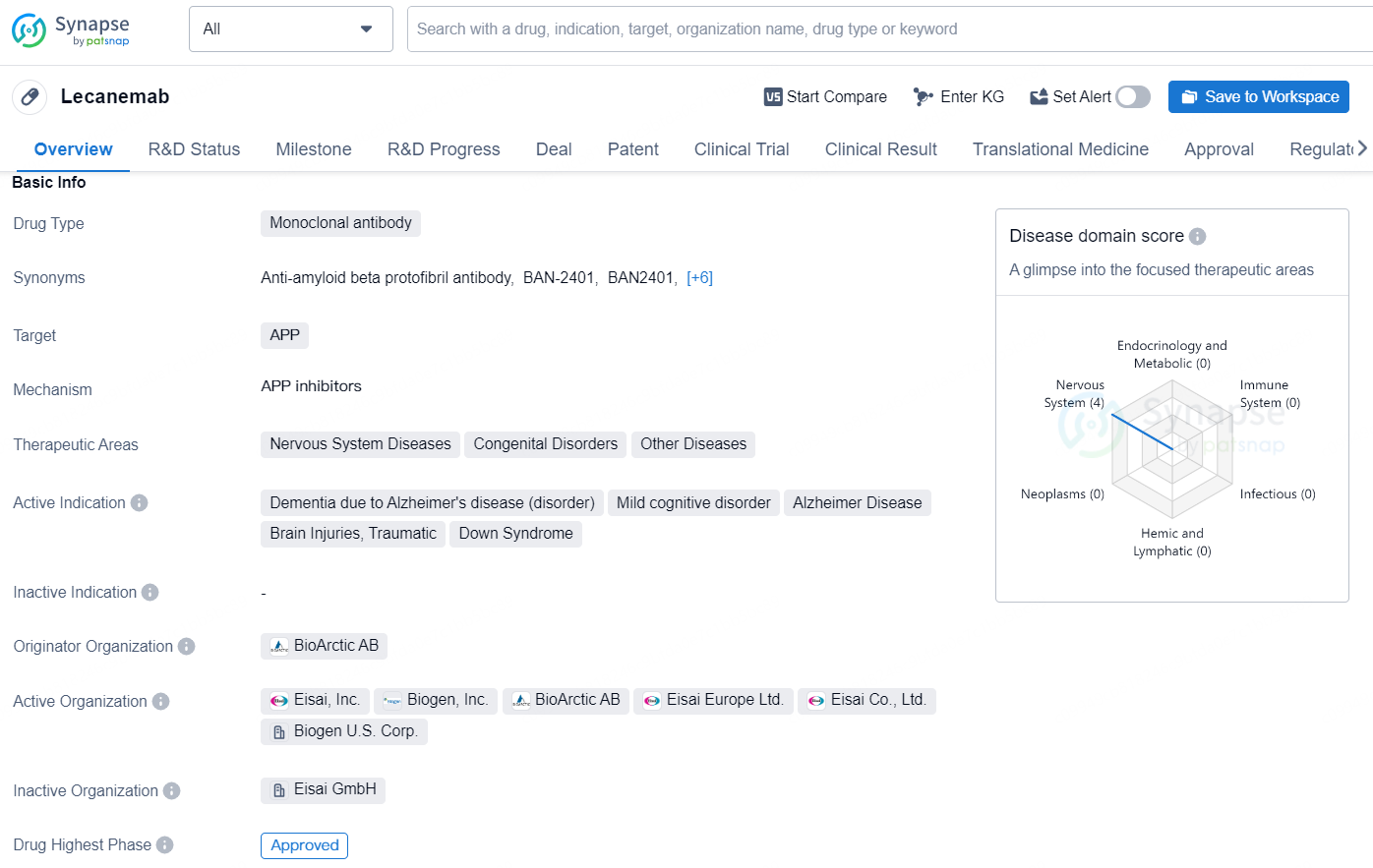
Lecanemab is a monoclonal antibody drug developed by BioArctic AB, which targets amyloid precursor protein (APP). It is primarily intended for the treatment of various nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, and other diseases. The drug has been approved for use in multiple indications, including dementia due to Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive disorder, Alzheimer's disease, traumatic brain injuries, and Down syndrome.