Infliximab-abda: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Infliximab-abda's R&D Progress
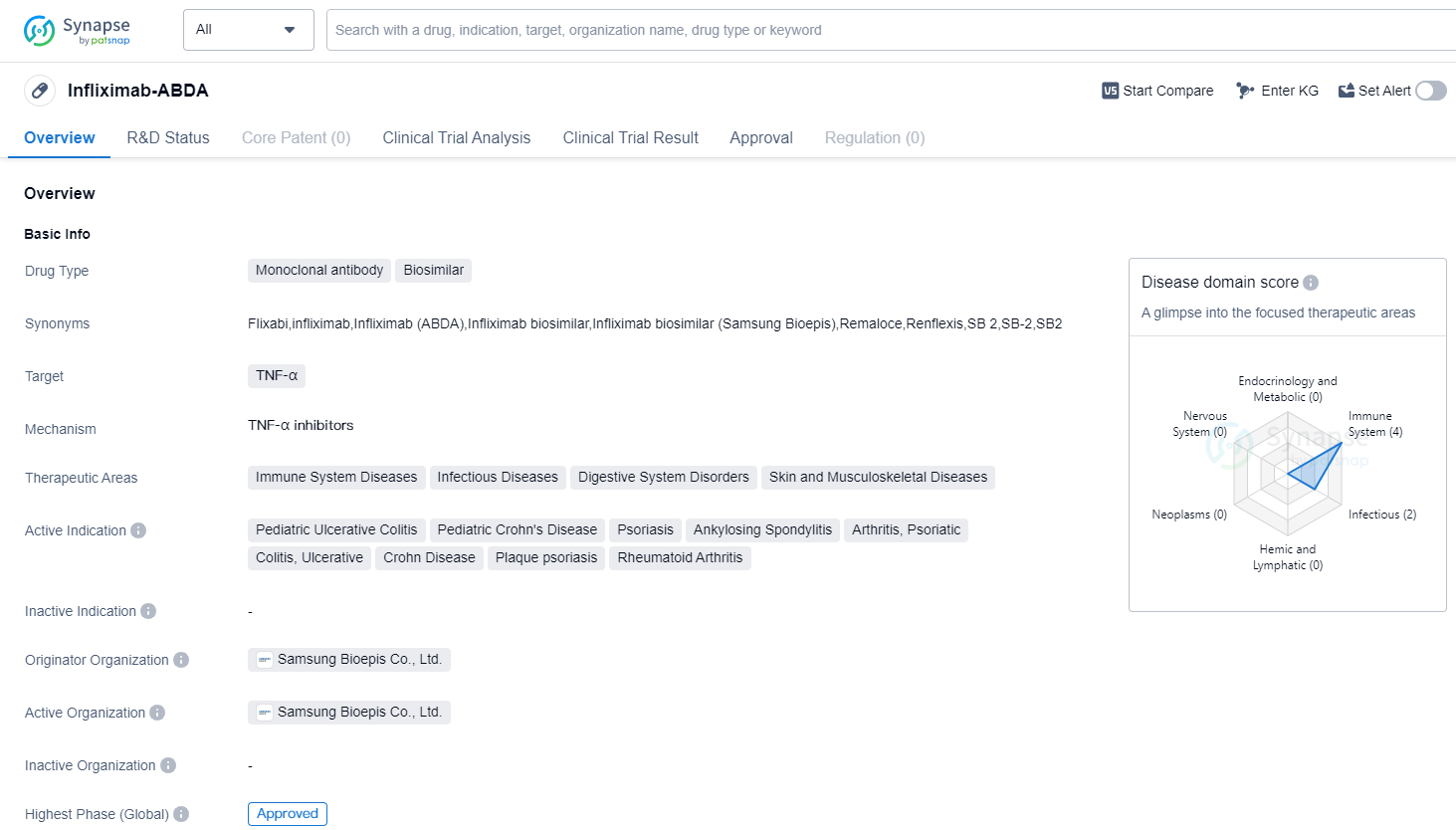
Infliximab-ABDA is a monoclonal antibody biosimilar drug that targets TNF-α. It is primarily used in the treatment of various immune system diseases, infectious diseases, digestive system disorders, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. The drug has been approved for several indications, including pediatric ulcerative colitis, pediatric Crohn's disease, psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, arthritis (psoriatic and rheumatoid), colitis (ulcerative and Crohn's disease), and plaque psoriasis.
The originator organization of Infliximab-ABDA is Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd. This South Korean company developed the drug and obtained its first global approval in December 2015. The approval was granted in South Korea, indicating that the drug met the necessary regulatory requirements and demonstrated its safety and efficacy in treating the specified conditions.
As a monoclonal antibody biosimilar, Infliximab-ABDA is designed to mimic the effects of the original drug, infliximab, which is marketed under various brand names. Biosimilars are highly similar versions of approved biological drugs, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety and efficacy compared to the reference product.
The approval of Infliximab-ABDA signifies its successful development and validation as a biosimilar drug. This achievement allows for increased accessibility and affordability of the medication, as biosimilars are typically more cost-effective than their reference products. By offering a biosimilar alternative, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd. aims to provide patients with a more affordable treatment option without compromising on quality or effectiveness.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for infliximab-abda: TNF-α inhibitors
TNF-α inhibitors are a type of medication used in biomedicine to treat inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) is a cytokine, or a small protein, that plays a crucial role in promoting inflammation in the body. In conditions where there is excessive inflammation, such as autoimmune diseases, TNF-α inhibitors are prescribed to block the action of TNF-α and reduce inflammation.
By inhibiting TNF-α, these medications help to alleviate symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and skin lesions. They work by binding to TNF-α and preventing it from interacting with its receptors on cells, thereby reducing the inflammatory response. This can lead to a decrease in disease activity and an improvement in the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
Some examples of TNF-α inhibitors include infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept. These medications are typically administered through injections or infusions and are prescribed under the supervision of a healthcare professional. It is important to note that TNF-α inhibitors can have potential side effects, including an increased risk of infections, so regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are necessary during treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for infliximab-abda
TNF-α, or Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha, is a cytokine that plays a crucial role in the human body's immune response. It is primarily produced by immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, and is involved in various physiological processes. TNF-α acts as a signaling molecule, regulating inflammation and immune cell activation. It promotes the recruitment of immune cells to sites of infection or injury, enhances the production of other inflammatory molecules, and helps initiate the immune response against pathogens. However, dysregulation of TNF-α can lead to chronic inflammation and is associated with various autoimmune diseases, making it an important target for pharmaceutical interventions.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 302 TNF-α drugs worldwide, from 388 organizations, covering 204 indications, and conducting 4316 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape of target TNF-α reveals that Pfizer Inc., Amgen, Inc., Novartis AG, and SAMSUNG BIOLOGICS Co., Ltd. are the leading companies in terms of R&D progress. These companies have drugs in the approved stage, indicating successful clinical trials and regulatory approval. The indications with the highest number of approved drugs are Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriasis, Arthritis, Psoriatic, Crohn Disease, and Colitis, Ulcerative. Biosimilars, monoclonal antibodies, and fusion proteins are the drug types progressing most rapidly, with biosimilars ranking high, indicating intense competition around the innovative drug. China, the United States, the European Union, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current targets, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target TNF-α has a competitive landscape with multiple companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations involved in its development. The future development of target TNF-α is expected to continue with advancements in R&D and competition among companies in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Infliximab-ABDA is a monoclonal antibody biosimilar drug that targets TNF-α and is approved for the treatment of various immune system diseases, infectious diseases, digestive system disorders, and skin and musculoskeletal diseases. Developed by Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., the drug received its first global approval in South Korea in December 2015. Its approval signifies a significant milestone in the pharmaceutical industry, as it offers a more accessible and cost-effective treatment option for patients in need.