Is Sirolimus approved by the FDA?
Sirolimus (Brand name: Rapamune) is an immunosuppressive medication that plays a crucial role in preventing organ rejection after a kidney transplant. Sirolimus was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on September 15, 1999. It was approved for use in combination with other medications to prevent organ rejection in patients receiving kidney transplants.
Uses and Benefits
Sirolimus works by weakening the body’s immune system, preventing it from attacking a newly transplanted kidney. Organ rejection occurs when the immune system treats the new organ as an invader and attacks it. Additionally, sirolimus is used to treat a rare lung disorder called lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), which primarily affects women and causes non-cancerous lung tumors that can impede breathing.
How to Take Sirolimus
- Sirolimus is usually taken once a day, with or without food, but consistently the same way each time.
- If you also take cyclosporine, take it at least 4 hours before sirolimus.
- The oral liquid form should be mixed only with water or orange juice, not with any other juices or liquids.
- Follow your doctor’s dosage instructions precisely and read all medication guides provided.
Side Effects
Common side effects of sirolimus may include:
- Fever, cold symptoms (stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat)
- Mouth sores
- Nausea, stomach pain, diarrhea
- Headache, muscle aches
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Acne
Serious side effects can include:
- Serious brain infection leading to disability or death
- Redness, oozing, or slow healing of skin wounds
- New skin lesions or changes in moles
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Sudden chest pain, cough, shortness of breath
- Tenderness around the transplanted kidney
- Signs of infection (fever, chills, painful mouth sores, skin sores, cold or flu symptoms, pain or burning when urinating)
- Low red blood cells (anemia) leading to pale skin, unusual tiredness, light-headedness, shortness of breath, cold hands and feet
Warnings and Precautions
- Sirolimus should not be used by individuals who have had a lung or liver transplant.
- The medication can cause the body to overproduce white blood cells, increasing the risk of cancer, severe brain infection, or viral infection leading to kidney transplant failure.
- Sirolimus can interact with a variety of medications, including certain antibiotics, antivirals, heart or blood pressure medications, and more. Inform your doctor of all medications you are taking.
- Avoid exposure to sunlight or tanning beds and use protective measures as sirolimus can increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can interact with sirolimus and should be avoided.
Conclusion
Sirolimus (Rapamune) is a vital medication approved by the FDA on September 15, 1999, for preventing organ rejection in kidney transplant patients. It offers significant benefits in immunosuppression and treatment of rare lung disorders but comes with potential side effects and necessary precautions. Always follow your healthcare provider's instructions and report any adverse effects promptly.
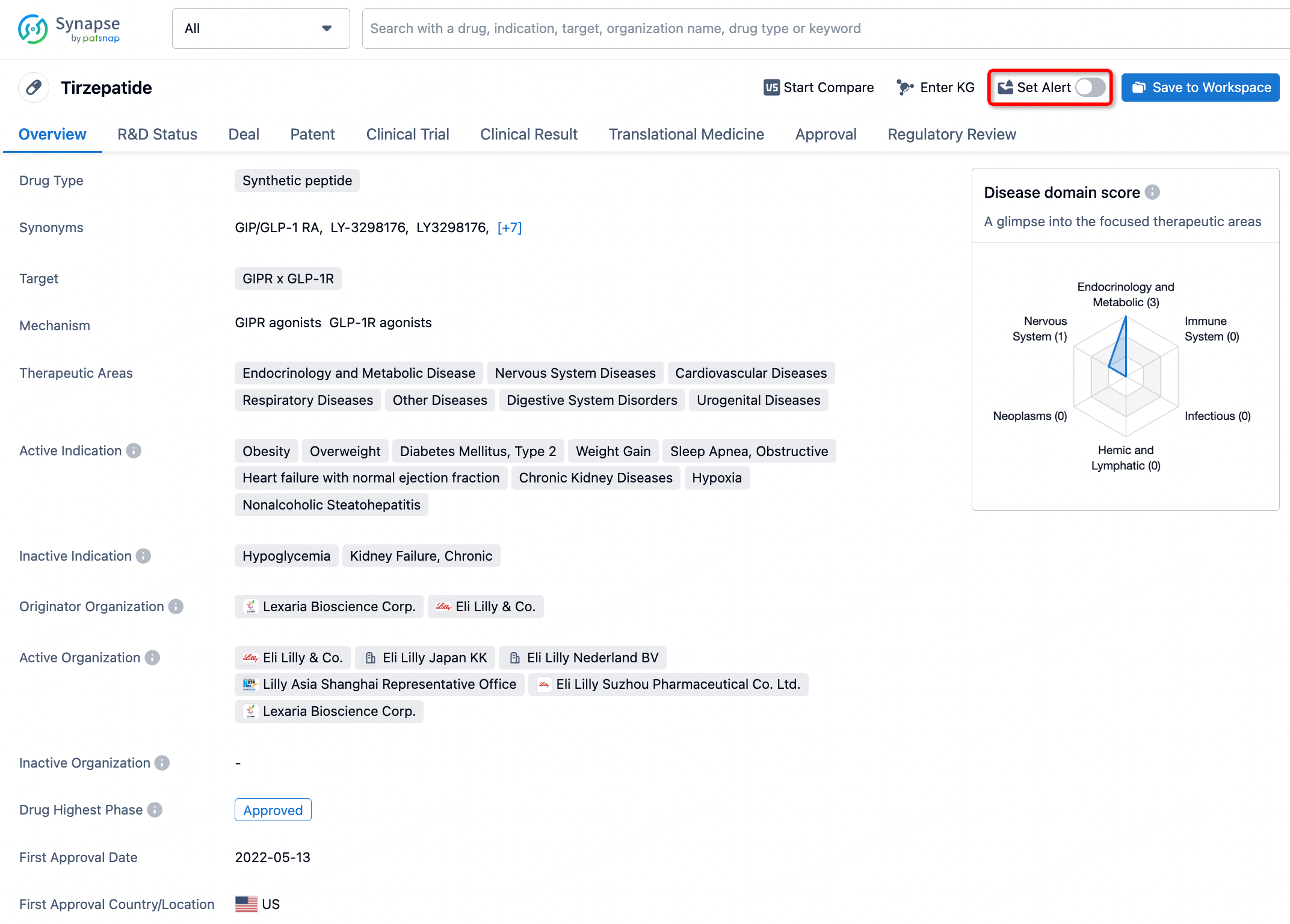
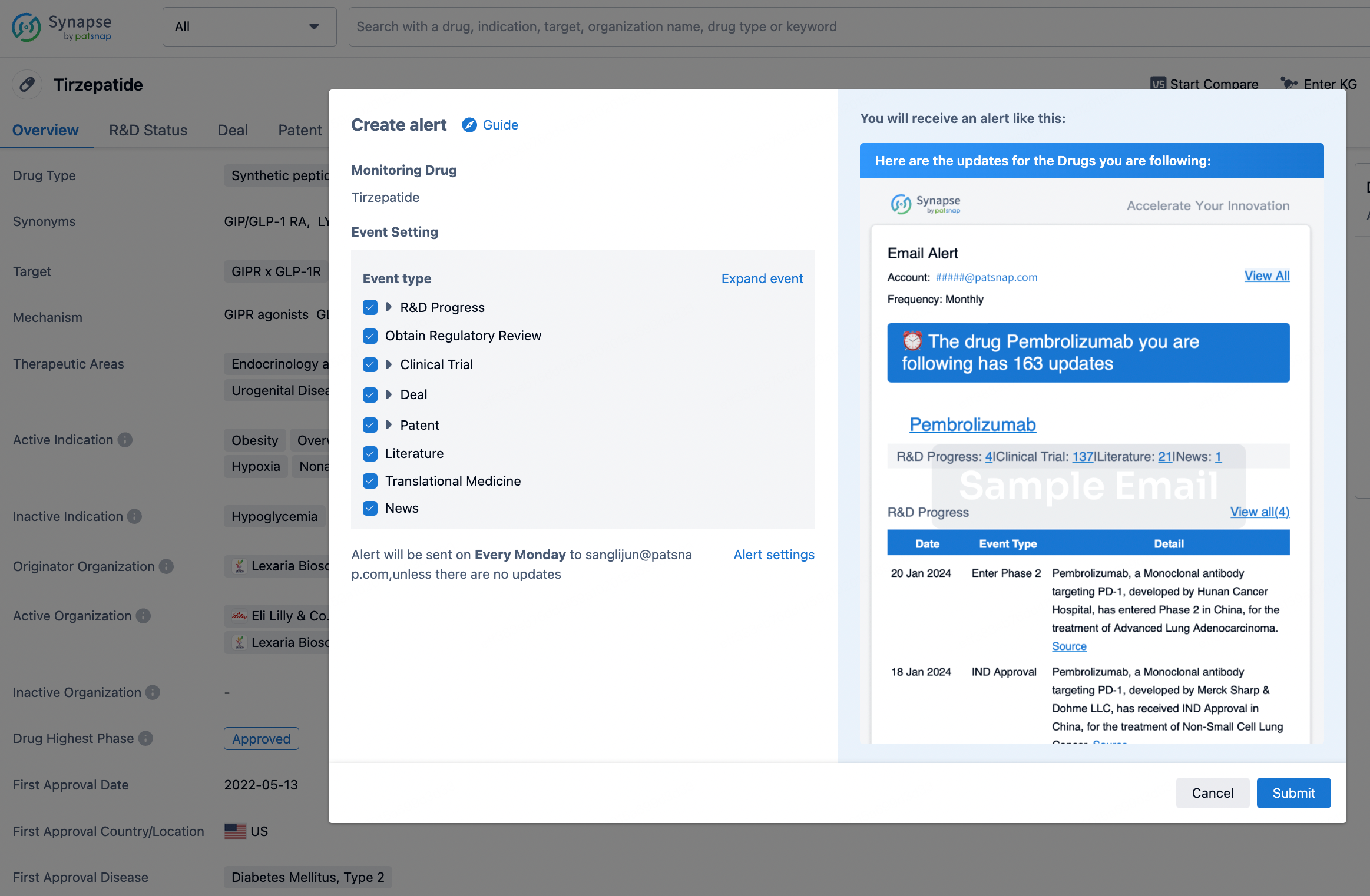
How to obtain the latest development progress of all drugs?
In the Synapse database, you can stay updated on the latest research and development advances of all drugs. This service is accessible anytime and anywhere, with updates available daily or weekly. Use the "Set Alert" function to stay informed. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!