Latest Research Progress on Adenosine Antagonists
Adenosine receptors play a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. These receptors are found in different tissues and organs, including the brain, heart, and immune system. Adenosine, a naturally occurring molecule, binds to these receptors and regulates numerous functions such as neurotransmission, vasodilation, and immune response modulation.
Activation of adenosine receptors can have diverse effects, including sedation, anti-inflammatory actions, and regulation of heart rate and blood flow. Understanding the role of adenosine receptors is essential for developing targeted therapies in the pharmaceutical industry, as they can be potential targets for treating various conditions like cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and immune-related disorders.
Adenosine receptor Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 321 Adenosine receptor drugs worldwide, from 275 organizations, covering 226 indications, and conducting 1085 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
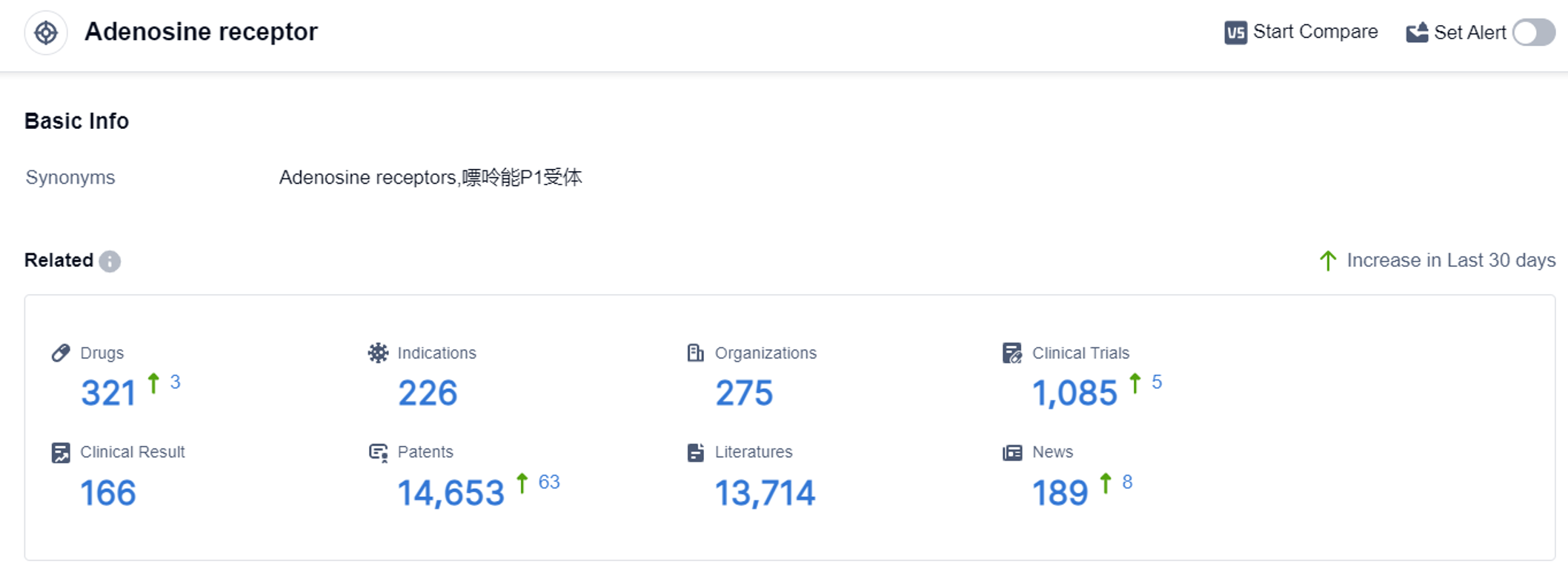
The target Adenosine receptor in the pharmaceutical industry shows a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. The highest stage of development is the Approved phase, with small molecule drugs being the most common drug type.
The indications for drugs under the target Adenosine receptor cover a wide range of medical conditions, including Common Cold, Asthma, Headache, Pain, Neuralgia, Migraine Disorders, Fever, Cardiovascular Diseases, Bronchitis, Chronic, Dysmenorrhea, Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive, Bronchitis, Bronchiectasis, Toothache, Asthmatic bronchitis, Pulmonary Emphysema, Heart Diseases, Parkinson Disease, Heart Failure, and Myocardial Ischemia.
China is leading in terms of drug development, followed by the United States and Japan. Further analysis of the R&D progress of companies, biosimilars, and specific progress in China would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the current competitive landscape and future development of the target Adenosine receptor.
Key Drug: Caffeine
Caffeine is a small molecule drug that acts on multiple targets including A1R, A2aR, adenosine receptor, and PDE. It is primarily used in the treatment of respiratory diseases and other diseases. The drug has been approved for use in various indications such as respiration disorders, consciousness, mental fatigue, fatigue, and sleepiness.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
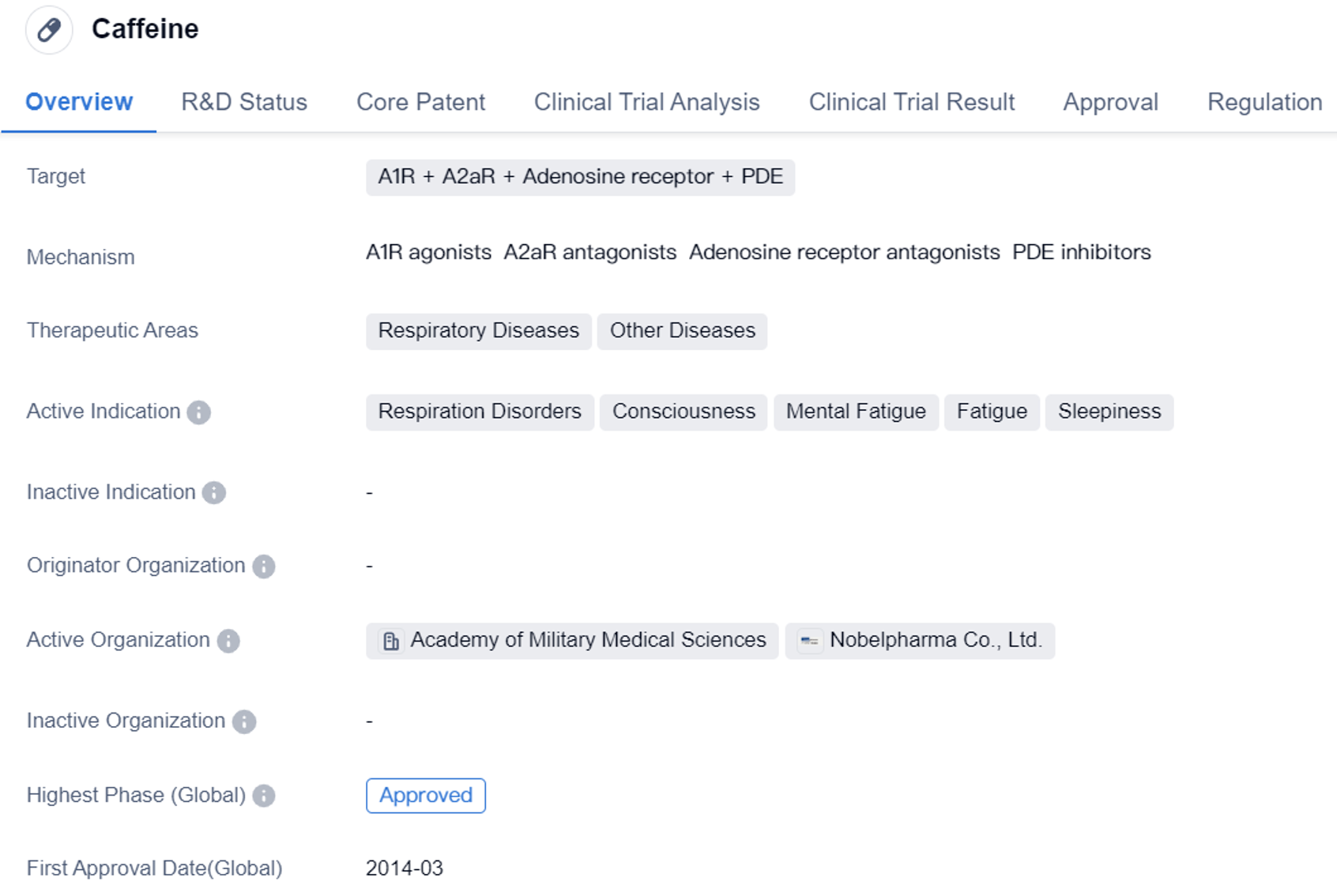
Caffeine's highest phase of development is approved, both globally and in China. It received its first approval in March 2014 in Japan. The drug is regulated as an orphan drug, indicating that it is used to treat rare diseases or conditions.
Caffeine is widely known for its stimulant effects on the central nervous system. It is commonly found in beverages such as coffee, tea, and energy drinks. The drug works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, which helps to increase alertness and reduce drowsiness.
In the field of respiratory diseases, caffeine has shown potential in the treatment of conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It acts as a bronchodilator, helping to relax the muscles in the airways and improve breathing.
Additionally, caffeine has been studied for its effects on mental fatigue and sleepiness. It is often used to enhance cognitive performance and increase wakefulness. However, it is important to note that excessive consumption of caffeine can lead to side effects such as increased heart rate, anxiety, and insomnia.
Overall, caffeine is a small molecule drug that targets multiple receptors and is approved for use in various indications. Its therapeutic areas include respiratory diseases and other conditions related to consciousness, mental fatigue, fatigue, and sleepiness. With its stimulant effects on the central nervous system, caffeine has shown potential in improving respiratory function and reducing fatigue. However, it is important to use caffeine responsibly and be aware of its potential side effects.




