Master Doxycycline Search on Synapse
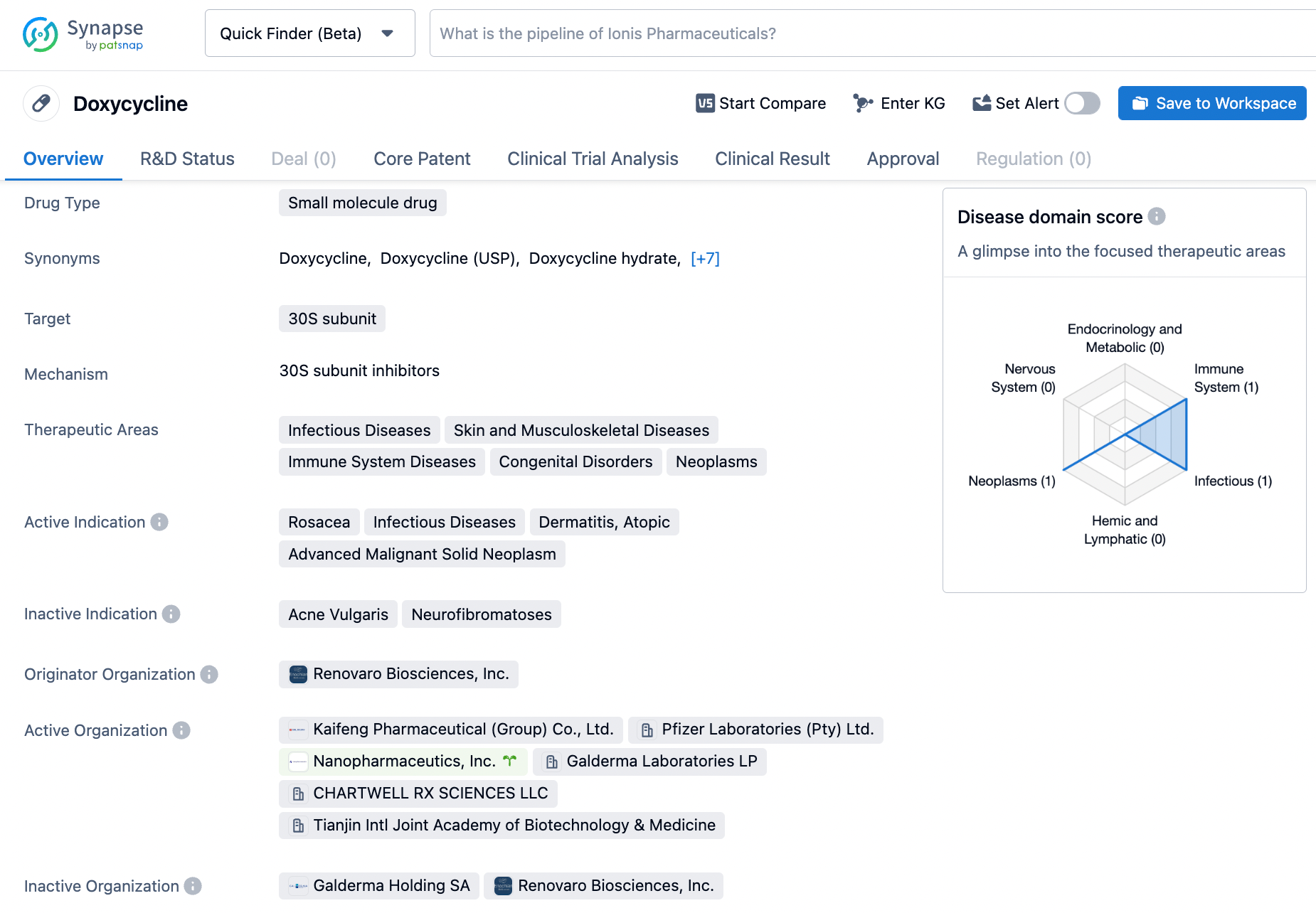
Doxycycline is a tetracyclin-like broad-spectrum antibiotic that stops bacteria from growing and replicating by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial proteins. Doxycycline mechanisms by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the ribosome A site. This hinders the production of proteins and ultimately leads to the death of bacterial cells. Doxycycline is widely used to treat respiratory infections, urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted infections caused by bacteria. Its effectiveness, versatility and low cost make it a valuable tool in the fight against infectious diseases. Click on the image below to begin the exploration journey of Doxycycline through the Synapse database!
You can search for the latest pharmaceutical information such as drugs, targets, patents, transactions, clinical results, etc. through the Synapse database. Come and experience it!