Olopatadine hydrochloride: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Olopatadine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
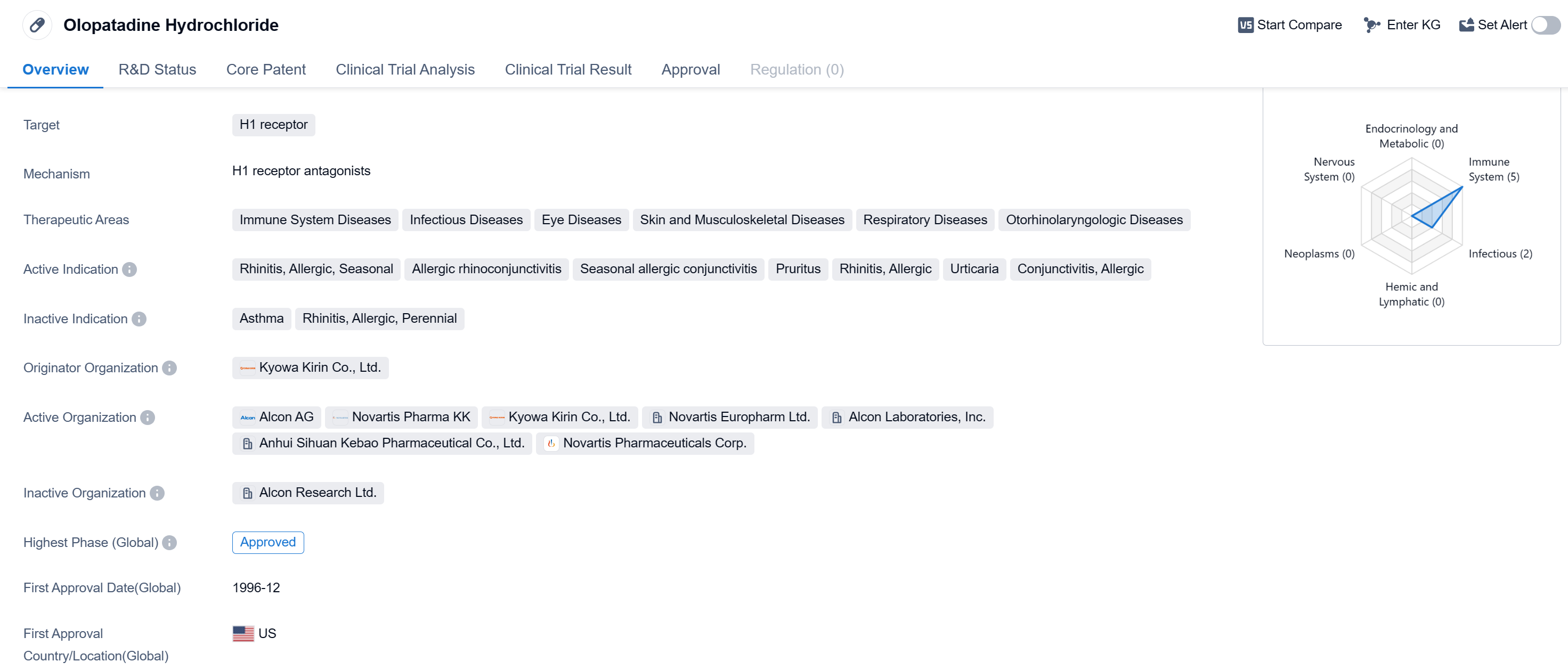
Olopatadine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the H1 receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of various immune system diseases, infectious diseases, eye diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, respiratory diseases, and otorhinolaryngologic diseases. The active indications for this drug include seasonal allergic rhinitis, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, pruritus, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and allergic conjunctivitis.
The drug was first approved in the United States in December 1996 and has since gained approval in other countries as well. It is considered to be in the highest phase of development, with global approvals already obtained. Olopatadine Hydrochloride was developed by Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., an originator organization in the pharmaceutical industry.
Olopatadine Hydrochloride has shown efficacy in treating allergic conditions such as rhinitis and conjunctivitis. These conditions are characterized by inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages and eyes, often triggered by allergens such as pollen or pet dander. By targeting the H1 receptor, the drug helps to alleviate symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and watery eyes.
The drug's approval in multiple therapeutic areas highlights its versatility and potential to address various medical conditions. It has been widely used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis, a common condition affecting a significant portion of the population. Additionally, its effectiveness in managing urticaria, a skin condition characterized by hives and itching, further demonstrates its broad applicability.
Its success in the pharmaceutical market can be attributed to its ability to effectively target the H1 receptor and provide relief for patients suffering from allergic and inflammatory conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Olopatadine hydrochloride: H1 receptor antagonists
H1 receptor antagonists, also known as H1 blockers or antihistamines, are a class of drugs that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptors. Histamine is a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction, causing symptoms such as itching, sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes. H1 receptor antagonists work by binding to the H1 receptors on cells, preventing histamine from binding and exerting its effects.
From a biomedical perspective, H1 receptor antagonists are commonly used to treat allergic conditions, including allergic rhinitis (hay fever), urticaria (hives), and allergic conjunctivitis. By blocking the H1 receptors, these medications help alleviate symptoms associated with histamine release, providing relief from itching, sneezing, and other allergic reactions.
There are different generations of H1 receptor antagonists, with varying degrees of sedative effects. First-generation antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine, can cause drowsiness and are often used for their sedative properties in addition to their antihistamine effects. Second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine, are less likely to cause sedation and are preferred for their non-sedating properties.
In summary, H1 receptor antagonists are drugs that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptors, providing relief from symptoms associated with allergic reactions. They are commonly used in the treatment of allergic conditions and are available in different generations with varying sedative effects.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Olopatadine hydrochloride
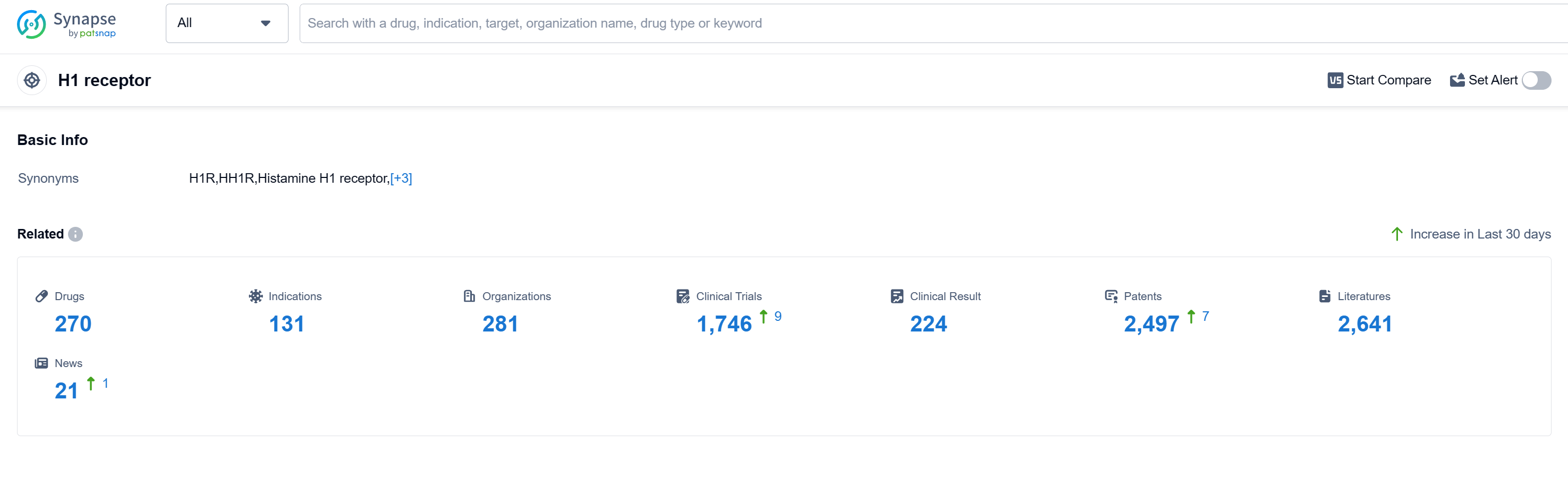
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 270 H1 receptor drugs worldwide, from 281 organizations, covering 131 indications, and conducting 1746 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target H1 receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs. GSK Plc, Sanofi, and Bayer AG are the companies growing fastest under this target. Rhinitis, Allergic and Common Cold are the most common indications for approved drugs. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition in this area. China is leading in terms of drug development under the target H1 receptor, followed by the United States and Japan. The future development of the target H1 receptor is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts by various companies and countries/locations.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Olopatadine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. It targets the H1 receptor and is approved for use in various therapeutic areas, including immune system diseases, infectious diseases, eye diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, respiratory diseases, and otorhinolaryngologic diseases. Its active indications include seasonal allergic rhinitis, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, pruritus, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and allergic conjunctivitis. With its long history of approval and widespread use, Olopatadine Hydrochloride has proven to be an effective treatment option for patients suffering from allergic and inflammatory conditions.