Pharmaceutical Insights: darifenacin hydrobromide's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Darifenacin hydrobromide's R&D Progress
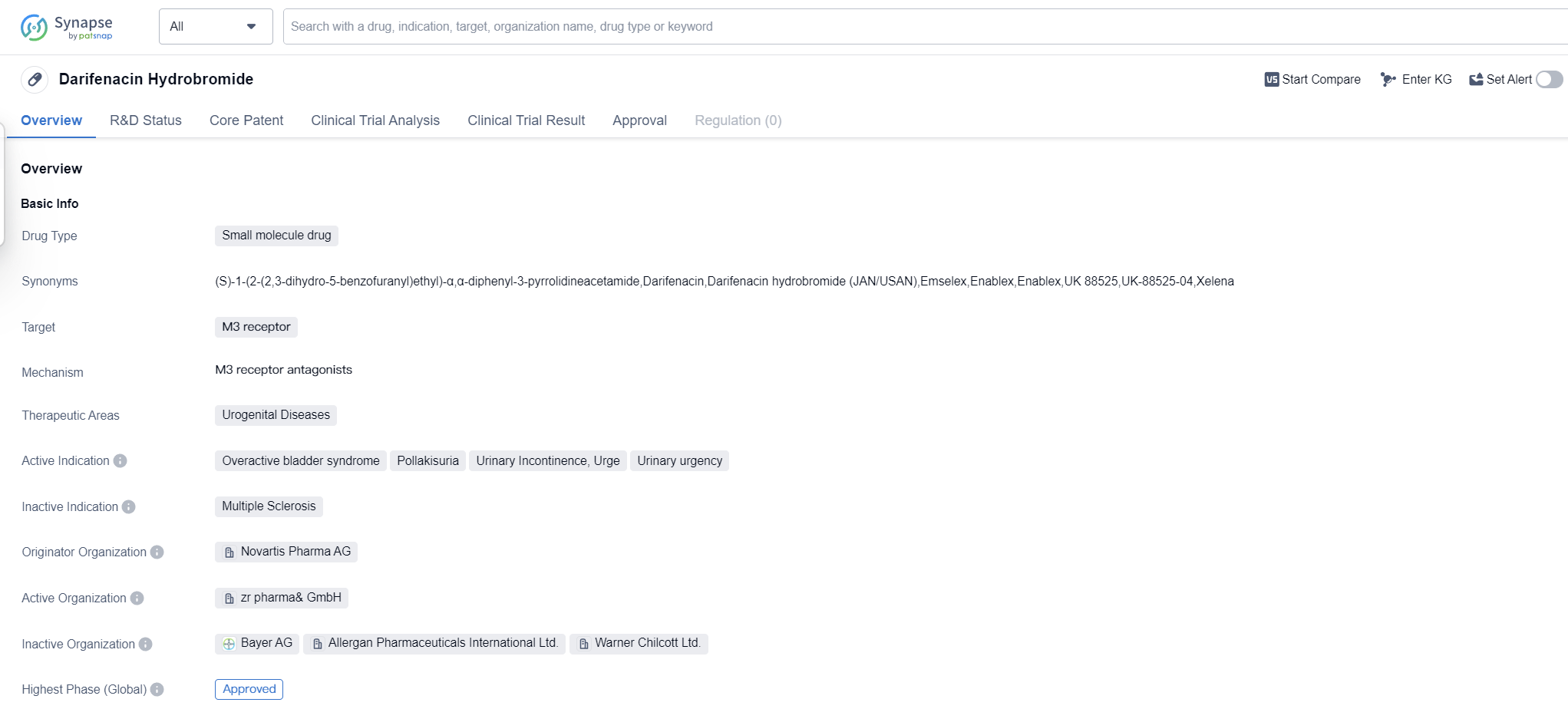
Darifenacin Hydrobromide is a small molecule drug that targets the M3 receptor and is primarily used in the treatment of urogenital diseases. It has been approved for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome, pollakisuria, urinary incontinence, urge, and urinary urgency. The drug was developed by Novartis Pharma AG and received its first approval in the European Union in October 2004.
Darifenacin Hydrobromide belongs to the class of drugs known as antimuscarinics, which work by blocking the action of acetylcholine at the M3 receptor. By doing so, it helps to relax the smooth muscles of the bladder, reducing the frequency and urgency of urination.
The drug's approval in the European Union in 2004 marked an important milestone in the treatment of urogenital diseases, particularly overactive bladder syndrome. This condition is characterized by a sudden and uncontrollable urge to urinate, often accompanied by frequent urination and urinary incontinence. Darifenacin Hydrobromide provides patients with a much-needed treatment option to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Since its approval, Darifenacin Hydrobromide has been widely used in clinical practice and has demonstrated efficacy in reducing the symptoms associated with overactive bladder syndrome and other urogenital diseases. It has been shown to significantly decrease the number of daily urinations, urgency episodes, and incontinence episodes, leading to improved patient outcomes.
As a small molecule drug, Darifenacin Hydrobromide is easily absorbed by the body and has a relatively long half-life, allowing for once-daily dosing. This convenience factor has contributed to its widespread use and patient compliance.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for darifenacin hydrobromide: M3 receptor antagonists
M3 receptor antagonists are a type of medication that blocks the activity of the M3 receptor. The M3 receptor is a subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor found in various tissues and organs in the body, including smooth muscles, glands, and the central nervous system. By antagonizing or inhibiting the M3 receptor, these drugs can reduce the effects of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that activates the M3 receptor.
In a biomedical perspective, M3 receptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and overactive bladder. By blocking the M3 receptor in the airways, these medications can relax the smooth muscles and help alleviate symptoms of bronchoconstriction and airway constriction. Similarly, in the case of overactive bladder, M3 receptor antagonists can reduce bladder muscle contractions and improve urinary control.
It's important to note that M3 receptor antagonists may have side effects related to the inhibition of the M3 receptor in other tissues. These can include dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and urinary retention. Therefore, the use of M3 receptor antagonists should be carefully monitored and prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Drug Target R&D Trends for darifenacin hydrobromide
The M3 receptor, also known as the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype 3, plays a crucial role in the human body. It is primarily found in smooth muscle tissues, glands, and the central nervous system. Activation of the M3 receptor by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine leads to various physiological responses, including smooth muscle contraction, secretion of glands, and regulation of neurotransmitter release. This receptor is involved in numerous bodily functions, such as digestion, regulation of heart rate, control of bladder function, and modulation of cognitive processes. Understanding the role of the M3 receptor is essential for developing drugs that target this receptor for therapeutic purposes.
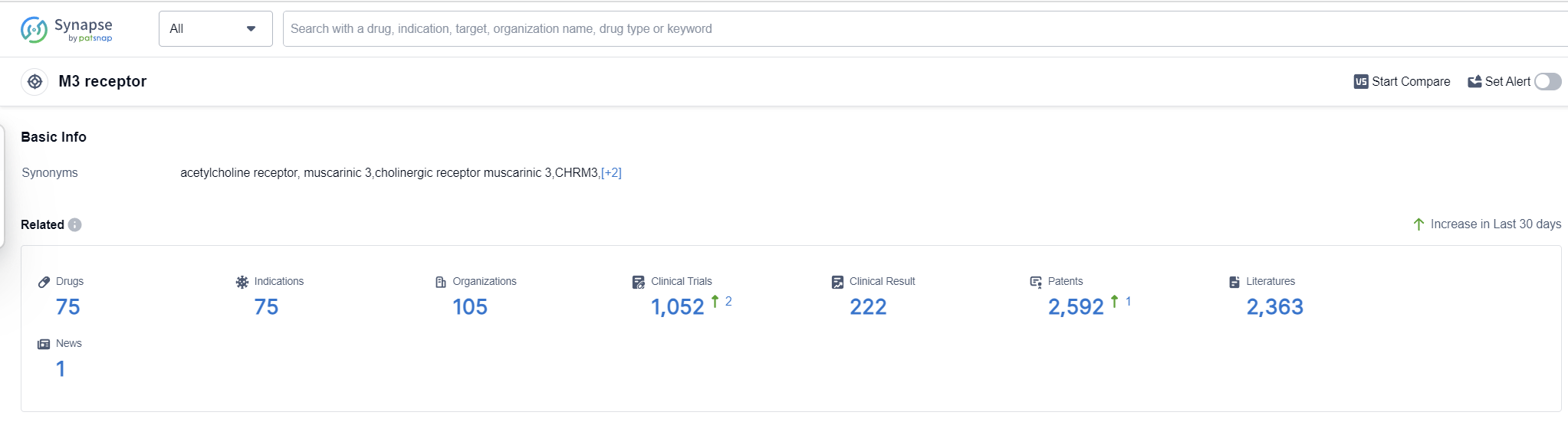
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 75 M3 receptor drugs worldwide, from 105 organizations, covering 75 indications, and conducting 1052 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target M3 receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in R&D and the development of drugs. Pfizer Inc., Astellas Pharma, Inc., GSK Plc, AstraZeneca PLC, and C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. KG are the companies growing fastest under this target. The most common approved indication is Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive, followed by Urinary Bladder, Overactive, Bronchitis, Chronic, and Asthma. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly under the target M3 receptor. China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the target M3 receptor presents a promising area for the development of innovative drugs in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Darifenacin Hydrobromide has proven to be a valuable therapeutic option for patients suffering from urogenital diseases, particularly overactive bladder syndrome. Its approval in the European Union in 2004 marked a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine, providing healthcare professionals with an effective tool to manage the symptoms of these conditions. With its continued use and further research, Darifenacin Hydrobromide has the potential to improve the lives of many individuals affected by urogenital diseases worldwide.