Pharmaceutical Insights: Miglustat's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Miglustat's R&D Progress
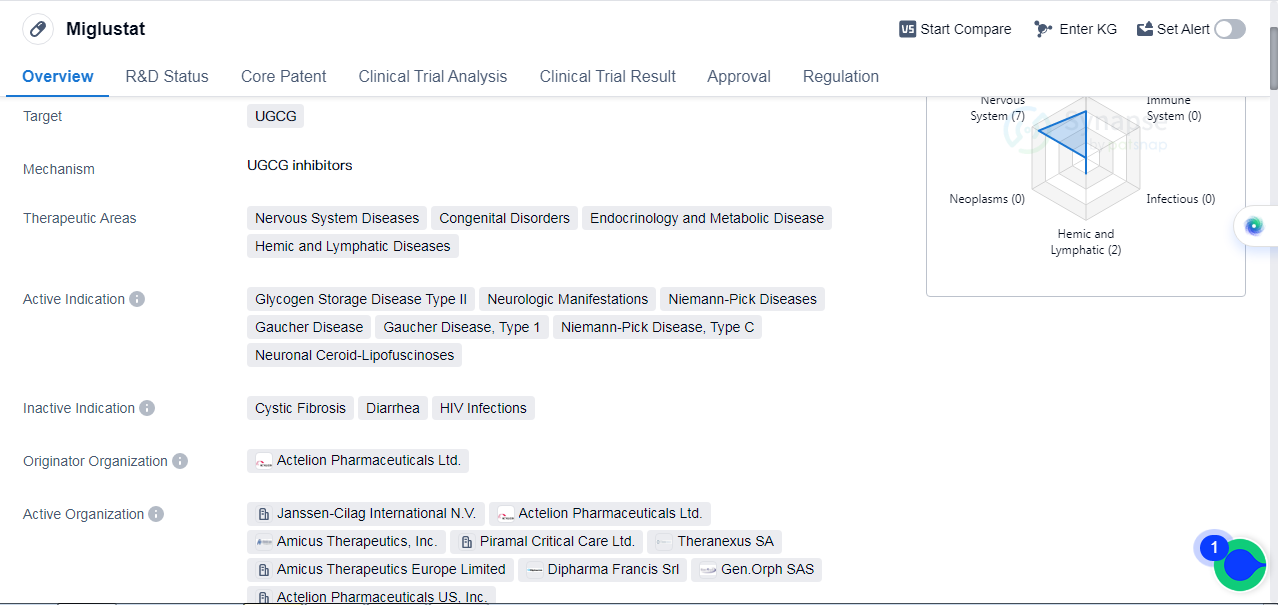
Miglustat is a small molecule drug that targets the UGCG enzyme. It is primarily used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases, congenital disorders, endocrinology and metabolic diseases, as well as hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug has been approved for the treatment of glycogen storage disease type II, neurologic manifestations, Niemann-Pick diseases, Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease type C, etc.
Miglustat was developed by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd., a pharmaceutical company specializing in the field of biomedicine. The drug has reached the highest phase of development, with approvals obtained in the global market. The first approval for Miglustat was granted in November 2002 by the European Union.
In terms of regulatory status, Miglustat has undergone priority review and has been designated as an orphan drug. Orphan drug designation is granted to drugs that are intended to treat rare diseases, providing incentives for their development and commercialization.
Miglustat's approval and regulatory designations highlight its potential as a therapeutic option for patients suffering from various diseases affecting the nervous system, metabolism, and other related areas.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Miglustat: UGCG inhibitors
UGCG inhibitors are a type of chemical compounds that specifically target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme called UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase (UGCG). UGCG is an important enzyme involved in the synthesis of ceramide, a lipid molecule that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including cell growth, cell death, and cell signaling.
From a biomedical perspective, UGCG inhibitors have gained significant attention as potential therapeutic agents for various diseases, particularly cancer. By inhibiting UGCG activity, these inhibitors can disrupt the synthesis of ceramide, leading to altered cellular processes and potentially inhibiting the growth and survival of cancer cells. Additionally, UGCG inhibitors may also have implications in other diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic disorders, where ceramide dysregulation is observed.
The development of UGCG inhibitors involves extensive research and drug discovery efforts to identify small molecules or compounds that can selectively bind to the UGCG enzyme and inhibit its activity. These inhibitors can be designed and optimized to have high specificity and potency, minimizing off-target effects and maximizing therapeutic benefits.
Overall, UGCG inhibitors hold promise as potential therapeutic agents in biomedicine, particularly in the field of cancer research. Further studies and clinical trials are needed to evaluate their efficacy, safety, and potential applications in various disease conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Miglustat
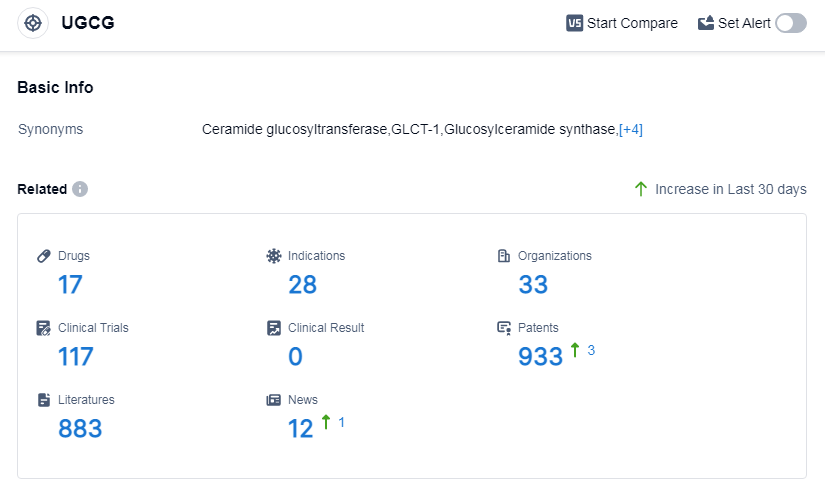
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 17 UGCG drugs worldwide, from 33 organizations, covering 28 indications, and conducting 117 clinical trials.
The current competitive landscape of target UGCG shows that Sanofi is the leading company with drugs in the highest stage of development. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type under this target. The United States, European Union, and Japan are the leading countries in terms of drug development, with the United States having the highest number of drugs in various stages of development. While there is some progress in China, it is not as significant as in other countries. The future development of target UGCG is expected to continue with a focus on these indications and drug types, with potential for increased competition and advancements in research and development.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Miglustat's approval and regulatory status, along with its target and therapeutic areas, position it as a valuable asset in the pharmaceutical industry. Its successful development and commercialization by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. demonstrate the company's expertise in the field of biomedicine.