Pharmaceutical Insights: Natamycin's R&D Progress and its Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Natamycin's R&D Progress
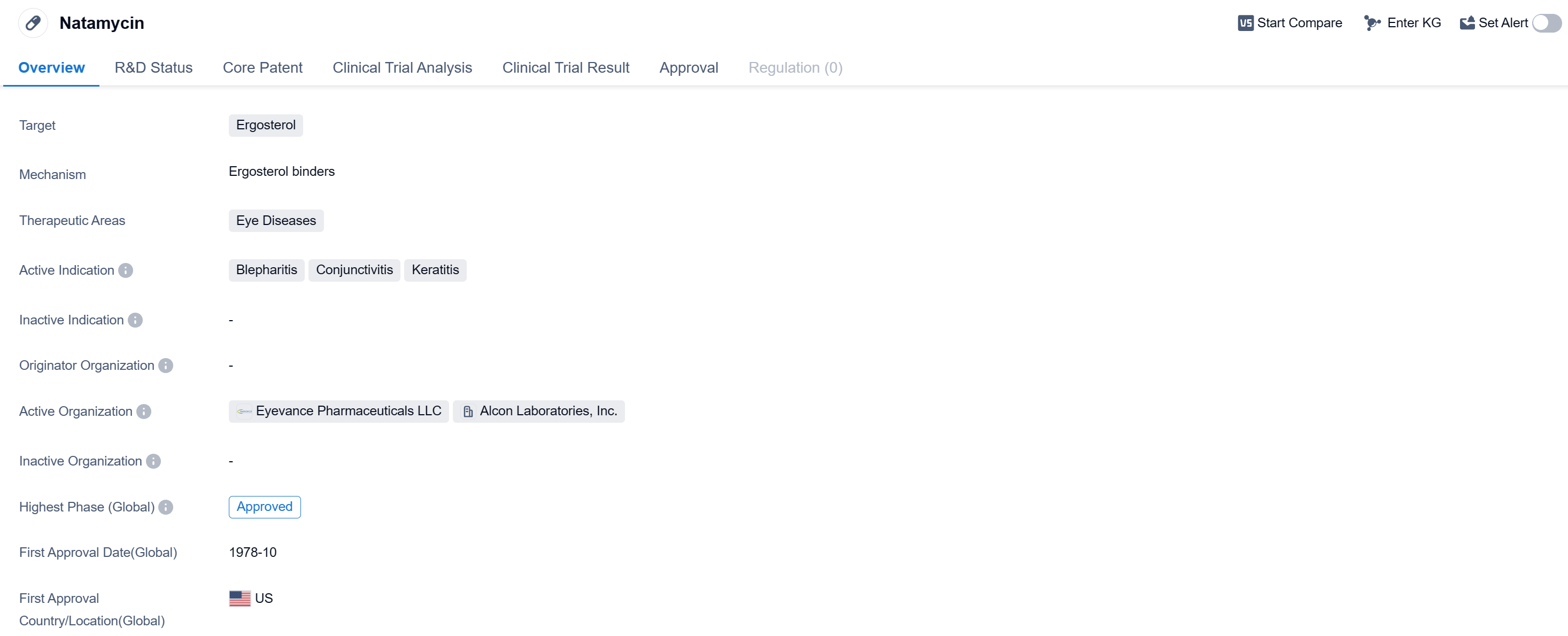
Natamycin is a small molecule drug that targets ergosterol and is primarily used in the treatment of eye diseases. It has been approved for use in the United States since October 1978 and is indicated for the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis.
Natamycin is classified as a small molecule drug, which means it is composed of relatively low molecular weight compounds. It specifically targets ergosterol, a key component of fungal cell membranes. By inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, natamycin effectively disrupts the integrity of fungal cells, leading to their death.
The therapeutic areas in which natamycin is primarily used are eye diseases. Specifically, it is indicated for the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelids, conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva (the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids), and keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye).
Natamycin has achieved the highest phase of approval in the global markets. The first approval of natamycin occurred in the United States in October 1978, indicating its long history of use in this market.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Natamycin: Ergosterol binders
Ergosterol binders are substances or compounds that have the ability to bind to ergosterol. Ergosterol is a sterol found in the cell membrane of fungi, including yeast and molds. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and fluidity of the fungal cell membrane.
From a biomedical perspective, ergosterol binders are of interest because they can be used as antifungal agents. By binding to ergosterol, these compounds disrupt the fungal cell membrane, leading to cell death. This makes ergosterol binders an important class of drugs in the treatment of fungal infections.
Ergosterol binders can be used topically or systemically, depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection. They may be formulated as creams, ointments, or oral medications. Common examples of ergosterol binders include azoles, polyenes, and allylamines.
It's worth noting that ergosterol binders specifically target fungal cells and have minimal impact on human cells. This selectivity is due to the structural differences between fungal and human cell membranes, making ergosterol binders an effective and relatively safe treatment option for fungal infections.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Natamycin
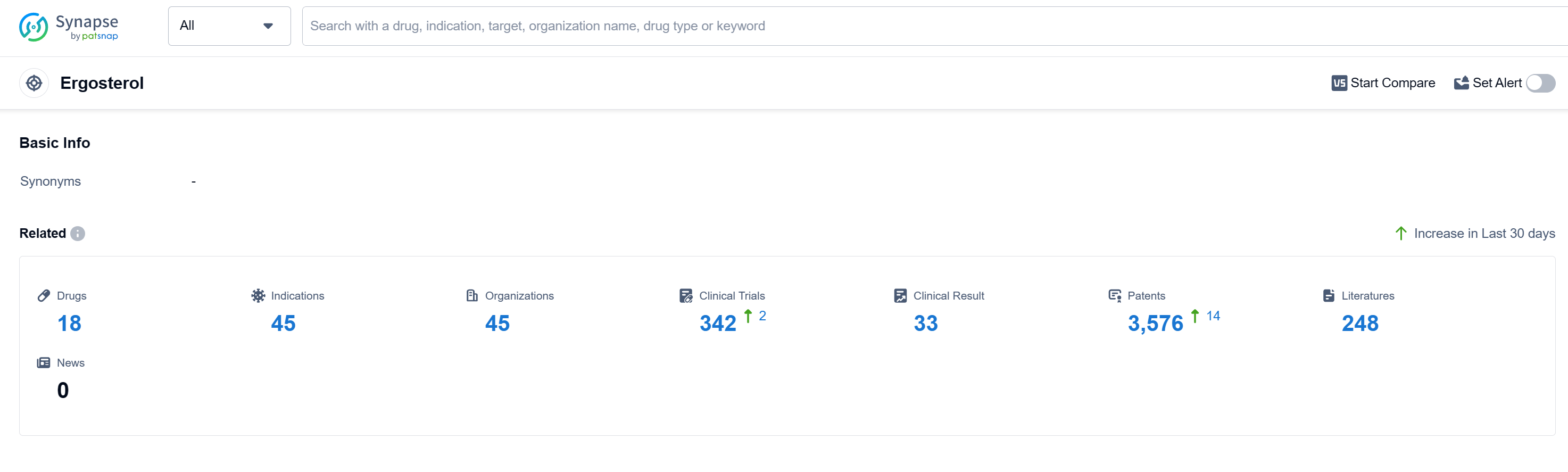
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 15 Sep 2023, there are a total of 18 Ergosterol drugs worldwide, from 45 organizations, covering 45 indications, and conducting 342 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target Ergosterol reveals several key findings. Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Gilead Sciences, Inc., and Astellas Pharma, Inc. are the companies with the highest number of drugs in the approved phase, indicating their strong presence and focus on research and development in this target. The indications for the approved drugs under this target cover a wide range of fungal infections and skin diseases. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating intense competition in the development of innovative drugs. China is a leading country in the development of drugs under this target, with the highest number of approved drugs. Overall, the target Ergosterol shows promising potential for the pharmaceutical industry, with active research and development efforts and a diverse range of indications being targeted.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, natamycin is a small molecule drug that targets ergosterol and is primarily used in the treatment of eye diseases. It has been approved for use in the United States since 1978 and is indicated for the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Its approval status in the global markets indicates its widespread recognition as a safe and effective treatment option for these conditions.