Potential Therapeutic Drug for Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Diseases - RIPK1 Inhibitors
RIPK1, also known as Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, is a multi-domain protein that includes an N-terminal kinase domain, intermediate domain, and a C-terminal death domain. The C-terminal death domain mediates homodimers and heterodimers with other death domain-containing proteins, while the N-terminal kinase domain mediates trans-auto-phosphorylation to promote self-activation. RIPK1 is widely expressed in different cell types, with the highest expression in adipose, endothelial, and perivascular cell clusters. It is also expressed in immune cell clusters such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and T cells.
RIPK1 has a dual immunomodulatory role. On one hand, it serves as a scaffold to promote the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, thereby promoting inflammatory responses and cell survival while inhibiting apoptosis. On the other hand, aberrant regulation of RIPK1 kinase activity can lead to cell necrosis.
RIPK1 is a key regulator in the transduction of NF-κB pro-survival signals and cell death signals. NF-κB signal transduction responds to broad inflammatory and pro-death stimuli in human diseases. Studies have found that the activation of RIPK1 kinase is present in pathological samples of autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Inhibition of RIPK1 kinase activity has shown efficacy in various human disease animal models.
RIPK1 Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 25 Sep 2023, there are a total of 34 RIPK1 drugs worldwide, from 37 organizations, covering 33 indications, and conducting 49 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.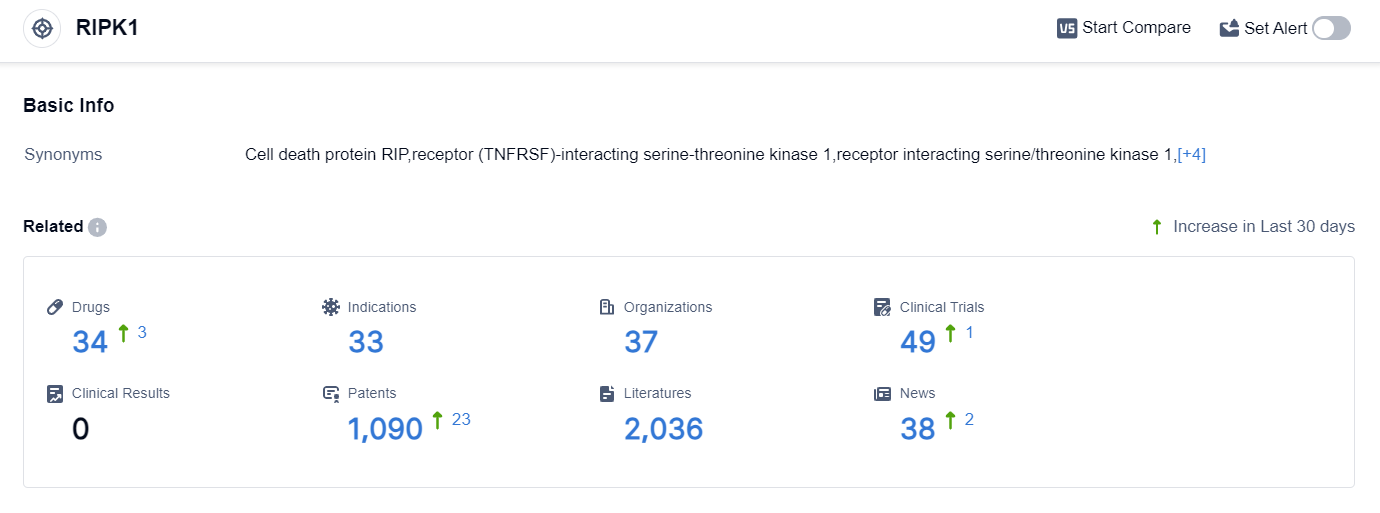
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape of target RIPK1 shows that Sanofi, GenFleet Therapeutics (H.K.) Limited, Eli Lilly & Co., and AbbVie, Inc. are the companies with significant R&D progress. These companies have drugs in advanced stages of development, such as Phase 2 and Phase 1.
The indications with the highest number of drugs in advanced stages include Colitis, Ulcerative, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Multiple Sclerosis. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, with the highest number of drugs in Phase 2 and Preclinical stages.
The United States, European Union, and China are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current target, with the United States leading in terms of the number of drugs in advanced stages.
Overall, the target RIPK1 presents a competitive landscape with multiple companies and a focus on advanced stages of development. The indications and drug types vary, indicating a broad range of potential therapeutic applications. Continued research and development efforts, particularly in countries like China, are expected to drive the future development of target RIPK1.
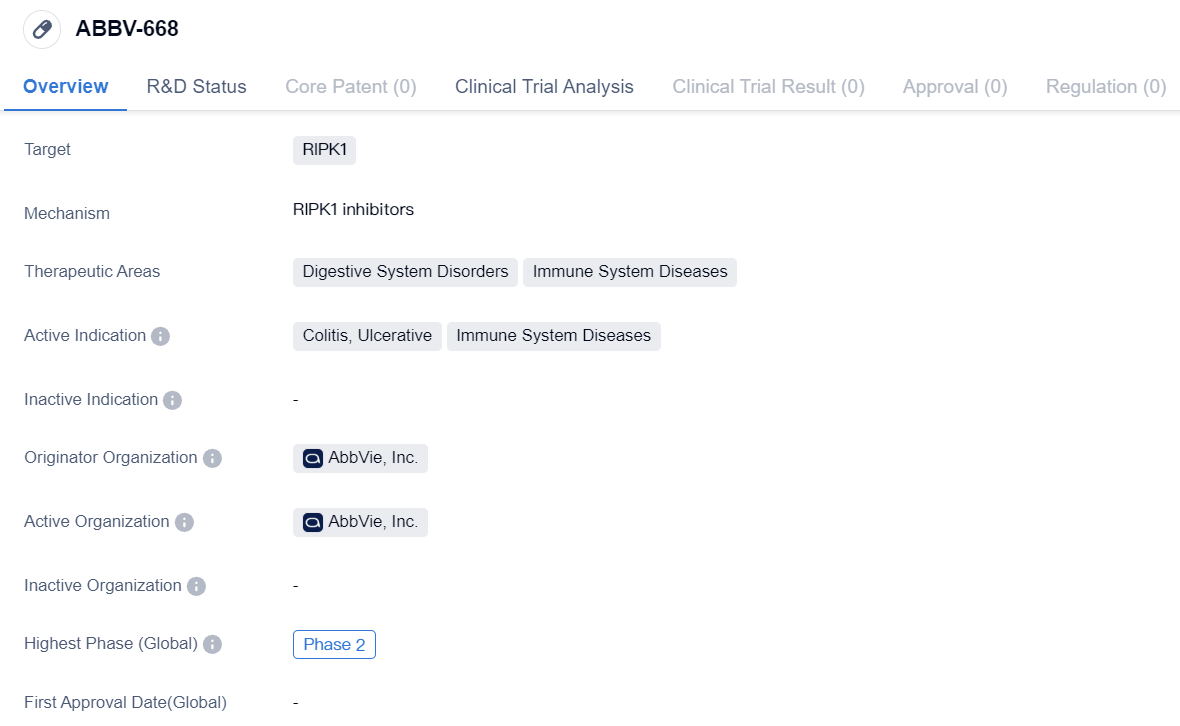
RIPK1 inhibitors entering into Phase II clinical trials: ABBV-668
ABBV-668is a small molecule drug developed by AbbVie, Inc. It is designed to target RIPK1, a protein involved in various cellular processes. The drug is primarily being developed for the treatment of digestive system disorders and immune system diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The therapeutic areas of focus for ABBV-668 include digestive system disorders and immune system diseases. Specifically, it is being investigated for its potential in treating colitis, ulcerative, and other immune system diseases. These conditions can cause inflammation and damage to the digestive system and immune system, leading to various symptoms and complications.
As a small molecule drug, ABBV-668 is a chemical compound with a relatively low molecular weight. This characteristic allows it to easily penetrate cells and interact with specific targets, such as RIPK1. By targeting this protein, ABBV-668 aims to modulate the cellular processes involved in digestive system disorders and immune system diseases, potentially providing therapeutic benefits.
ABBV-668 has reached Phase 2 of development. This phase involves testing the drug in a larger group of patients to further evaluate its safety and efficacy. Phase 2 trials are crucial in determining the potential of a drug and its suitability for further development.
The originator organization of ABBV-668 is AbbVie, Inc., a pharmaceutical company known for its expertise in developing innovative therapies. AbbVie, Inc. is committed to advancing the field of biomedicine and improving patient outcomes through its research and development efforts.
In summary, ABBV-668 is a small molecule drug developed by AbbVie, Inc. It targets RIPK1 and is being investigated for its potential in treating digestive system disorders and immune system diseases, specifically colitis, ulcerative, and other immune system diseases. The drug has reached Phase 2 of development, and AbbVie, Inc. is the originator organization behind its development.
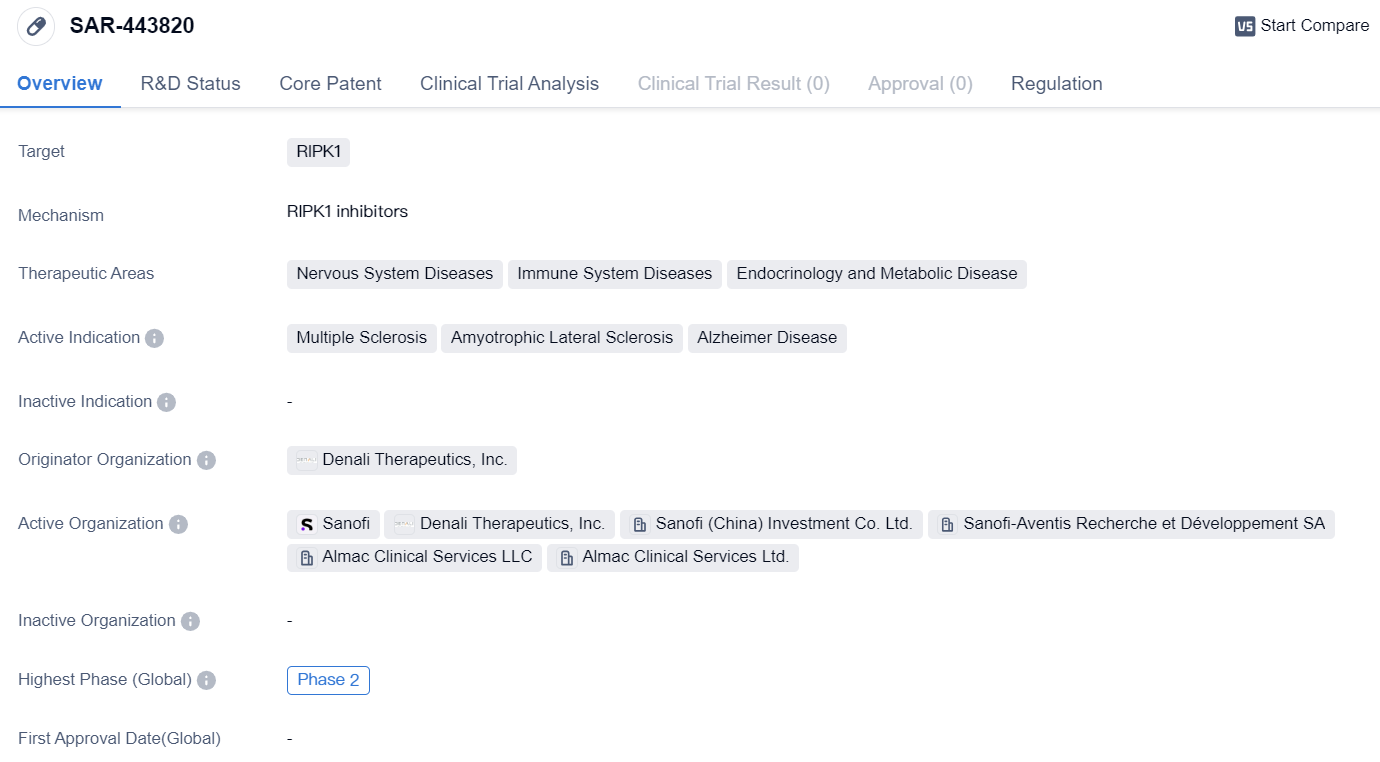
RIPK1 inhibitors entering into Phase II clinical trials: SAR-443820
SAR-443820 is a small molecule drug that is being developed by Denali Therapeutics, Inc. It is designed to target RIPK1, a protein involved in various cellular processes. The drug is being investigated for its potential therapeutic benefits in treating diseases related to the nervous system, immune system, and endocrinology and metabolic disorders.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The active indications for SAR-443820 include multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease. These are all debilitating conditions that affect different aspects of the nervous system and can have a significant impact on patients' quality of life.
Currently, SAR-443820 is in Phase 2 of clinical development, both globally and in China. Phase 2 trials involve a larger number of participants and aim to further evaluate the drug's safety and efficacy. This suggests that SAR-443820 has shown promising results in earlier stages of development and is now being tested in a larger population to gather more data.
One notable aspect of SAR-443820 is its regulatory status. It has been granted Fast Track designation, which is a program designed to expedite the development and review of drugs that address unmet medical needs. This designation indicates that SAR-443820 has the potential to provide significant benefits over existing treatments for the targeted diseases.
Based on the given information, SAR-443820 appears to be a promising small molecule drug that targets RIPK1 and is being developed by Denali Therapeutics, Inc. It is currently in Phase 2 of clinical development for multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease. The drug has been granted Fast Track designation, highlighting its potential to address unmet medical needs in these therapeutic areas.