Progress in Clinical Research of HDAC6 Inhibitors
Based on homology with yeast protein sequences, histone deacetylases (HDACs) can be divided into 18 types. Inhibitors against HDAC (HDACi) have been proven to be effective chemotherapeutic drugs. They alter the acetylation status of various proteins within cells, increase the expression level of genes such as p21, and inhibit tumor cell proliferation by inducing cell differentiation or apoptosis.
HDAC6 is the largest member of the HDAC family, consisting of 1215 amino acids. It is mainly composed of a nuclear export signal (NES), two functionally independent HDAC catalytic domains (CD1 and CD2, located at the N-terminus and central region respectively), and a ubiquitin-binding zinc finger domain at the C-terminus. The zinc finger ubiquitin-binding domain can be used to bind ubiquitin proteasome to clear misfolded proteins. The nuclear export signal (NES) can transport HDAC6 into the cytoplasm and target non-histone substrates located in the cytoplasm, such as α-tubulin, tau protein, cortical protein, heat shock protein (HSP90), and peroxidase. HDAC6 plays an important physiological role in cellular pathways, and its abnormal activity directly leads to the occurrence of various diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and immune disorders. The latest research shows that HDAC6 is a potential target for various rare diseases, such as Rett syndrome (RTT), inherited retinal diseases (IRDS), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), etc.
HDAC6 Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 48 HDAC6 drugs worldwide, from 38 organizations, covering 49 indications, and conducting 30 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.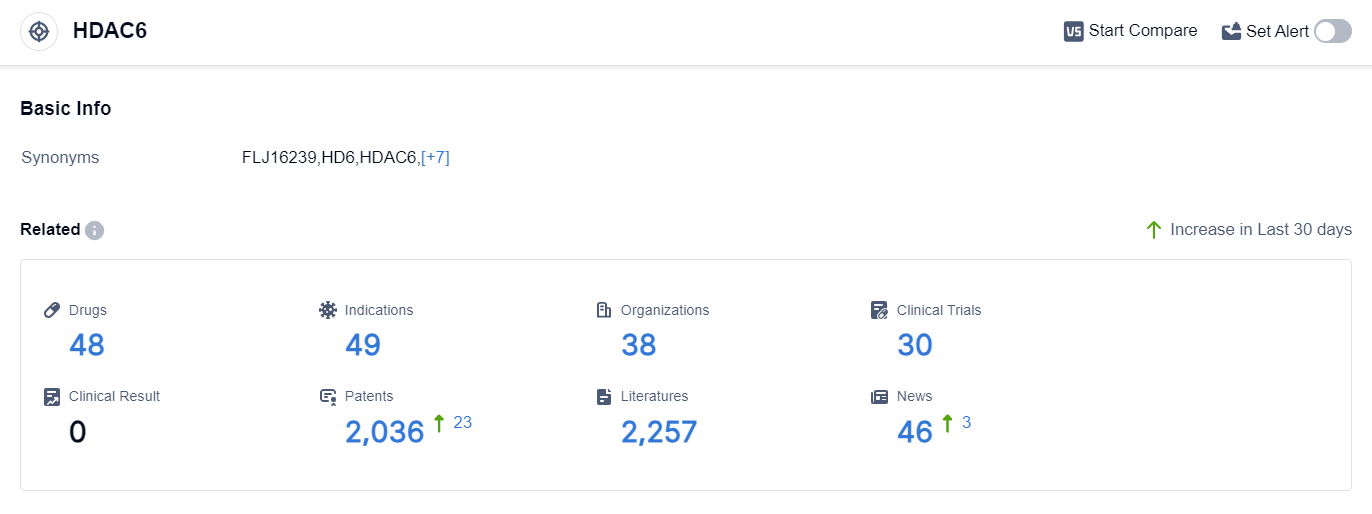
The analysis of target HDAC6 in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs at different stages of development. Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corp., and Regenacy Pharmaceuticals LLC are among the companies showing significant progress in the R&D of HDAC6-targeting drugs.
The indications for which drugs targeting HDAC6 have been approved cover a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurological disorders. This indicates the potential of HDAC6 as a therapeutic target for various indications.
The majority of drugs in development are small molecule drugs, indicating a focus on traditional pharmaceutical compounds. Other drug types, such as unknown drugs, chemical drugs, PROTACs, and cell therapy, are also being explored but to a lesser extent.
The United States, European Union, and South Korea are leading in the development of drugs targeting HDAC6. However, China has also shown progress in this area, indicating its growing presence in the pharmaceutical industry.
Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of HDAC6-targeting drugs, with a diverse range of indications and drug types being explored. Continued research and development efforts will be crucial to bring innovative treatments to patients in need.
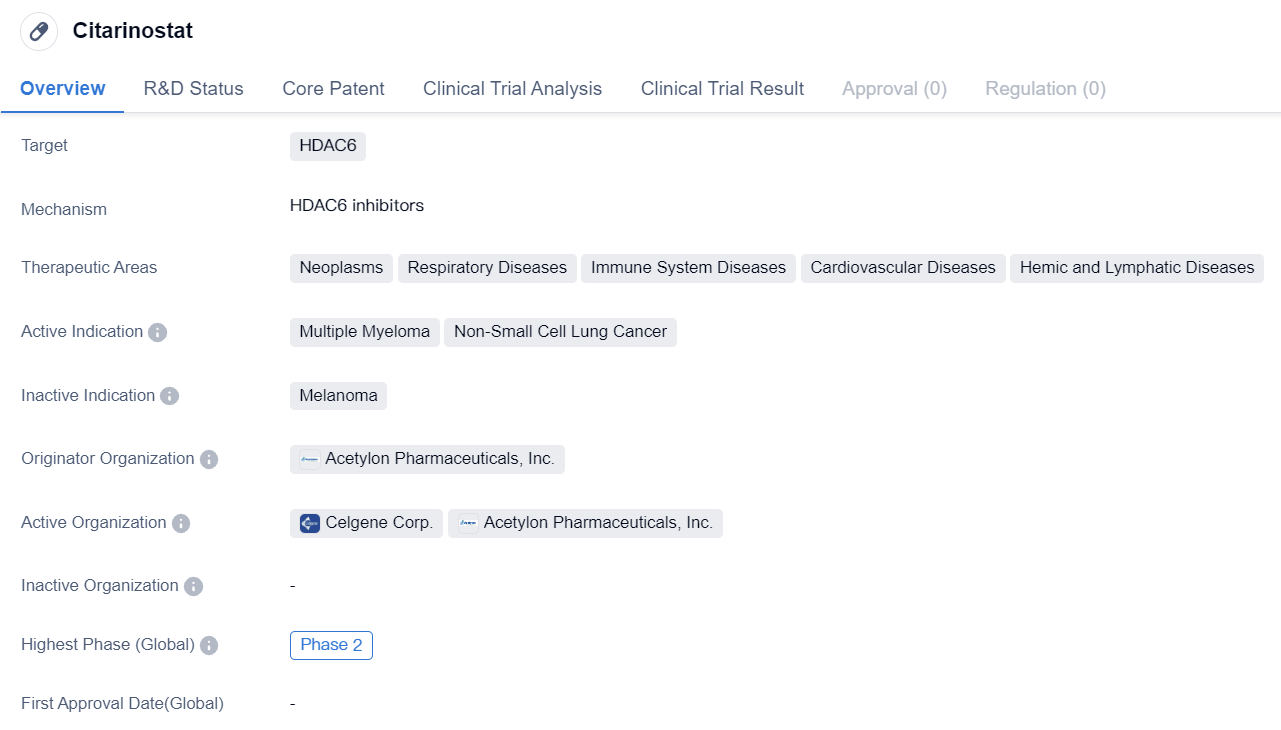
Clinical Phase II HDAC6 Inhibitors: Citarinostat
Citarinostat is a small molecule drug that is being developed by Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. It is designed to target HDAC6, a protein that plays a role in various diseases. The drug is being investigated for its potential therapeutic applications in neoplasms, respiratory diseases, immune system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
In terms of active indications, Citarinostat is primarily being studied for its efficacy in treating multiple myeloma and non-small cell lung cancer. These are both serious and life-threatening conditions that have limited treatment options available. By targeting HDAC6, Citarinostat aims to inhibit the activity of this protein and potentially provide a new treatment option for patients suffering from these diseases.
Currently, Citarinostat is in Phase 2 of clinical development. This means that the drug has already undergone initial testing in humans and has shown promising results in terms of safety and efficacy. Phase 2 trials typically involve a larger number of participants and are designed to further evaluate the drug's effectiveness and side effects.
Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is the originator organization behind Citarinostat. As the developer of the drug, they are responsible for conducting the necessary research and clinical trials to bring it to market. Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is likely collaborating with other organizations, such as research institutions and pharmaceutical companies, to advance the development of Citarinostat.
In summary, Citarinostat is a small molecule drug that targets HDAC6 and is being developed by Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. It is being investigated for its potential therapeutic applications in various diseases, including neoplasms, respiratory diseases, immune system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and hemic and lymphatic diseases. The drug is currently in Phase 2 of clinical development and is primarily being studied for its efficacy in treating multiple myeloma and non-small cell lung cancer.
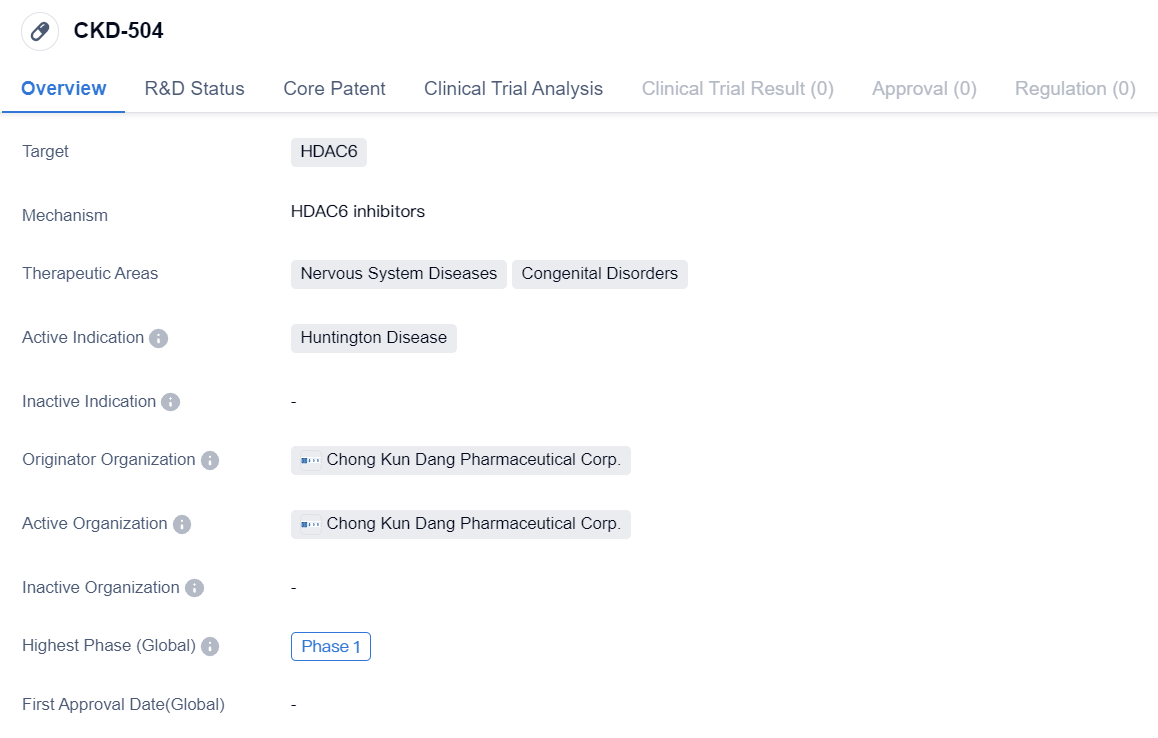
Clinical Phase Ⅰ HDAC6 inhibitors: CKD-504
CKD-504 is a small molecule drug that targets HDAC6, a protein involved in various cellular processes. It is being developed by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corp., a pharmaceutical company based in South Korea. The drug is primarily focused on treating Huntington Disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Huntington Disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the nervous system, leading to the deterioration of both mental and physical abilities. Currently, there is no cure for this condition, and available treatments only aim to manage the symptoms. CKD-504, being in Phase 1 of clinical development, suggests that it is still in the early stages of testing and evaluation.
The therapeutic areas of CKD-504 also include congenital disorders, which are conditions that are present at birth and often result from genetic abnormalities. This indicates that the drug may have potential applications in treating other genetic disorders beyond Huntington Disease.
As a small molecule drug, CKD-504 is likely to have a low molecular weight and can easily penetrate cell membranes. This characteristic is advantageous as it allows the drug to reach its target, HDAC6, within cells and exert its therapeutic effects.
The information provided does not specify the specific mechanism of action of CKD-504 or any potential side effects associated with its use. Additionally, there is no information regarding the results of preclinical studies or any ongoing clinical trials beyond Phase 1.
In summary, CKD-504 is a small molecule drug developed by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corp. that targets HDAC6. It is primarily being developed for the treatment of Huntington Disease, a neurodegenerative disorder. The drug is currently in Phase 1 of clinical development, indicating that further testing and evaluation are required to determine its safety and efficacy