Revolutionizing Treatment Across Multiple Therapeutic Areas: The Global Approval and Impact of Iptacopan
Iptacopan is a small molecule drug that targets the complement factor B (CFB) and has been approved for various therapeutic areas, including hemic and lymphatic diseases, immune system diseases, neoplasms, cardiovascular diseases, and others. Iptacopan originated from Novartis Pharma AG and has obtained approval globally, with the first approval granted in the United States in December 2023. The drug is subject to various regulatory designations, including priority review, accelerated approval, rare pediatric disease, PRIME, orphan drug, and breakthrough therapy.
Log in to the Patsnap Chemical. Select the Multi-Structure search, and search for the reactants and products in the specific steps of the synthesis route of Iptacopan, and you can query the relevant literature. 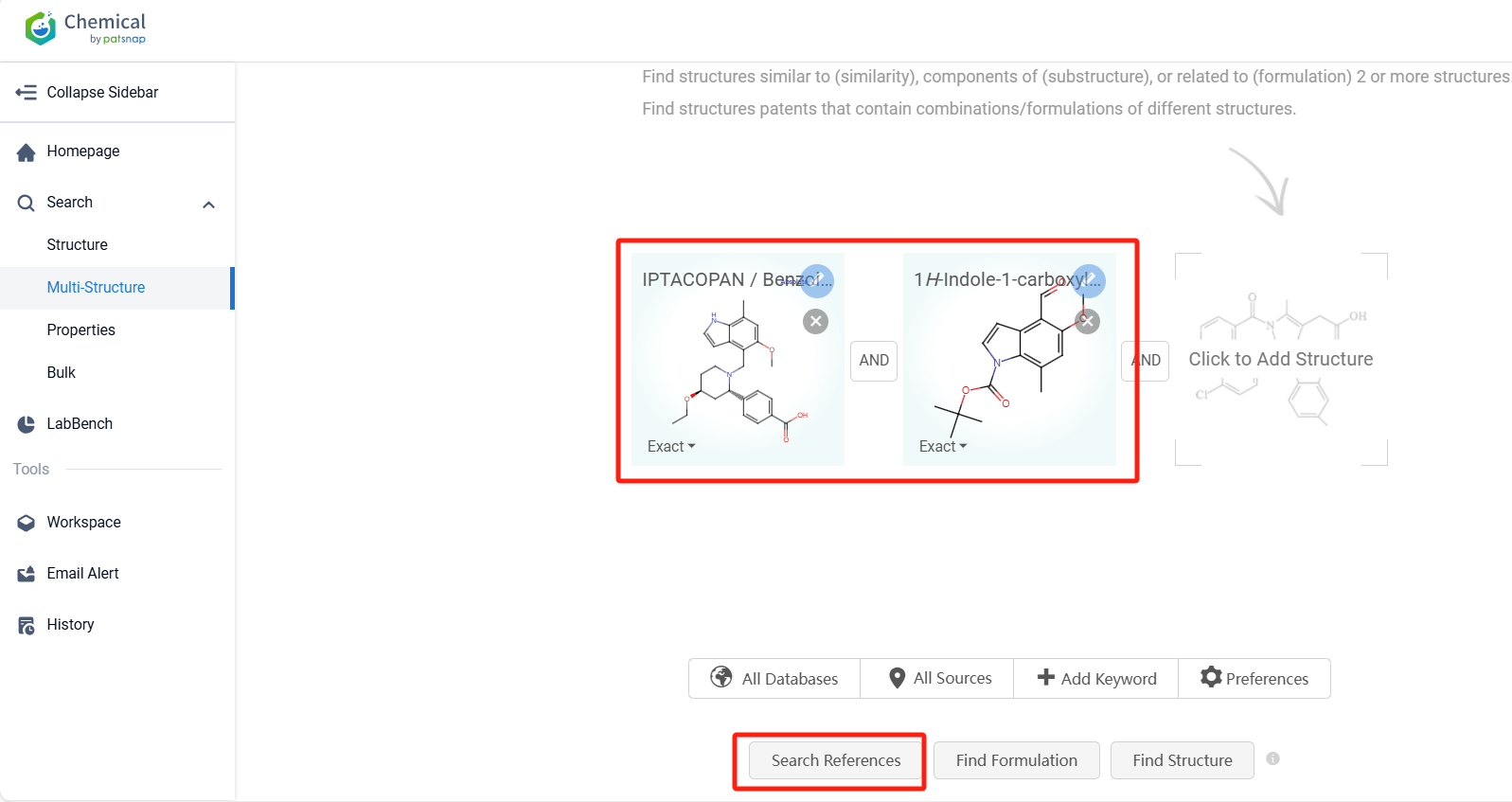
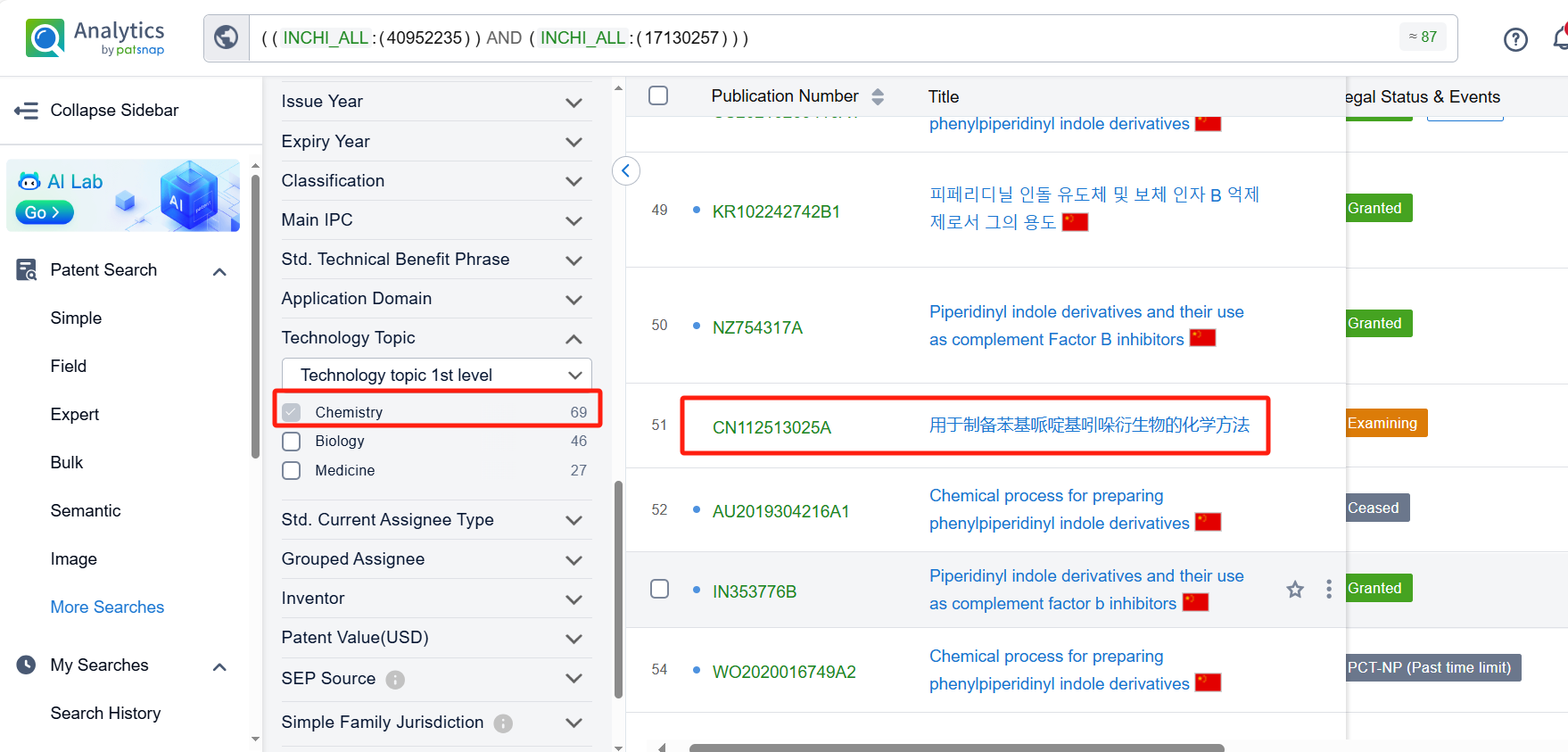
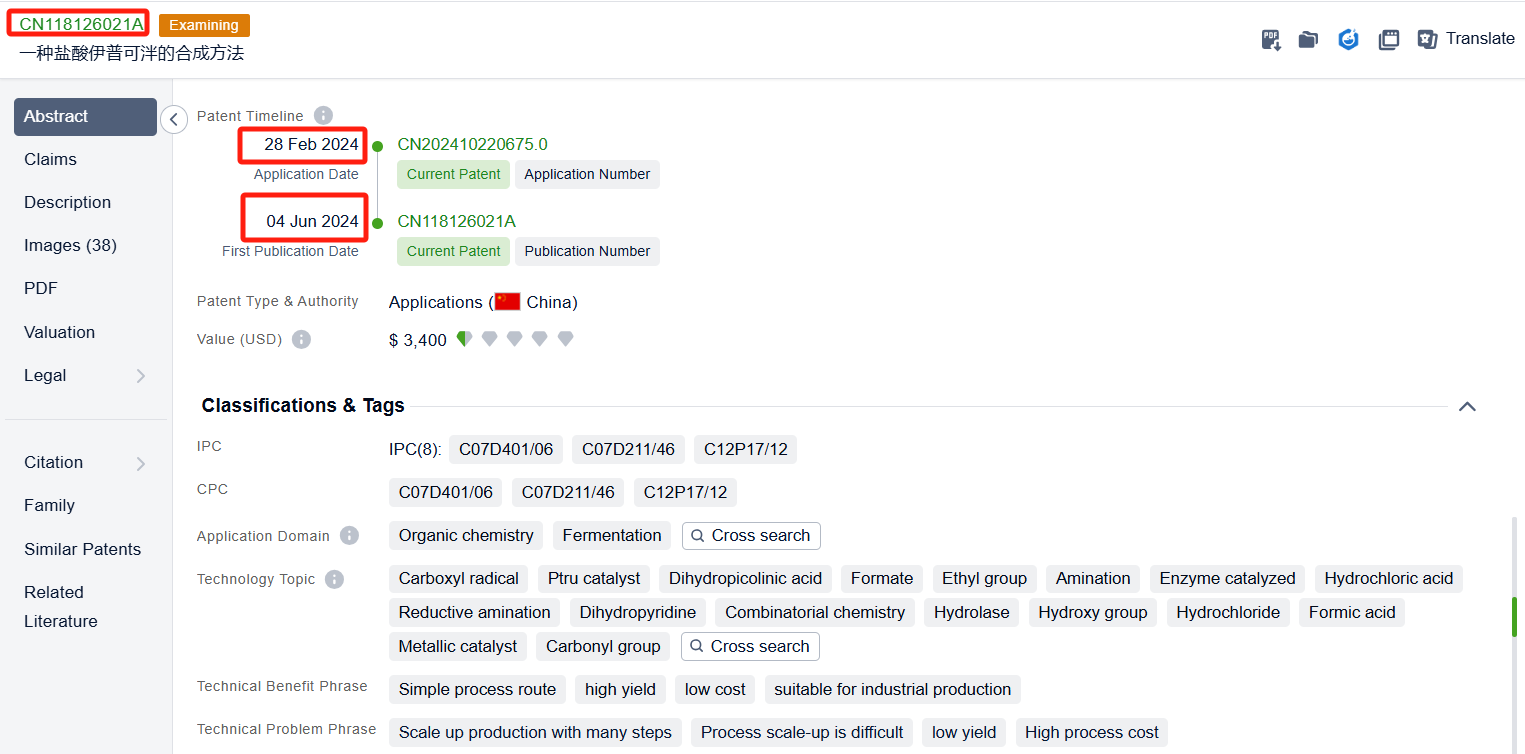
After jumping to the Patsnap Patent Database, check the 'Chemistry' category under the technical subject classification and click on the filter, which will allow you to accurately retrieve the design and improvement of the Iptacopan process route by Novartis and other companies,Such as Novartis' patent US11208398B2 describes a new and improved method for making a compound called Iptacopan. This new method involves using less hazardous chemicals, fewer reactions, and fewer by-products. The method is also more efficient and generates high quality compounds,Its corresponding Chinese patent CN112513025A has also entered substantive examination. HANGZHOU CHEMINSPIRE TECH Co., Ltd. also offers a method for synthesizing ipatacopan hydrochloride, which has the advantages of a short synthesis route, simple operation, and high yield.
The approval of Iptacopan represents an important milestone in the treatment of a wide range of diseases, particularly those related to the complement system and various rare and serious conditions. The drug's approval in the United States in 2023 indicates its potential to address unmet medical needs and provide therapeutic benefits to patients in need. As a small molecule drug targeting CFB, Iptacopan has showcased its efficacy in multiple therapeutic areas, paving the way for potential advancements in the treatment landscape for these conditions.
Overall, the approval of Iptacopan marks an important advancement in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in the field of biomedicine, and underscores the potential for novel therapeutic approaches to address complex and diverse medical conditions. The drug's regulatory designations further highlight its potential to address rare diseases and urgent medical needs, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
AI built to maximize IP and R&D efficiency
Redefine chemical FTO with a range of structure retrieval options at your fingertips, from exact matches to similarity searches, all powered by deep data processing techniques and proprietary AI algorithms to eliminate the risk of omitting key results.