Sanofi's phase 3 clinical trial data for teplizumab published in NEJM, for the treatment of type 1 diabetes
Recently, Sanofi announced the latest data from the Phase 3 clinical trial named PROTECT for Tzield (teplizumab). The results showed that compared to a placebo, Tzield slowed down the decline in β-cell function and preserved their function in children and adolescents aged 8-17 who were diagnosed with stage 3 autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D) within the previous six weeks.
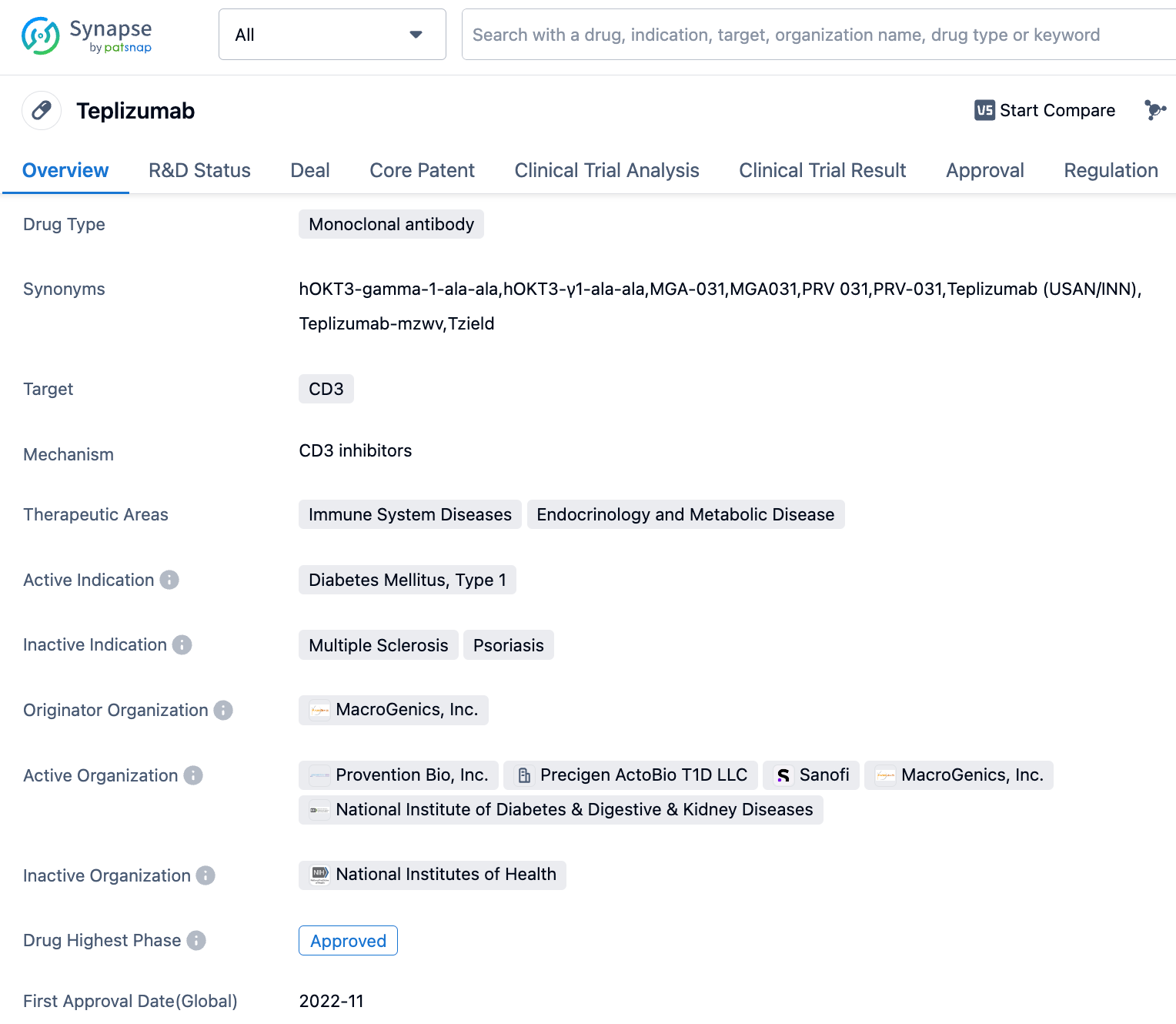
Teplizumab is an antibody drug used to treat type 1 diabetes (T1D). It is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD3 receptors. Its mechanism of action is to slow down the auto-immune attack on insulin-producing cells, thereby preventing and slowing down the damage and death of these cells. On November 17, 2022, the FDA approved Teplizumab (TzieldTM) as the first and only immune modulating therapy for delaying the onset of stage 3 T1D in adults and children aged 8 years and older.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The Phase 3 clinical trial named PROJECT is a randomized, double-blind study with a placebo control. Newly diagnosed children or adolescents underwent two 12-day treatment courses. The trial results showed that Tzield reached the primary endpoint of the study. At the end of the trial (78 weeks), it significantly slowed the decline in average levels of C-peptide compared to the placebo. In the Tzield group, 94.9% of participants maintained a peak C-peptide level ≥0.2 pmol/mL, while for the placebo group this value was 79.2% (p<0.001). C-peptide is a biomarker of β-cell function. This significant difference suggests that Tzield has the potential to slow the progression of type 1 diabetes in this population. Although the key secondary endpoint of the study did not reach statistical significance, there was a trend in favor of Tzield in relevant clinical parameters.
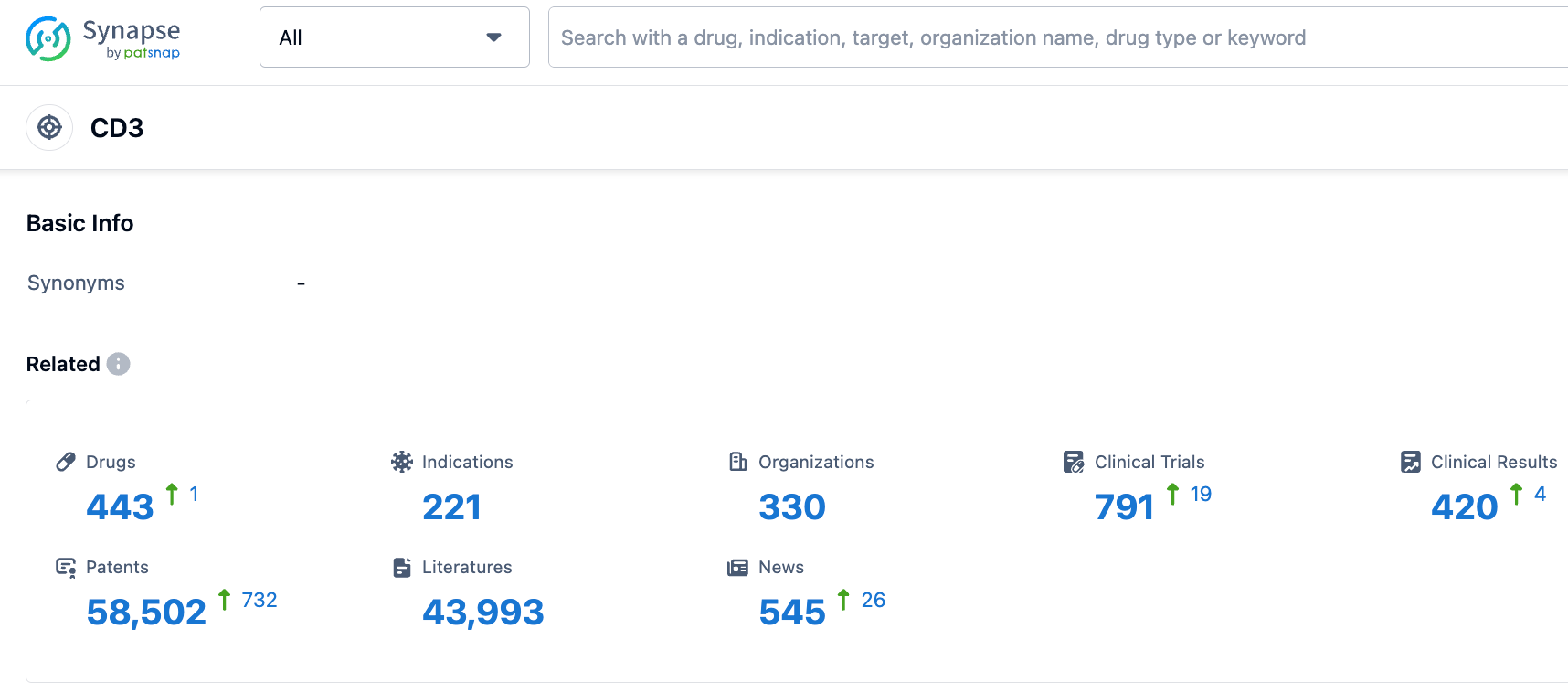
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
According to the synapse database, as of October 20, 2023, there are a total of 443 CD3 target drugs under investigation, with 221 indication types, 330 research institutes involved, involving 791 clinical trials, and up to 58433 patents... T1D is a chronic autoimmune disease. Because the autoimmune system progressively destroys the insulin-producing β-cells, the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is affected. T1D is more common in children or adolescents, with a family hereditary nature, accounting for about 5~10% of all patients with diabetes. The development path of Teplizumab has lasted for 24 years, and we look forward to more new T1D drugs being marketed in the future.