Star of transcriptional pathway potential: CDK9 inhibitor
CDK9, also known as cyclin-dependent kinase 9, plays a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression and cell cycle progression in the human body. It forms a part of the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) complex, which controls the release of RNA polymerase II from promoter-proximal pausing, allowing for efficient transcription elongation. CDK9 also phosphorylates various transcription factors and chromatin-associated proteins, influencing their activity and promoting gene transcription. Additionally, CDK9 has been implicated in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and DNA damage response. Understanding the role of CDK9 provides valuable insights for the development of targeted therapies in the pharmaceutical industry.
CDK9 Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 10 Sep 2023, there are a total of 52 CDK9 drugs worldwide, from 71 organizations, covering 87 indications, and conducting 173 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.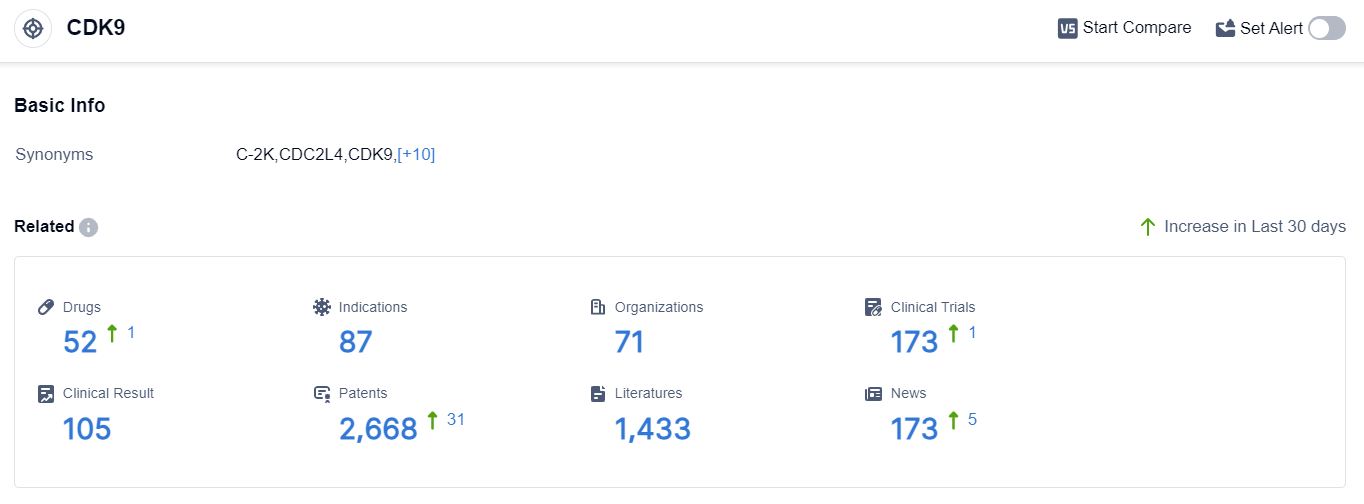
The analysis of the target CDK9 in the pharmaceutical industry reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in R&D. Merck KGaA, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC, Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd., and Sanofi are among the companies with significant R&D progress.
Drugs targeting CDK9 have been approved for indications such as B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Hematologic Neoplasms, Multiple Myeloma, and others. Small molecule drugs, biological products, PROTACs, and chemical drugs are progressing rapidly under the current target.
The United States, European Union, and other countries/locations are actively developing drugs targeting CDK9. The future development of the target CDK9 is expected to witness further advancements in R&D and potential competition among innovative drugs and biosimilars.
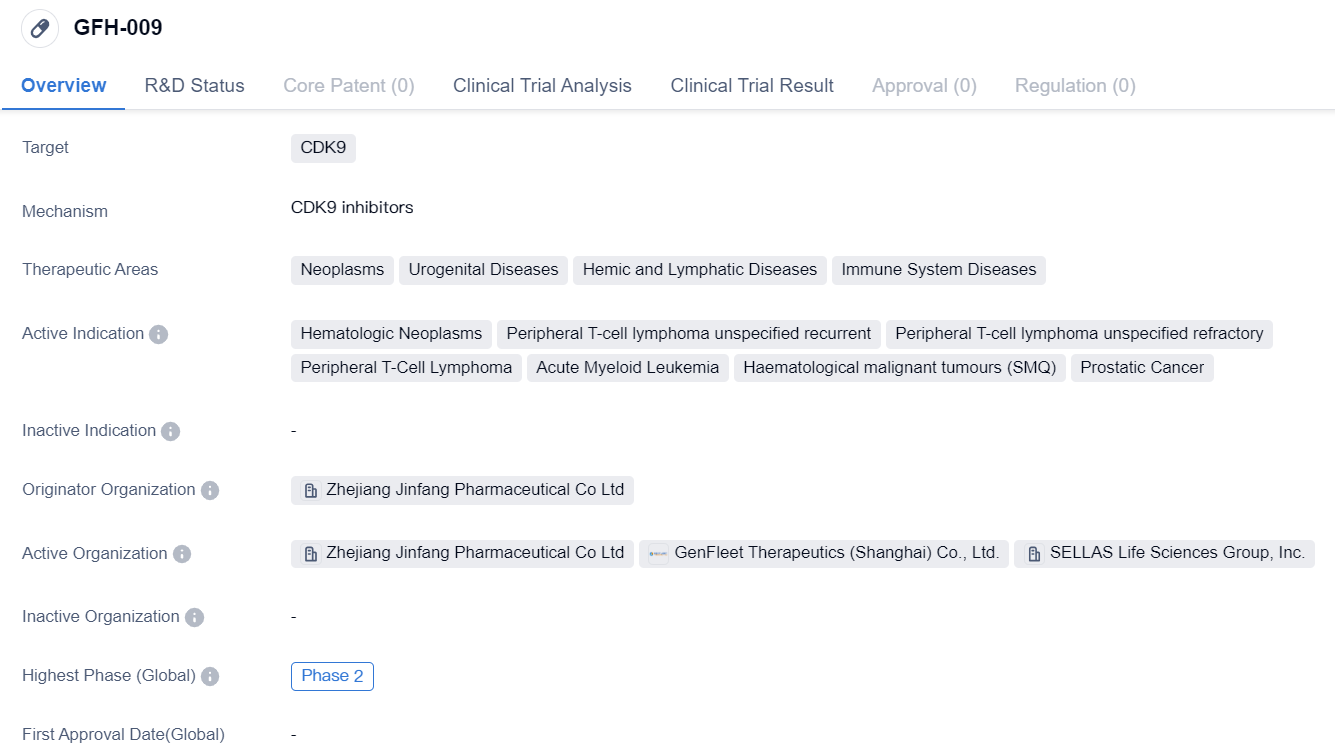
CDK9 inhibitor entering phase II clinical trials:GFH-009
GFH-009 is a small molecule drug that targets CDK9, a protein involved in cell cycle regulation and transcriptional control. This drug is being developed by Zhejiang Jinfang Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, a pharmaceutical company based in China.
The therapeutic areas that GFH-009 aims to address include neoplasms (abnormal growth of cells), urogenital diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and immune system diseases. Specifically, it is being investigated for its potential in treating hematologic neoplasms, peripheral T-cell lymphoma (both recurrent and refractory), acute myeloid leukemia, haematological malignant tumors, and prostatic cancer.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Currently, GFH-009 has reached Phase 2 of clinical development globally. In China, it has reached Phase 1/2, indicating that it is still in the early stages of clinical testing within the country.
The development of GFH-009 as a small molecule drug targeting CDK9 is significant in the field of biomedicine. CDK9 plays a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle and gene expression, making it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in various diseases, particularly cancer. By inhibiting CDK9, GFH-009 has the potential to disrupt the growth and survival of cancer cells, offering a promising approach for the treatment of hematologic neoplasms, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and prostatic cancer.
As GFH-009 progresses through clinical trials, further research will be conducted to evaluate its safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. The results obtained from these trials will determine the drug's future development and its potential to become a valuable treatment option for patients suffering from the mentioned diseases.
In conclusion, GFH-009 is a small molecule drug developed by Zhejiang Jinfang Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, targeting CDK9. It is being investigated for its potential in treating various neoplasms, urogenital diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and immune system diseases. With its current highest phase of development being Phase 2 globally and Phase 1/2 in China, GFH-009 shows promise as a potential therapeutic option for hematologic neoplasms, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and prostatic cancer. Further research and clinical trials will determine its efficacy and safety profile.
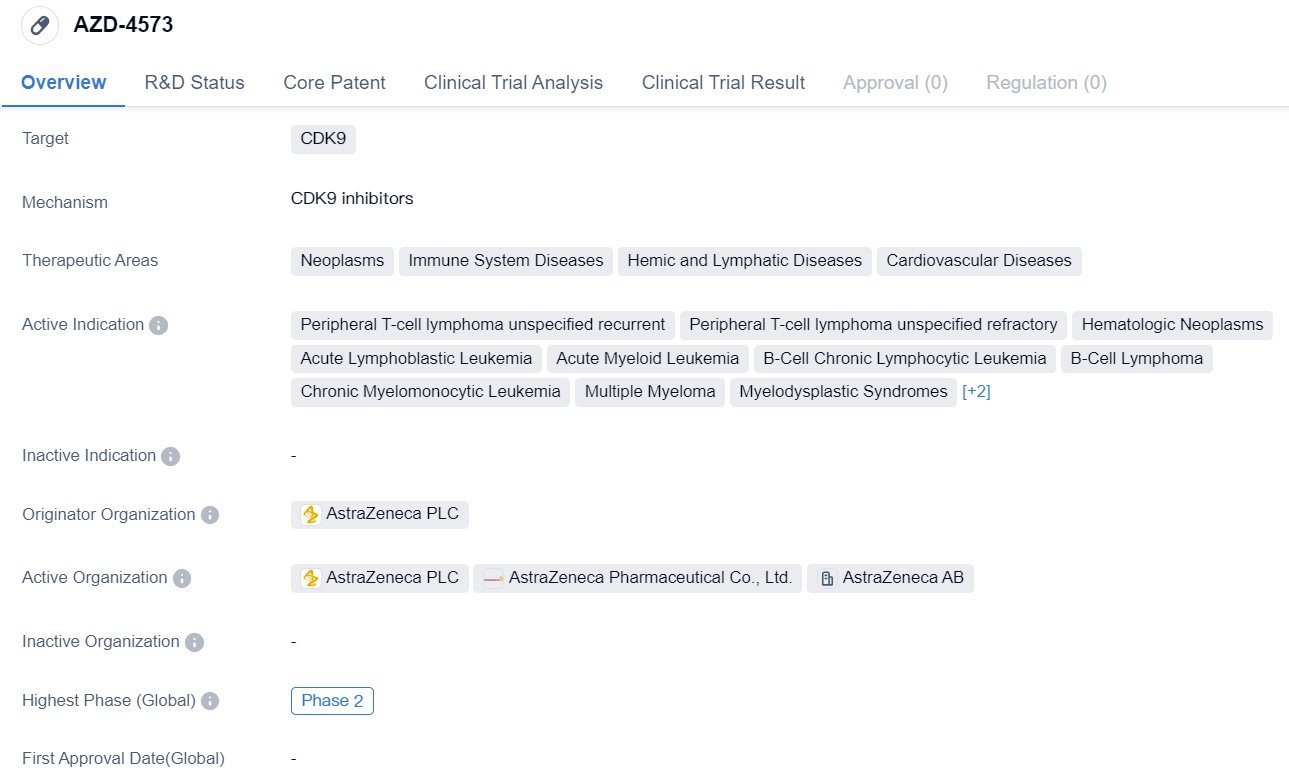
AZD-4573
AZD-4573 is a small molecule drug that targets CDK9, a protein involved in cell cycle regulation and transcriptional control. It is being developed by AstraZeneca PLC, a leading pharmaceutical company. The drug is currently in Phase 2 of clinical development globally, indicating that it has shown promising results in early-stage trials and is being further evaluated for its safety and efficacy.
The therapeutic areas for AZD-4573 include neoplasms (abnormal growth of cells), immune system diseases, hemic and lymphatic diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. This suggests that the drug has potential applications in treating a wide range of conditions related to these areas. Specifically, AZD-4573 is being investigated for its effectiveness in treating peripheral T-cell lymphoma that is recurrent or refractory, as well as various hematologic neoplasms such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes, and T-cell lymphoma.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
The drug's mechanism of action, targeting CDK9, suggests that it may inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells by interfering with their ability to divide and replicate. CDK9 is involved in the regulation of gene expression, and its inhibition can potentially disrupt the transcriptional machinery of cancer cells, leading to their death or reduced growth.
In terms of development progress, AZD-4573 has reached the highest phase of Phase 2 globally, indicating that it has advanced beyond early-stage trials and is now being tested in larger patient populations to assess its safety and efficacy. In China, the drug has received IND (Investigational New Drug) approval, which allows it to be tested in clinical trials in the country.
Overall, AZD-4573 shows promise as a potential treatment for various cancers and immune-related diseases. Its specific targeting of CDK9 and its advancement to Phase 2 trials suggest that it has demonstrated positive results in early-stage studies. Further clinical trials will be needed to determine its effectiveness and safety profile in larger patient populations.