Targeting 5-lipoxygenase - Leukotriene inhibitor
Leukotrienes are a group of inflammatory mediators produced by the metabolism of arachidonic acid (AA) through the 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) pathway, featuring a conjugated triene structure of a 20-carbon unsaturated acid. They are classified into six types - A, B, C, D, E, F, based on their substituents. Among these, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 all contain cysteinyl at C-6, collectively referred to as cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs). Leukotrienes can be produced by cells after various immunological or non-immunological stimuli, through autocrine or paracrine mechanisms. These stimuli include antigens, immune complexes, complements, cytokines, osmotic pressure, and environmental pollutants.
Once leukotrienes bind with specific G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) on the cell surface, they activate Gq proteins leading to an increase in intracellular calcium concentrations, and activating Gi proteins causing a decrease in cAMP, both of which can trigger a cascade of kinase protein signal transduction, inducing intracellular transcription responses and cell movement, thereby widely participating in the body's immune response. Currently, anti-leukotriene drugs are primarily divided into two categories: the first are leukotriene receptor antagonists, which inhibit tissue responses to leukotrienes by blocking leukotriene receptors, including Montelukast, Zafirlukast, and Pranlukast; the second one are leukotriene synthesis inhibitors, which inhibit the activity of the key enzyme 5-LO in the leukotriene synthesis pathway, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of cysteinyl leukotrienes and LTB4.
Leukotriene Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 142 5-LOX drugs worldwide, from 105 organizations, covering 60 indications, and conducting 52 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
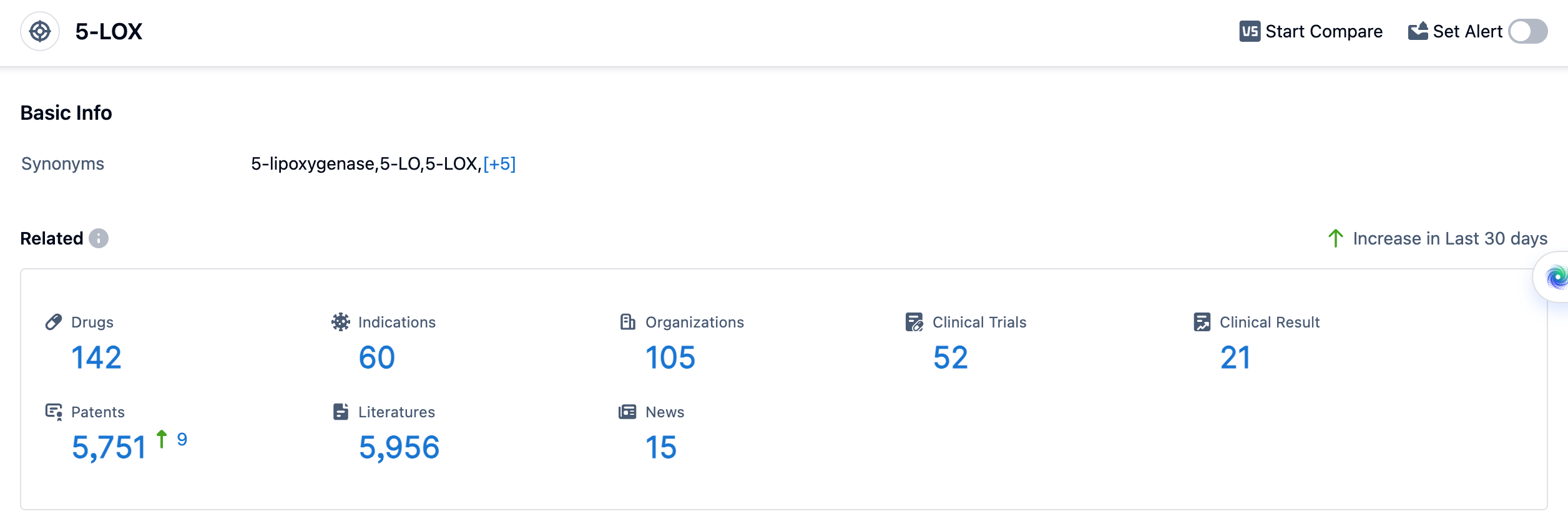 5-LOX, or 5-lipoxygenase, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the human body's inflammatory response. It is responsible for the conversion of arachidonic acid into leukotrienes, which are potent mediators of inflammation. These leukotrienes are involved in various physiological processes, including immune response, allergic reactions, and the development of certain diseases such as asthma and arthritis. Due to its involvement in inflammation, 5-LOX has become an attractive target for pharmaceutical research, with the aim of developing drugs that can modulate its activity and potentially alleviate inflammatory conditions. Drugs under this target have been approved for indications such as asthma. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, with one approved and six in preclinical development. The United States is the leading country in terms of drug development for target 5-LOX, followed by Australia, Israel, and the European Union. China has made progress in preclinical development for this target.
5-LOX, or 5-lipoxygenase, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the human body's inflammatory response. It is responsible for the conversion of arachidonic acid into leukotrienes, which are potent mediators of inflammation. These leukotrienes are involved in various physiological processes, including immune response, allergic reactions, and the development of certain diseases such as asthma and arthritis. Due to its involvement in inflammation, 5-LOX has become an attractive target for pharmaceutical research, with the aim of developing drugs that can modulate its activity and potentially alleviate inflammatory conditions. Drugs under this target have been approved for indications such as asthma. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, with one approved and six in preclinical development. The United States is the leading country in terms of drug development for target 5-LOX, followed by Australia, Israel, and the European Union. China has made progress in preclinical development for this target.
The current competitive landscape for target 5-LOX is characterized by a diverse range of companies and drug types. The presence of biosimilars indicates intense competition around the innovative drugs. Further research and development are needed to explore the potential of target 5-LOX in various indications and to expand its market presence globally.
Leukotriene Pathway Inhibitor: Zileuton
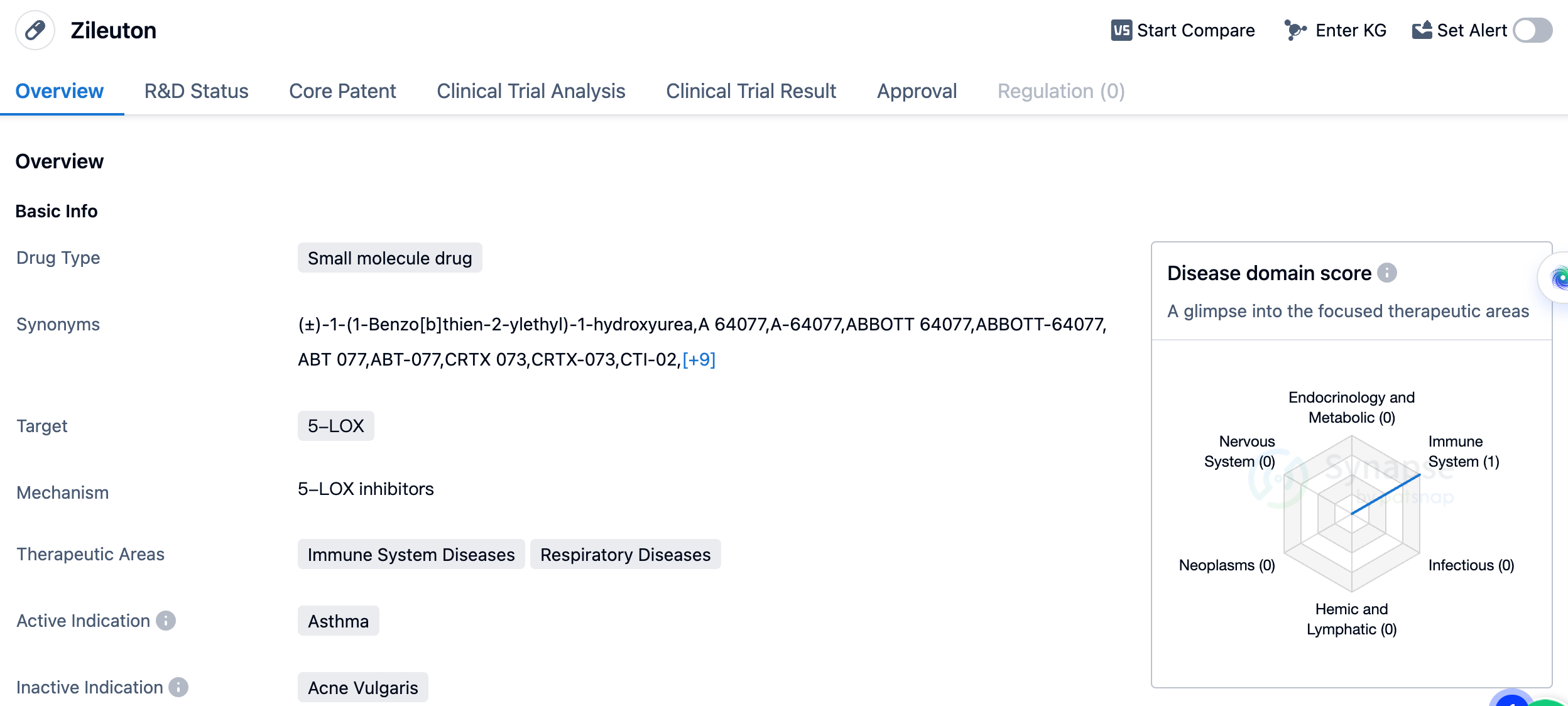
Zileuton is a Leukotriene pathway inhibitor, classified as a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, used for the treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Zileuton is associated with rare drug-induced liver disease and is considered contraindicated in patients with active liver disease. The 5- lipoxygenase is responsible for the conversion of arachidonic acid into leukotriene A4, leukotriene A4 is an effective mediator of the inflammatory cascade reaction, playing a pivotal role in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Zileuton has been shown to improve the symptoms of asthma and allergic rhinitis and was approved for use in the United States in 1996. Current indications include the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children aged 12 and above.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Given its approval for asthma, Zileuton is expected to have a positive impact on patients suffering from this condition. By targeting 5-LOX, the drug helps to reduce the production of leukotrienes, which are known to contribute to airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction in asthma patients. By inhibiting this pathway, Zileuton can potentially alleviate symptoms and improve lung function in individuals with asthma.
In summary, Zileuton is a small molecule drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that targets 5-LOX and is indicated for the treatment of asthma. Its approval in 1996 in the United States signifies its efficacy and safety in managing this respiratory condition. As a therapeutic option, Zileuton has the potential to provide relief to asthma patients by reducing airway inflammation and constriction.
Targeted 5-LOX Small Molecule Drugs:A-72694
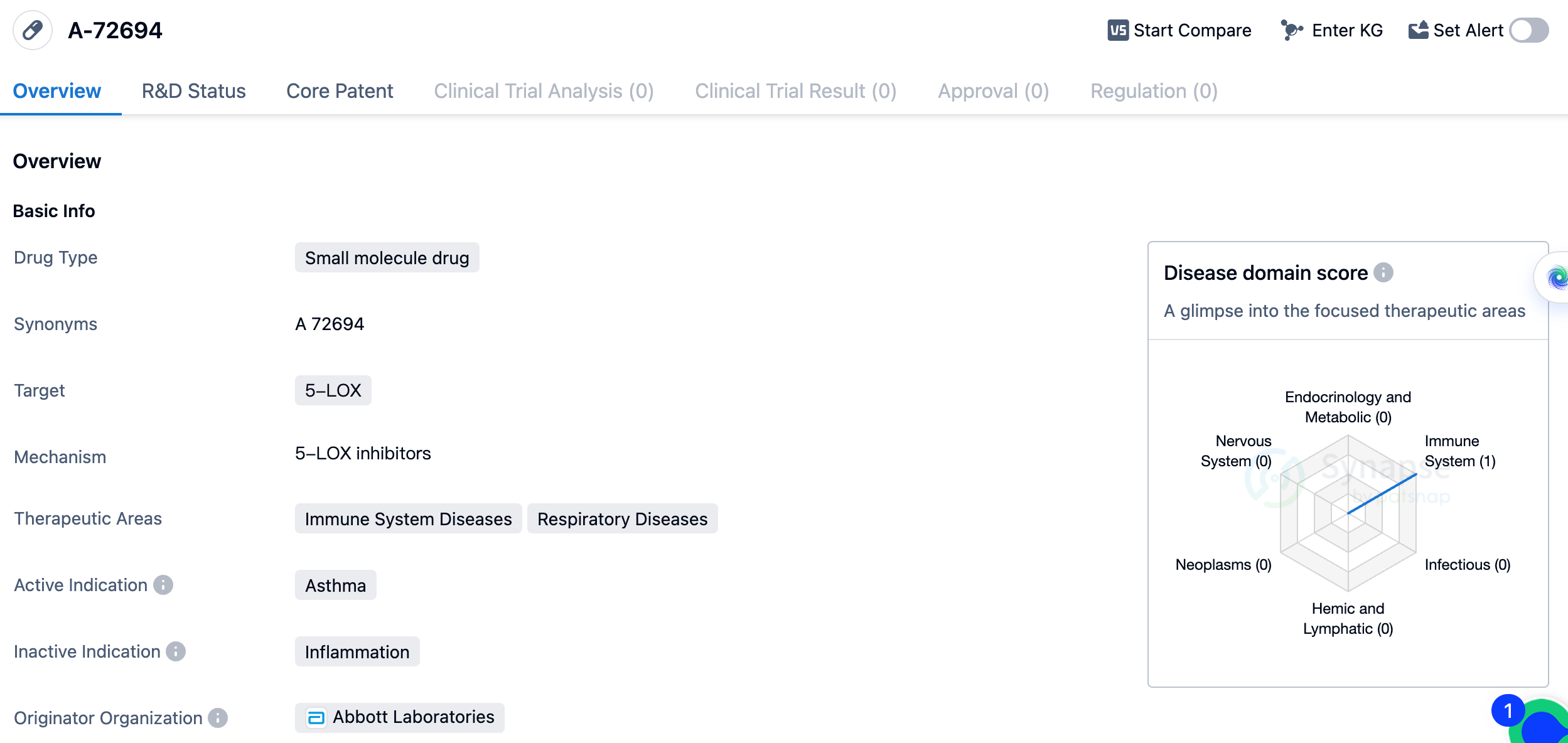
The drug A-72694 is a small molecule drug that targets 5-LOX, which stands for 5-lipoxygenase. It is primarily developed for the treatment of asthma, a respiratory disease that affects the immune system. The drug is currently in the preclinical phase, indicating that it is still undergoing laboratory testing and has not yet progressed to human clinical trials. A-72694 is being developed by Abbott Laboratories, a well-known pharmaceutical company with expertise in the field of biomedicine. The therapeutic areas of A-72694 include immune system diseases and respiratory diseases, with asthma being the active indication. This indicates that the drug is specifically designed to target and treat asthma, a chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
As a small molecule drug, A-72694 is likely to have a low molecular weight and can be easily synthesized in a laboratory setting. Small molecule drugs are typically orally administered and can easily penetrate cell membranes, allowing them to interact with specific targets within the body. Although the drug is still in the preclinical phase, it shows promise for the treatment of asthma by targeting 5-LOX. 5-LOX is an enzyme involved in the production of leukotrienes, which are inflammatory molecules that play a role in asthma pathogenesis. By inhibiting 5-LOX, A-72694 may help reduce inflammation and improve respiratory symptoms in asthma patients.
In summary, A-72694 is a small molecule drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that targets 5-LOX for the treatment of asthma. It is currently in the preclinical phase, and further research and development are needed to determine its safety and efficacy in human clinical trials.