The Clinical Application of Histamine Receptor Antagonists
Histamine receptors are proteins found in various tissues throughout the human body. They play a crucial role in mediating the effects of histamine, a chemical released by cells in response to injury or allergic reactions. There are four types of histamine receptors, namely H1, H2, H3, and H4, each with distinct functions. H1 receptors are primarily involved in allergic responses, regulating smooth muscle contraction, and promoting inflammation. H2 receptors are mainly found in the stomach, where they stimulate the production of gastric acid. H3 receptors are primarily located in the brain and regulate the release of neurotransmitters. H4 receptors are involved in immune responses and inflammation. Understanding the role of histamine receptors is essential for developing drugs that target these receptors to treat various conditions.
Histamine receptor Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 18 Sep 2023, there are a total of 454 Histamine receptor drugs worldwide, from 408 organizations, covering 216 indications, and conducting 2271 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.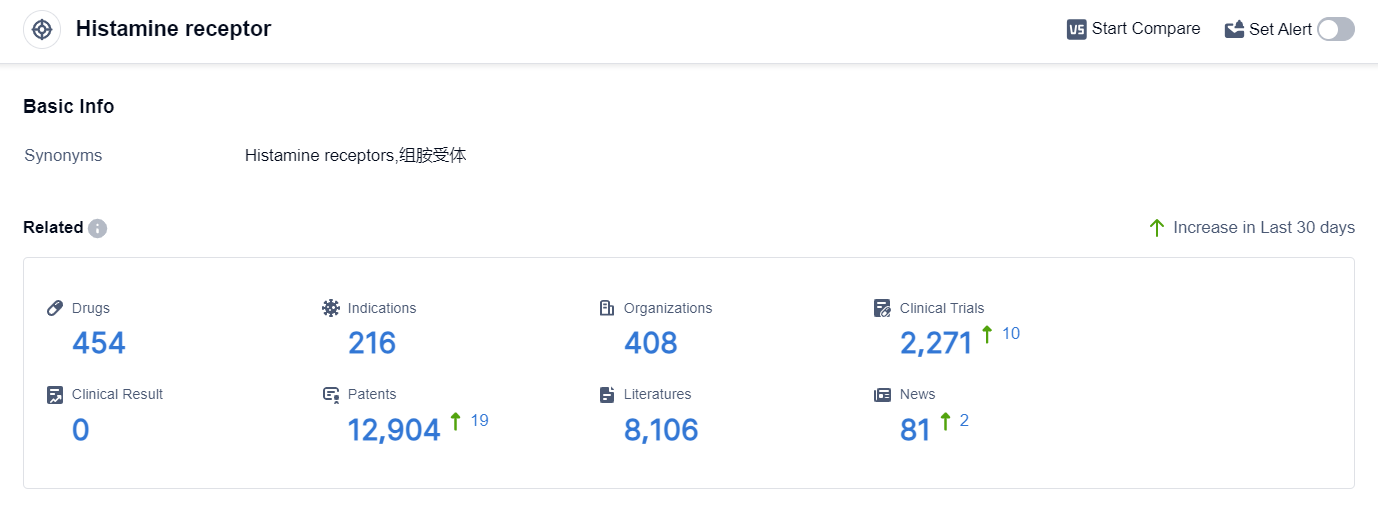
In conclusion, the target Histamine receptor is being actively researched and developed by various pharmaceutical companies. GSK Plc has the highest stage of development on this target, with several approved drugs.
The indications for drugs targeting the Histamine receptor cover a wide range of allergic and inflammatory conditions. Small molecule drugs are the most common type of drugs being developed, but there are also other drug types in progress.
China, the United States, and Japan are the leading countries in the development of drugs targeting the Histamine receptor. The current competitive landscape is characterized by intense competition, especially in the small molecule drug category. Future development in this field will likely focus on further research and development of small molecule drugs, as well as exploring the potential of other drug types.
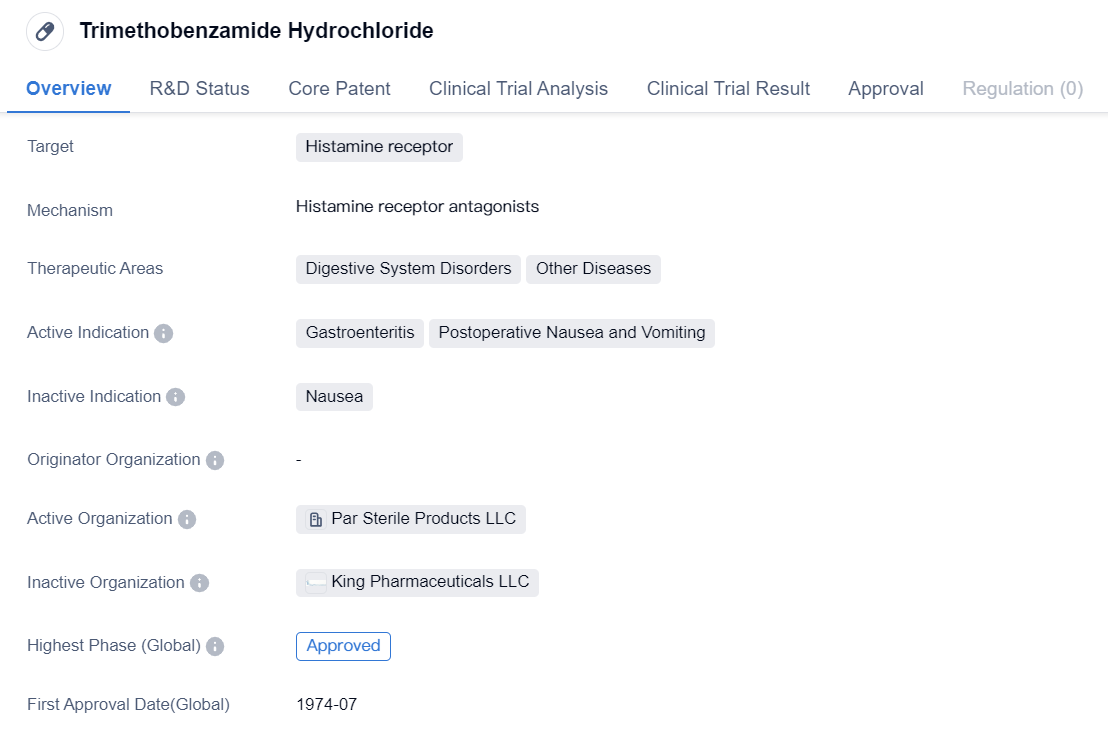
Key Drug: Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride
Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the histamine receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of digestive system disorders and other diseases. The drug is indicated for the management of gastroenteritis and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride has been approved for use and is currently in the highest phase of development globally. It received its first approval in the United States in July 1974. Since then, it has been widely used in the treatment of various conditions related to the digestive system.
As a small molecule drug, Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride is designed to interact with the histamine receptor, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. By targeting this receptor, the drug aims to alleviate symptoms associated with digestive system disorders, such as nausea and vomiting.
Gastroenteritis, commonly known as the stomach flu, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines. It often leads to symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride has been found to be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting associated with gastroenteritis, providing relief to patients suffering from this condition.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) is a common complication following surgical procedures. It can significantly impact the recovery process and patient comfort. Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride has been approved for use in managing PONV, helping to alleviate these symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
Since its first approval in 1974, Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride has been widely used in the United States and other countries for the treatment of digestive system disorders and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Its long history of use and approval status indicate its safety and efficacy in managing these conditions.
In summary, Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the histamine receptor. It is approved for use in the treatment of gastroenteritis and postoperative nausea and vomiting. With its first approval dating back to 1974 in the United States, the drug has been widely used and proven effective in managing these conditions.
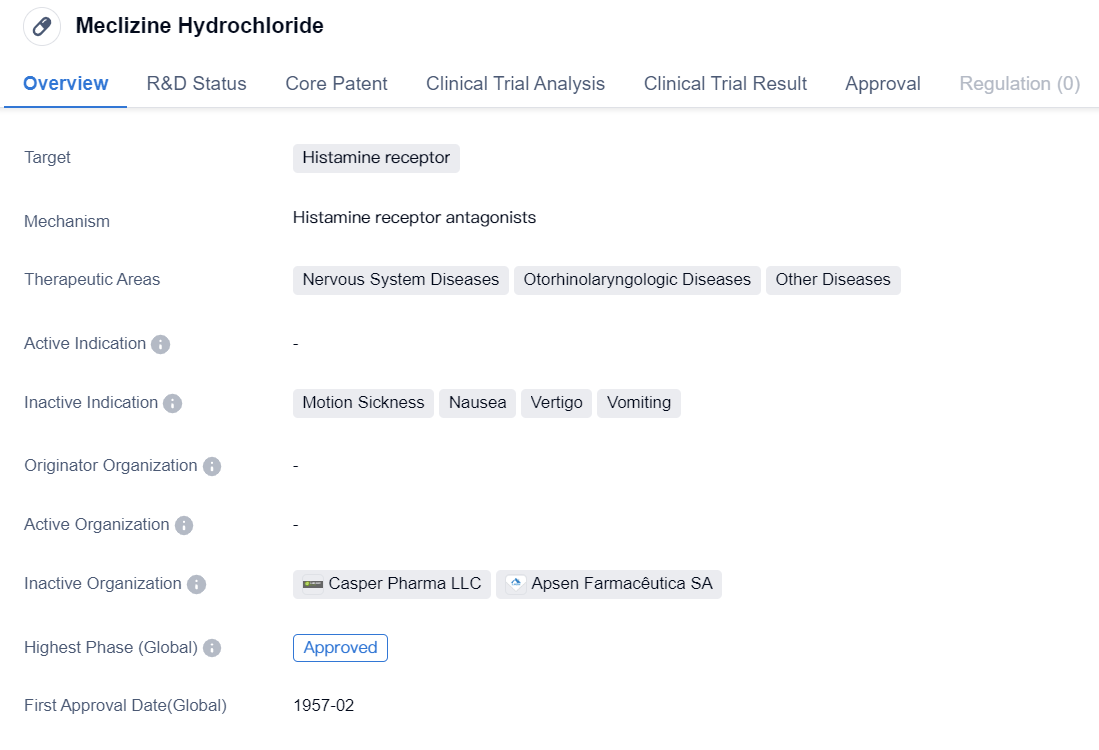
Meclizine Hydrochloride
Meclizine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that primarily targets the histamine receptor. It has been approved for use in the treatment of various diseases related to the nervous system, otorhinolaryngologic diseases, and other conditions. The drug received its first approval in the United States in February 1957.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
As a small molecule drug, Meclizine Hydrochloride is designed to interact with specific receptors in the body, in this case, the histamine receptor. By targeting this receptor, the drug aims to modulate the effects of histamine, a chemical involved in various physiological processes. This mechanism of action suggests that Meclizine Hydrochloride may be effective in managing conditions related to the nervous system and otorhinolaryngologic diseases.
The fact that Meclizine Hydrochloride has reached the highest phase of approval, both globally and in China, indicates that it has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation to demonstrate its safety and efficacy. This suggests that the drug has met the necessary regulatory requirements and has been deemed suitable for use in patients.
The first approval of Meclizine Hydrochloride in the United States in 1957 highlights its long history of use in the pharmaceutical industry. This suggests that the drug has been widely studied and utilized for several decades, potentially indicating its effectiveness and safety profile.
The therapeutic areas associated with Meclizine Hydrochloride, including nervous system diseases, otorhinolaryngologic diseases, and other conditions, suggest its potential versatility in treating a range of medical conditions. However, without further information, it is difficult to determine the specific diseases or conditions for which Meclizine Hydrochloride is most commonly prescribed.
In summary, Meclizine Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets the histamine receptor. It has received approval in both the global and Chinese markets and was first approved in the United States in 1957. The drug is indicated for the treatment of nervous system diseases, otorhinolaryngologic diseases, and other conditions. Its long history of use and highest phase of approval suggest its potential effectiveness and safety in managing various medical conditions.