The Multifunctional Novel Products of DNA Recombinant Technology: Fusion Protein
The term "Fusion protein" has two distinct definitions. One refers to the expression product of two recombined genes obtained through DNA recombinant technology, while the other refers to a group of proteins that mediate the fusion of two cytoplasmic membranes, such as one of the two glycoproteins contained in the outer leaflet of theSendai virus lipid bilayer, which mediates the fusion of the enveloped virus with the host cell cytoplasmic membrane. The other glycoprotein is the erythrocyte agglutinin neuramidase. The two different proteins can be linked into a large molecule either by chemical methods or by the fusion of genes.
Fusion protein technology is a purposeful gene fusion and protein expression method to obtain large amounts of standard fusion proteins. Using fusion protein technology, it is possible to construct and express novel target proteins with various functions.
Clinical Application of Fusion Proteins
1. DNA Vaccines
At present, vaccines have gone through three generations: The first generation vaccines activate the immune system with attenuated or killed pathogens; The second generation vaccines are component vaccines developed using biotechnology and recombinant DNA technology to induce an immune response; The third generation vaccines directly inject gene-recombined antigen genes to activate the human immune system, namely DNA vaccines.
DNA vaccines have obvious advantages compared to traditional vaccines, such as easy production, strong stability, low cost, and the ability to simultaneously induce both humoral and cellular immune responses.
2. Dual-Function Enzymes (Multi-Function Enzymes)
Research has found that in a large enzyme molecule constructed using gene fusion, if the entire encoding sequences of each enzyme molecule used to form the fusion protein are preserved in the new enzyme molecule, then the fusion protein generally retains the enzymatic activity of each of the enzyme molecules it was constructed from.
It has also been found that in these newly constructed fusion proteins, the proper folding of proteins and the active sites of each enzyme were not affected. Compared to single enzymes, the specific activity of the enzyme in the fusion protein is 50%-100%. For two or several enzymes that catalyze consecutive reactions, fusion proteins formed by gene fusion methods can produce a "proximity effect".
3. Targeted Drugs
Targeted drugs generally consist of two parts: one part is the drug; the other part is a ligand that can bind specifically to the lesion. Through fusion protein technology, these two parts can be fused together to form a protein with unique conformation and function.
4. Gene Expression
Gene fusion technology was first used to express exogenous proteins in bacteria (mainly E. coli). For foreign genes (especially eukaryotic genes), fusion expression in E. coli has many advantages. For one, since foreign genes are generally connected to the C-terminal encoding sequence of a suitable fusion protein, there's no need to design SD sequences separately. Also, due to the presence of N-terminal fusion genes, foreign gene expression is relatively easier. Secondly, the expression products of foreign genes are often degraded by the host cell's proteases. When a foreign gene forms a fusion gene with a certain protein of the host itself, such as a part of the encoding sequence of β-galactosidase, its expression as a fusion protein often reduces degradation by the host cell.
Common fusion proteins include immunoglobulin (Ig) fusion proteins, parathyroid hormone (PTH) fusion proteins, and recombinant fusion proteins of cytokines.
Fusion proteins possess superior pharmacokinetic properties. Therefore, these drugs can be used in lower doses and are more effective compared to their unfused equivalents. So far, Fc fusion and HSA fusion techniques are the most widely used, but in recent years, XTEN fusion, CTP fusion, ELP fusion, and transferrin fusion techniques have made significant progress. Some drugs based on these technologies have already been launched, and a large number of drugs are currently undergoing clinical trials; they hold the promise to produce excellent outcomes, benefiting patients with various diseases worldwide.
Fusion protein Competitive Landscape
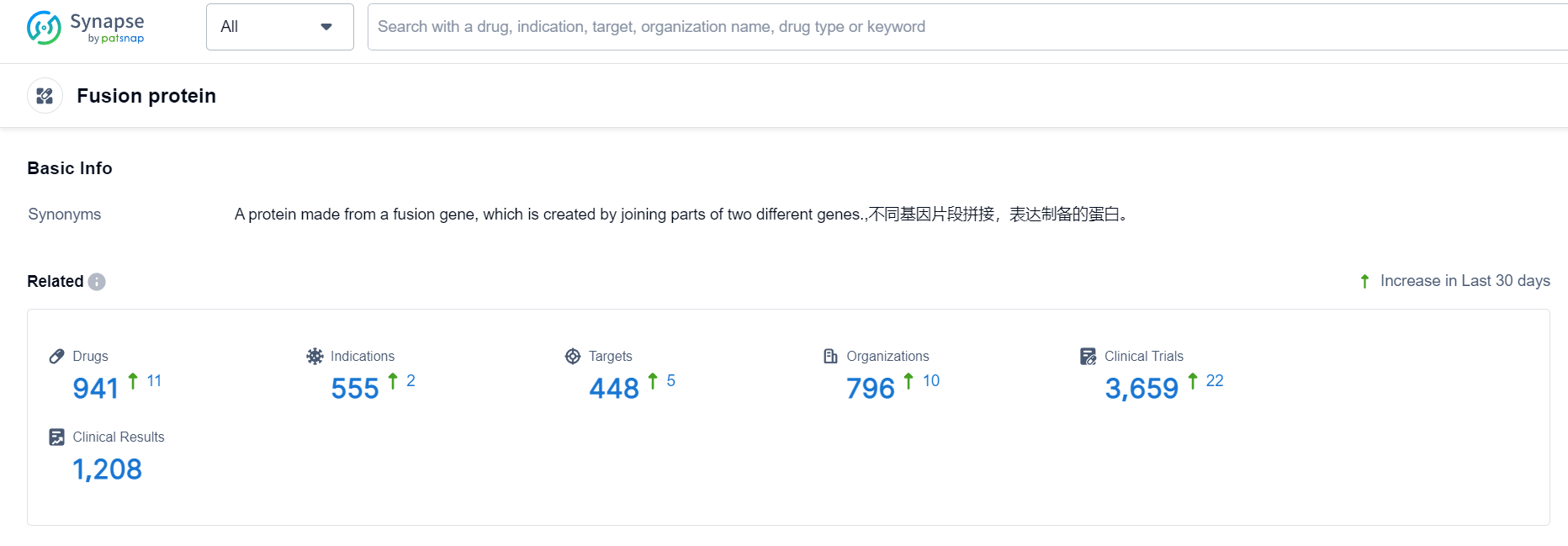
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 24 Sep 2023, there are a total of 941 Fusion protein drugs worldwide, from 796 organizations, covering 448 targets, 555 indications, and conducting 3659 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, targets, organizations, clinical trials, and clinical results related to this drug type.
Approved Recombinant protein Medicinal: Nirsevimab
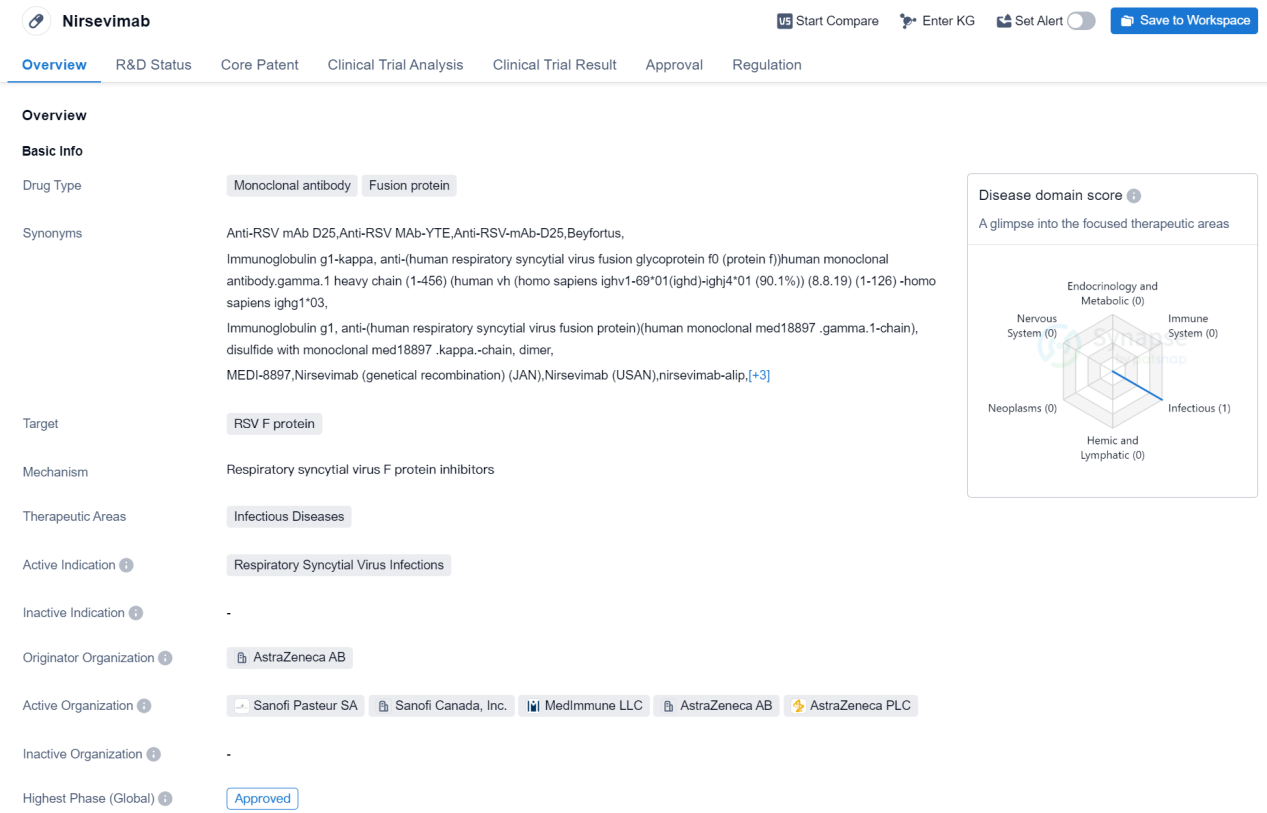
Nirsevimab is a monoclonal antibody fusion protein drug that targets the RSV F protein. It falls under the therapeutic area of infectious diseases, specifically Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infections. The drug is developed by AstraZeneca AB, a renowned pharmaceutical organization.
As of the highest phase, Nirsevimab has been approved globally. In China, it is currently in the NDA/BLA phase, indicating that it is awaiting approval from the Chinese regulatory authorities. The drug received its first approval globally in October 2022, with the European Union being the first country/location to grant approval.
Nirsevimab has undergone various regulatory processes to expedite its development and approval. It has been granted priority review, indicating that it is considered a high-priority drug due to its potential impact on public health. Additionally, it has received designations such as PRIME (PRIority MEdicines) and Fast Track, which aim to accelerate the development and review process for promising drugs. The drug has also undergone accelerated assessment, a regulatory mechanism that allows for a faster evaluation of drugs that address unmet medical needs. Furthermore, Nirsevimab has been designated as a Breakthrough Therapy, indicating its potential to provide significant improvement over existing treatments. Lastly, it has been recognized as a Promising Innovative Medicine, highlighting its innovative nature and potential benefits.
In summary, Nirsevimab is a monoclonal antibody fusion protein drug developed by AstraZeneca AB. It targets the RSV F protein and is indicated for the treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infections. The drug has received global approval, with the European Union being the first to grant approval. It has undergone various regulatory processes, including priority review, PRIME designation, Fast Track, accelerated assessment, Breakthrough Therapy designation, and recognition as a Promising Innovative Medicine. These regulatory mechanisms aim to expedite the development and review process for drugs that address unmet medical needs and have the potential to provide significant improvements in patient outcomes.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Benegrastim
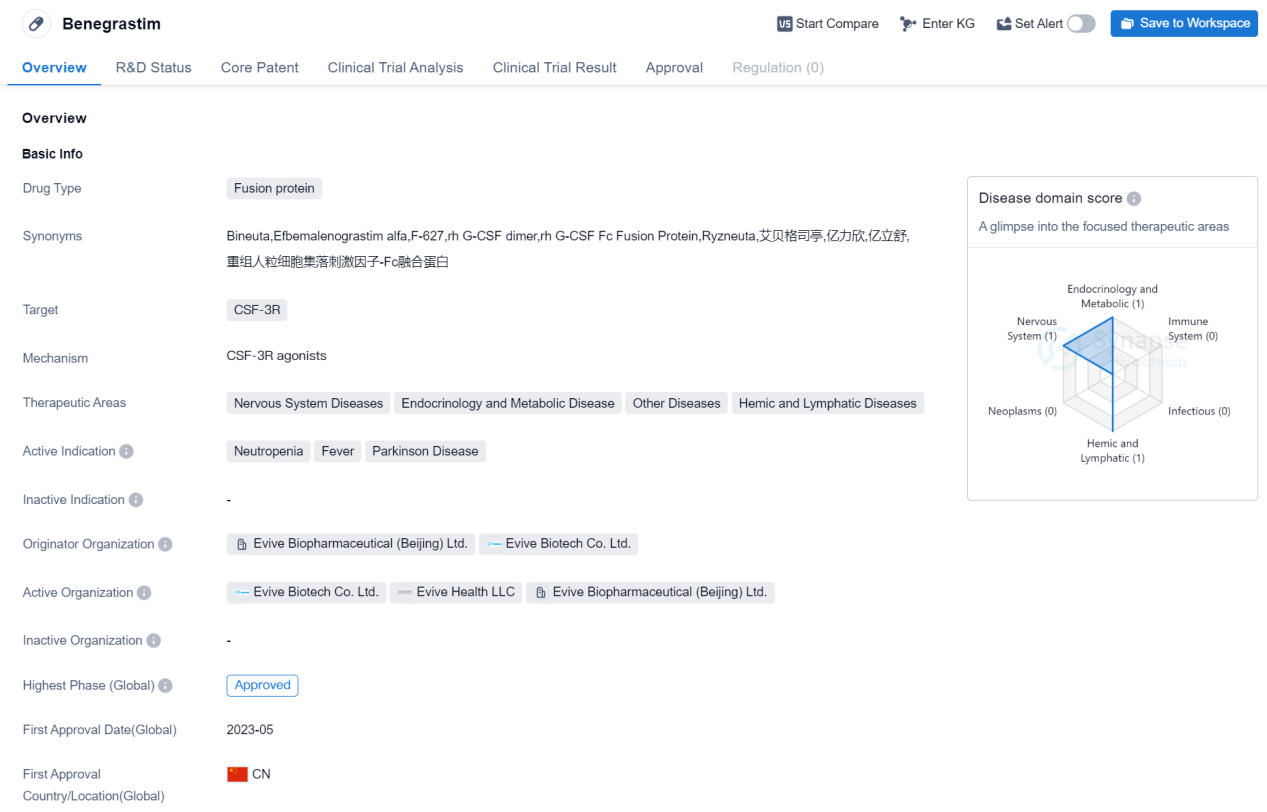
Benegrastim is a fusion protein drug that targets CSF-3R and is used in the treatment of various diseases. It falls under the therapeutic areas of Nervous System Diseases, Endocrinology and Metabolic Disease, Other Diseases, and Hemic and Lymphatic Diseases. The drug is primarily indicated for the treatment of Neutropenia, Fever, and Parkinson's Disease.
Benegrastim is developed by Evive Biopharmaceutical (Beijing) Ltd. and Evive Biotech Co. Ltd., both organizations based in China. It has received approval for use in the global market as well as in China. The drug's highest phase of development is approved, indicating that it has successfully completed clinical trials and met the necessary regulatory requirements.
The first approval for Benegrastim was granted in China in May 2023. As a fusion protein drug, Benegrastim is designed to target CSF-3R, a receptor involved in regulating the production and differentiation of white blood cells. Neutropenia, a condition characterized by a low count of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell), is one of the active indications for Benegrastim. By targeting CSF-3R, the drug aims to stimulate the production of neutrophils and restore their levels in the body.
In addition to Neutropenia, Benegrastim is also indicated for the treatment of Fever and Parkinson's Disease. The drug's therapeutic areas suggest that it may have potential applications in various diseases affecting the nervous system, endocrine system, metabolism, and the hematopoietic and lymphatic systems.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Overall, Benegrastim is a fusion protein drug developed by Evive Biopharmaceutical (Beijing) Ltd. and Evive Biotech Co. Ltd. It has received approval for use in China and globally, with its highest phase being approved. The drug targets CSF-3R and is indicated for the treatment of Neutropenia, Fever, and Parkinson's Disease. Its first approval was granted in China in May 2023.