Unleashing the Power of eperisone hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Review on R&D Breakthroughs
Eperisone hydrochloride's R&D Progress
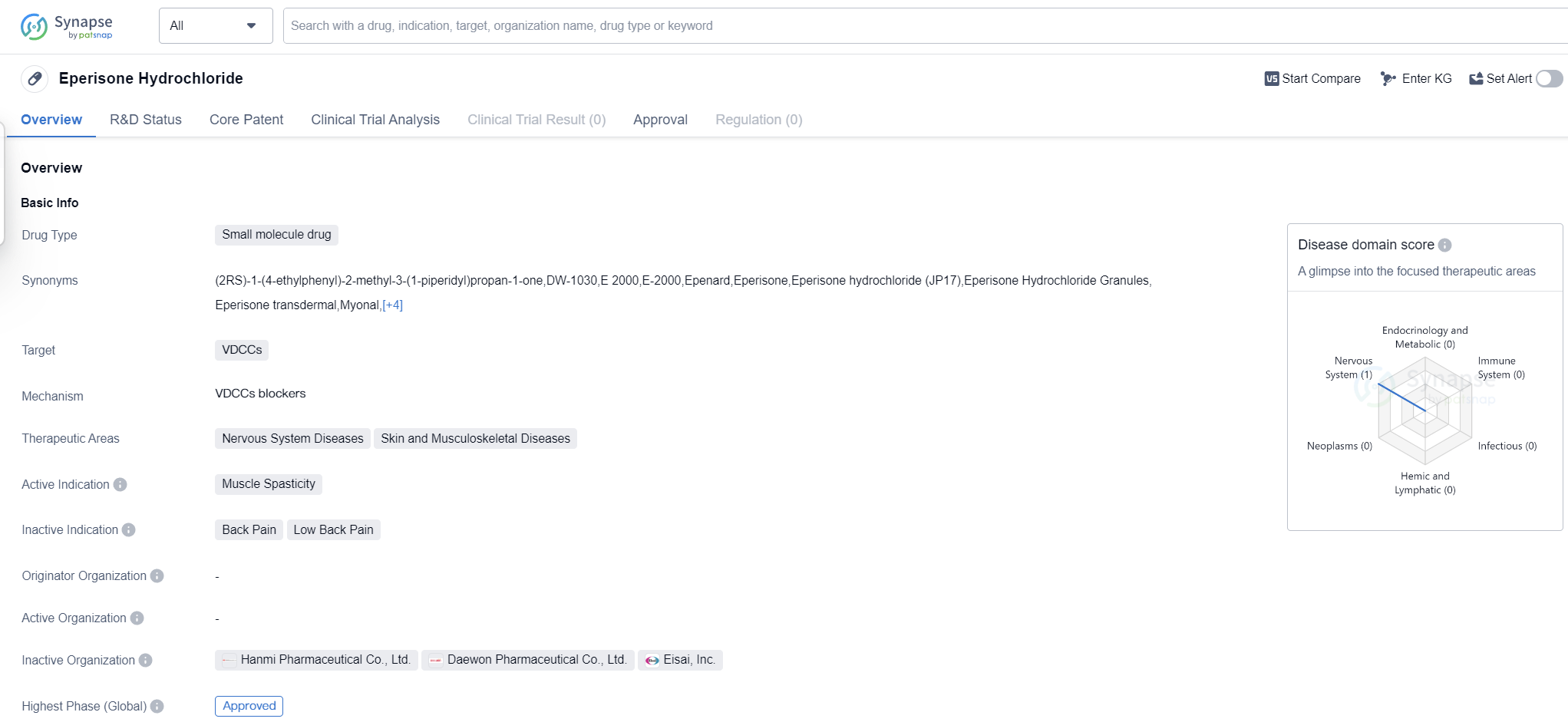
Eperisone Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets VDCCs (Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channels). It is primarily used in the treatment of muscle spasticity, making it a valuable therapeutic option for patients suffering from conditions such as cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries.
The drug has shown promising results in the treatment of nervous system diseases, as well as skin and musculoskeletal diseases. This indicates its potential to address a wide range of conditions affecting these areas of the body. Muscle spasticity, in particular, is a common symptom in many of these diseases, and Eperisone Hydrochloride offers a targeted approach to managing this symptom.
Eperisone Hydrochloride has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. This signifies that it has met the necessary safety and efficacy requirements set by regulatory authorities. The drug has undergone rigorous testing to ensure its effectiveness and safety profile, providing healthcare professionals and patients with confidence in its use.
As a small molecule drug, Eperisone Hydrochloride offers several advantages. It can be easily synthesized and manufactured, allowing for cost-effective production and widespread availability. Additionally, its small size enables it to penetrate cell membranes and reach its target sites efficiently, enhancing its therapeutic potential.
The approval of Eperisone Hydrochloride in global markets highlights its potential as a valuable treatment option for muscle spasticity and related conditions in patients. Its efficacy in targeting VDCCs, combined with its successful clinical trials, positions it as a promising drug in the field of biomedicine.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for eperisone hydrochloride: VDCCs blockers
VDCCs blockers refer to Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channel blockers. These are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of voltage-gated calcium channels (VDCCs). Voltage-gated calcium channels are membrane proteins that play a crucial role in regulating the entry of calcium ions into cells. They are found in various tissues and cell types, including neurons, cardiac muscle cells, and smooth muscle cells.
In a biomedical perspective, VDCCs blockers are primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure) and certain cardiac arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms). By blocking the activity of VDCCs, these drugs reduce the influx of calcium ions into cells, resulting in relaxation of smooth muscle cells in blood vessels and a decrease in cardiac contractility. This leads to vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) and a reduction in blood pressure.
Furthermore, VDCCs blockers can also have neuroprotective effects. In conditions like stroke or neurodegenerative diseases, excessive calcium influx through VDCCs can contribute to neuronal damage. By blocking these channels, VDCCs blockers help prevent the influx of calcium ions and protect neurons from excitotoxicity.
It's important to note that VDCCs blockers can have different selectivity towards specific types of voltage-gated calcium channels, such as L-type, N-type, or T-type channels. The specific subtype targeted by a particular VDCCs blocker will determine its therapeutic effects and potential side effects.
Drug Target R&D Trends for eperisone hydrochloride
Voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) play a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. These channels are responsible for regulating the influx of calcium ions into cells in response to changes in membrane potential. VDCCs are found in excitable cells such as neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells, where they control neurotransmitter release, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. Additionally, VDCCs are involved in modulating gene expression, cell proliferation, and differentiation. Dysfunction of VDCCs has been implicated in numerous diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, neurological disorders, and cancer. Understanding the role of VDCCs is essential for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
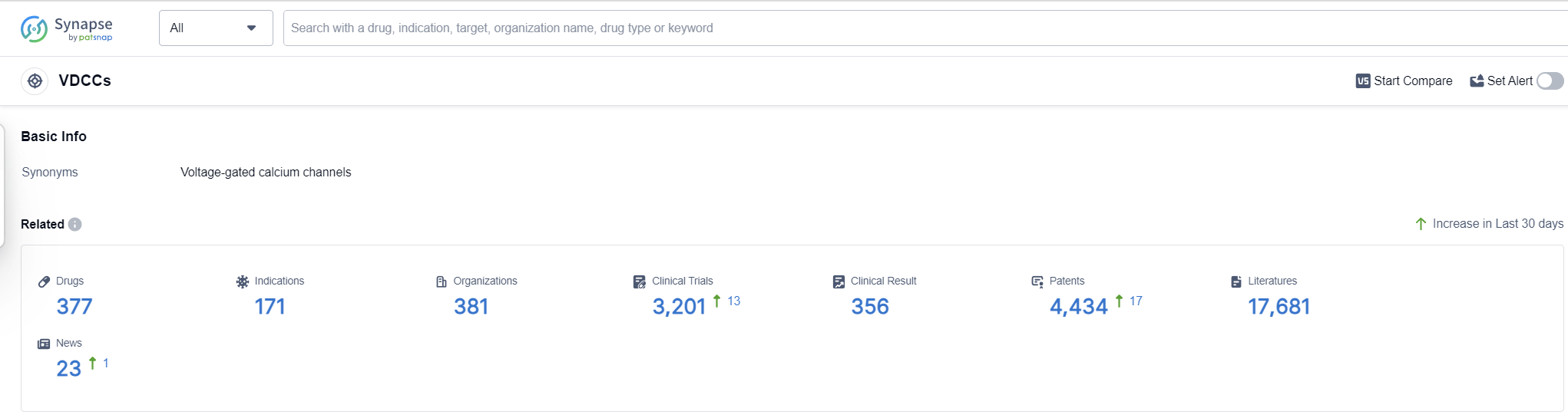
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 377 VDCCs drugs worldwide, from 381 organizations, covering 171 indications, and conducting 3201 clinical trials.
The analysis of target VDCCs from various perspectives provides valuable insights into the current competitive landscape and future development. Pfizer Inc., Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Eisai Co., Ltd. are the companies with the highest number of approved drugs, indicating their strong presence in this field. Hypertension is the most common approved indication, highlighting the importance of VDCCs in cardiovascular diseases. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition in this area. China, Japan, and the European Union are the countries/locations with the highest number of approved drugs, indicating their significant contributions to VDCC research and development. Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for target VDCCs, with potential applications in various therapeutic areas and a growing number of companies and countries involved in their development.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Eperisone Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets VDCCs and is primarily used in the treatment of muscle spasticity. It has shown potential to treat nervous system, skin, and musculoskeletal diseases. Its global approval offers hope for patients in need of therapy.