Unleashing the Power of Nitrazepam: A Comprehensive Review on R&D Breakthroughs, Action Mechanisms, and Drug Target
Nitrazepam's R&D Progress
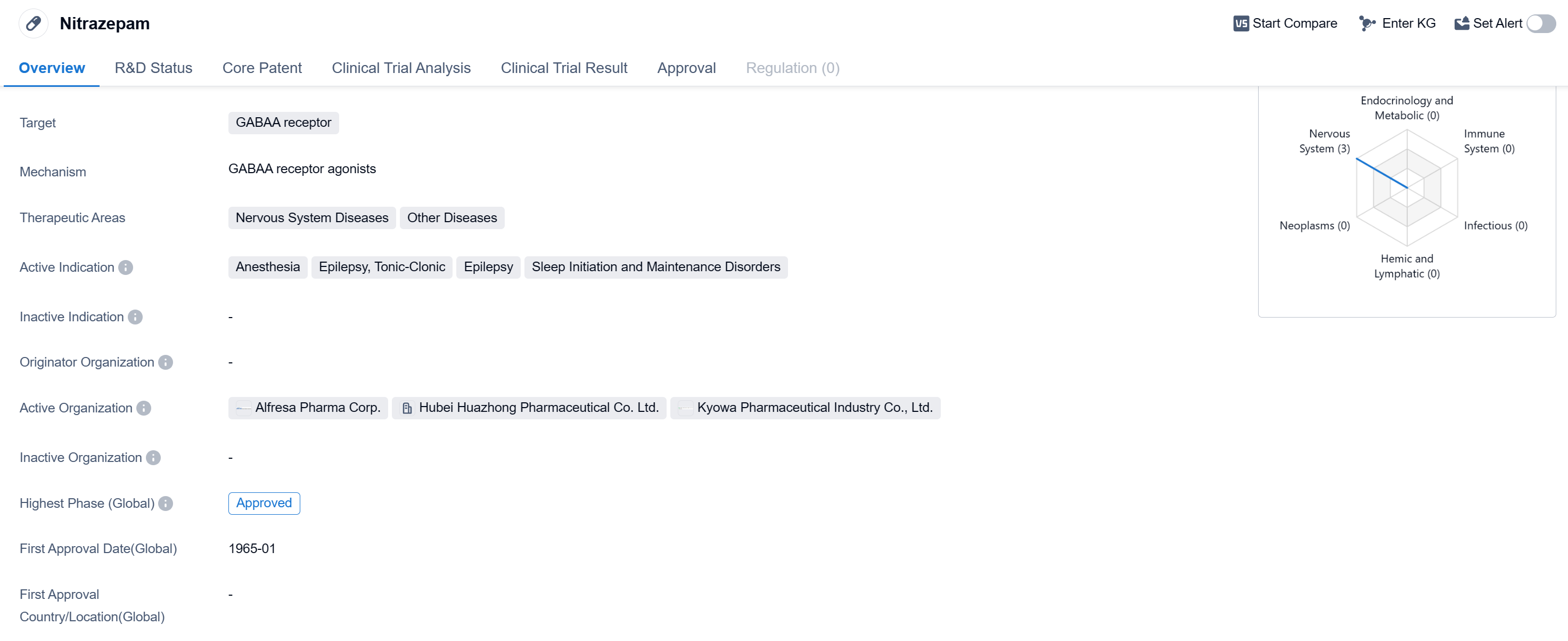
Nitrazepam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor. It is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases and other diseases. The drug has been approved for use in anesthesia, epilepsy (specifically tonic-clonic seizures), and sleep initiation and maintenance disorders.
Nitrazepam was first approved globally in January 1965, making it a well-established drug in the pharmaceutical industry. It has also received approval in China, indicating its widespread use and recognition in the international market.
As a small molecule drug, Nitrazepam is designed to interact with the GABAA receptor, which plays a crucial role in regulating the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system. By targeting this receptor, Nitrazepam can enhance the effects of GABA, leading to sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties.
The therapeutic areas in which Nitrazepam is indicated reflect its mechanism of action and pharmacological effects. Nervous system diseases, such as epilepsy, are the primary focus of this drug. Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, and Nitrazepam is specifically indicated for tonic-clonic seizures, which involve the entire body. Additionally, Nitrazepam is used in the treatment of sleep initiation and maintenance disorders, suggesting its potential as a sleep aid.
With a long history of use since its initial approval in 1965, Nitrazepam has likely undergone extensive clinical trials and demonstrated its therapeutic benefits. Its approval in China further indicates its acceptance and relevance in a significant pharmaceutical market.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Nitrazepam: GABAA receptor agonists
GABAA receptor agonists are a class of drugs that bind to and activate the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a type of neurotransmitter receptor that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). When GABAA receptors are activated, they inhibit the activity of neurons, leading to a calming and sedative effect.
GABAA receptor agonists enhance the effects of GABA by increasing its binding to the receptors, thereby increasing the inhibitory signals in the brain. This can result in various therapeutic effects, such as muscle relaxation, anxiety reduction, sedation, and anticonvulsant activity.
These drugs are used in the treatment of various conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, epilepsy, and muscle spasms. They can also be used as anesthesia adjuncts during surgical procedures to induce sedation and relaxation.
It's important to note that GABAA receptor agonists can have sedative and hypnotic effects, and their use should be carefully monitored to avoid excessive sedation or respiratory depression. Additionally, these drugs can be habit-forming, and long-term use may lead to tolerance and dependence. Therefore, they should be used under medical supervision and according to prescribed dosages.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Nitrazepam
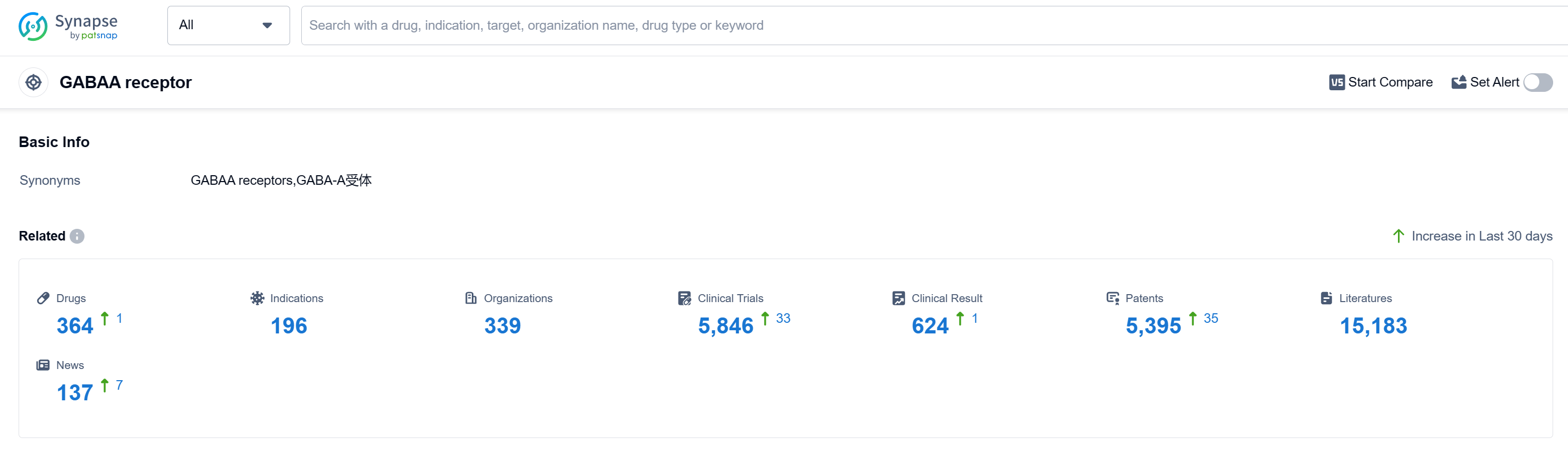
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 15 Sep 2023, there are a total of 364 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 339 organizations, covering 196 indications, and conducting 5846 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target GABAA receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively developing drugs for various indications. Pfizer Inc., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. are among the companies with the highest stage of development on this target. The approved indications include Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders, Anesthesia, Anxiety, Epilepsy, and others, providing potential treatment options for patients.
Small molecule drugs dominate the development pipeline, indicating their effectiveness and suitability for targeting the GABAA receptor. Biosimilars are not prominent in this context, suggesting a lack of intense competition around the innovative drug.
China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current target. China, in particular, has shown significant progress in the development of drugs targeting the GABAA receptor.
Overall, the target GABAA receptor presents a competitive landscape with diverse companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations. Further research and development in this area can lead to innovative treatments for various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Nitrazepam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor. It is approved for use in anesthesia, epilepsy (specifically tonic-clonic seizures), and sleep initiation and maintenance disorders. It has been approved globally. Nitrazepam's mechanism of action and therapeutic areas align with its ability to enhance the effects of GABA, making it a valuable drug in the treatment of nervous system diseases.