Viltolarsen: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Viltolarsen's R&D Progress
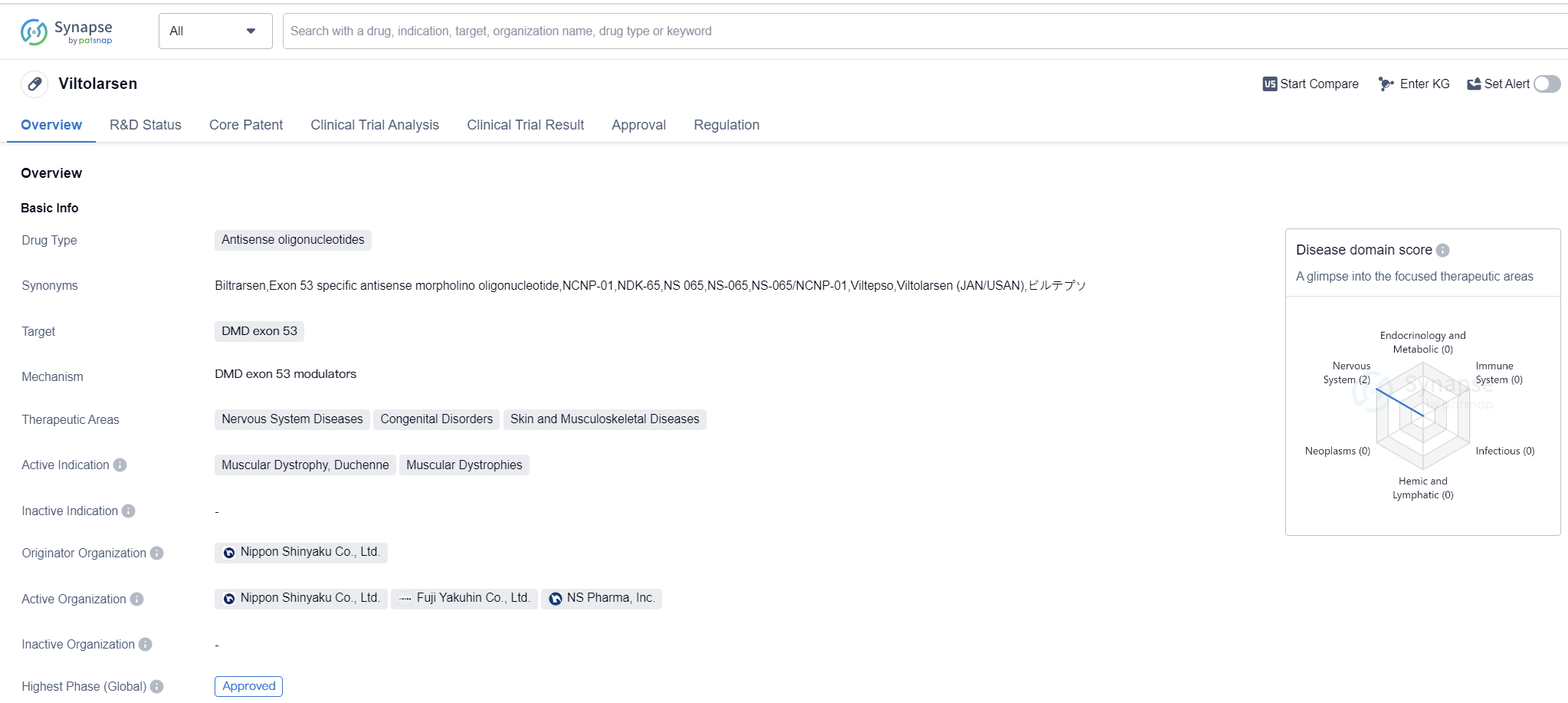
Viltolarsen is an antisense oligonucleotide drug that targets DMD exon 53. It falls under the therapeutic areas of Nervous System Diseases, Congenital Disorders, and Skin and Musculoskeletal Diseases. The drug is primarily indicated for the treatment of Muscular Dystrophy, specifically Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and other Muscular Dystrophies.
Viltolarsen was developed by Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd., a pharmaceutical company based in Japan. It has received approval for use in Japan, making it the first country to approve the drug. The approval was granted in March 2020, marking a significant milestone for the treatment of Muscular Dystrophy.
In terms of regulatory status, Viltolarsen has undergone various review processes and has been granted several designations. These include Priority Review, Conditional Marketing Approval, SAKIGAKE, Accelerated Approval, Rare Pediatric Disease, Fast Track, and Orphan Drug designations. These designations highlight the importance and urgency of addressing the unmet medical needs in the field of Muscular Dystrophy.
The approval of Viltolarsen represents a significant advancement in the treatment of Muscular Dystrophy, particularly for patients with DMD exon 53 mutations. Antisense oligonucleotides have shown promise in targeting specific genetic mutations and restoring protein production, thereby potentially improving the symptoms and prognosis of affected individuals.
The therapeutic areas of Nervous System Diseases, Congenital Disorders, and Skin and Musculoskeletal Diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, highlighting the potential for Viltolarsen to have a broader impact beyond Muscular Dystrophy. Further research and clinical trials may explore its efficacy in other related disorders within these therapeutic areas.
While Viltolarsen has received approval in Japan, it is still undergoing the regulatory process in other countries, including China. The drug is currently in the NDA/BLA phase in China.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for viltolarsen: DMD exon 53 Modulators
DMD exon 53 modulators are a type of drug used in the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). DMD is a genetic disorder characterized by the progressive weakening and degeneration of muscles. It is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which result in the absence or reduced production of dystrophin protein.
Exon 53 is a specific region of the dystrophin gene. In some cases of DMD, the mutation affects exon 53, leading to the production of a non-functional or truncated dystrophin protein. DMD exon 53 modulators are designed to target this specific mutation and promote the skipping of exon 53 during the production of dystrophin protein.
By skipping exon 53, the production of a partially functional dystrophin protein is restored. This can help improve muscle function and slow down the progression of DMD. DMD exon 53 modulators work by modifying the splicing process, which is responsible for the removal of introns (non-coding regions) and the joining of exons (coding regions) during the production of mRNA.
These modulators can be administered orally or through injection and are typically used in combination with other therapies for DMD. They are considered a promising approach in the development of targeted treatments for specific genetic mutations associated with DMD. However, it is important to note that DMD exon 53 modulators are specific to individuals with DMD who have mutations affecting exon 53, and their effectiveness may vary depending on the specific mutation and individual response to the treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for viltolarsen
DMD exon 53 is a crucial component in the human body that plays a significant role in the function of the dystrophin protein. Dystrophin is responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of muscle fibers. However, in individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a genetic mutation in exon 53 leads to the production of a non-functional dystrophin protein. This results in muscle weakness and degeneration. Targeting DMD exon 53 through innovative therapeutic approaches, such as exon skipping or gene editing, aims to restore the production of functional dystrophin, potentially offering a promising treatment strategy for individuals with DMD.
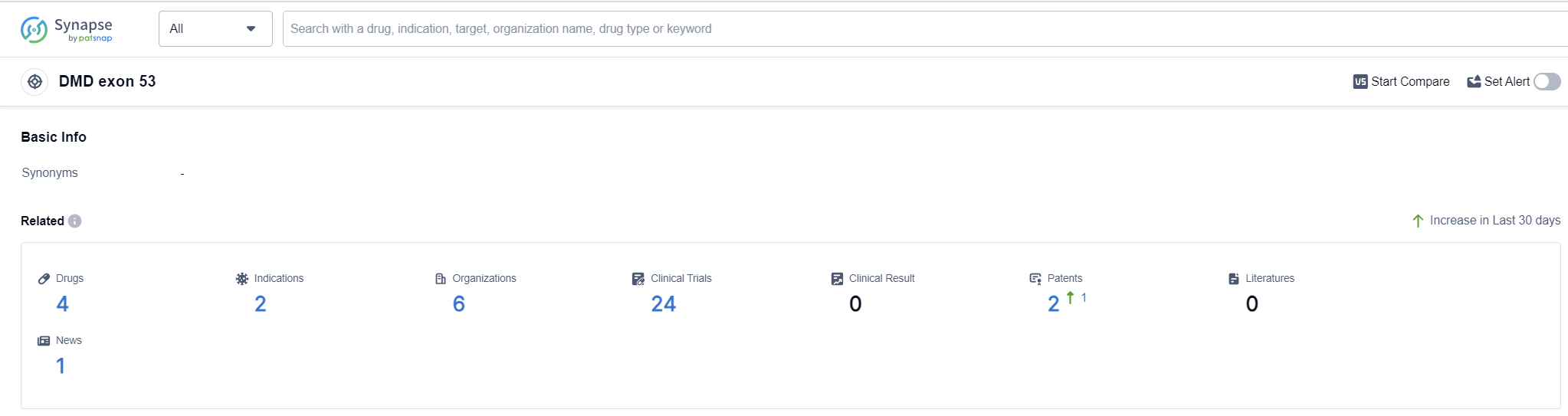
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 4 DMD exon 53 drugs worldwide, from 6 organizations, covering 2 indications, and conducting 24 clinical trials.
The analysis of the target DMD exon 53 reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in research and development. Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. and Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. are leading the way with drugs in advanced stages of development. The indication analysis indicates a focus on Muscular Dystrophy, Duchenne, and Muscular Dystrophies. Antisense oligonucleotides are the drug type progressing most rapidly, indicating potential competition around innovative drugs. The country/location analysis highlights the progress in the United States, Japan, China, and various countries in Europe. The future development of the target DMD exon 53 holds promise for the treatment of muscular dystrophy, with ongoing research and development efforts worldwide.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Viltolarsen is an antisense oligonucleotide drug developed by Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd. It has received approval in Japan for the treatment of Muscular Dystrophy, specifically targeting DMD exon 53 mutations. The drug holds significant potential in addressing the unmet medical needs of patients with Muscular Dystrophy and may have broader implications in related therapeutic areas. Further regulatory approvals are being sought, including in China.