Advancing Malaria Treatment: Novartis AG's IWY-357 Targets Falciparum Parasite in Phase 1 Development
IWY-357 is a small molecule drug developed by Novartis AG, with a focus on the therapeutic area of infectious diseases, specifically targeting malaria caused by the Falciparum parasite. The drug has progressed to the highest phase of development, which is Phase 1.As a small molecule drug, IWY-357 is designed to have a low molecular weight and the potential to interact with specific protein targets within the body. This makes it a promising candidate for the treatment of infectious diseases, where targeted interactions with the disease-causing agents are crucial for efficacy.
The choice of malaria, specifically the Falciparum strain, as the active indication for IWY-357 underscores the urgent need for novel and effective treatments for this disease. Malaria, especially the Falciparum type, is a significant global health concern, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare and preventive measures. Therefore, the development of a new drug for this indication has the potential to address a critical unmet medical need.
Novartis AG, the originator organization of IWY-357, is a well-established pharmaceutical company with a strong track record in research and development. The company's expertise and resources in drug development and infectious diseases may have played a pivotal role in advancing IWY-357 to its current phase of development.
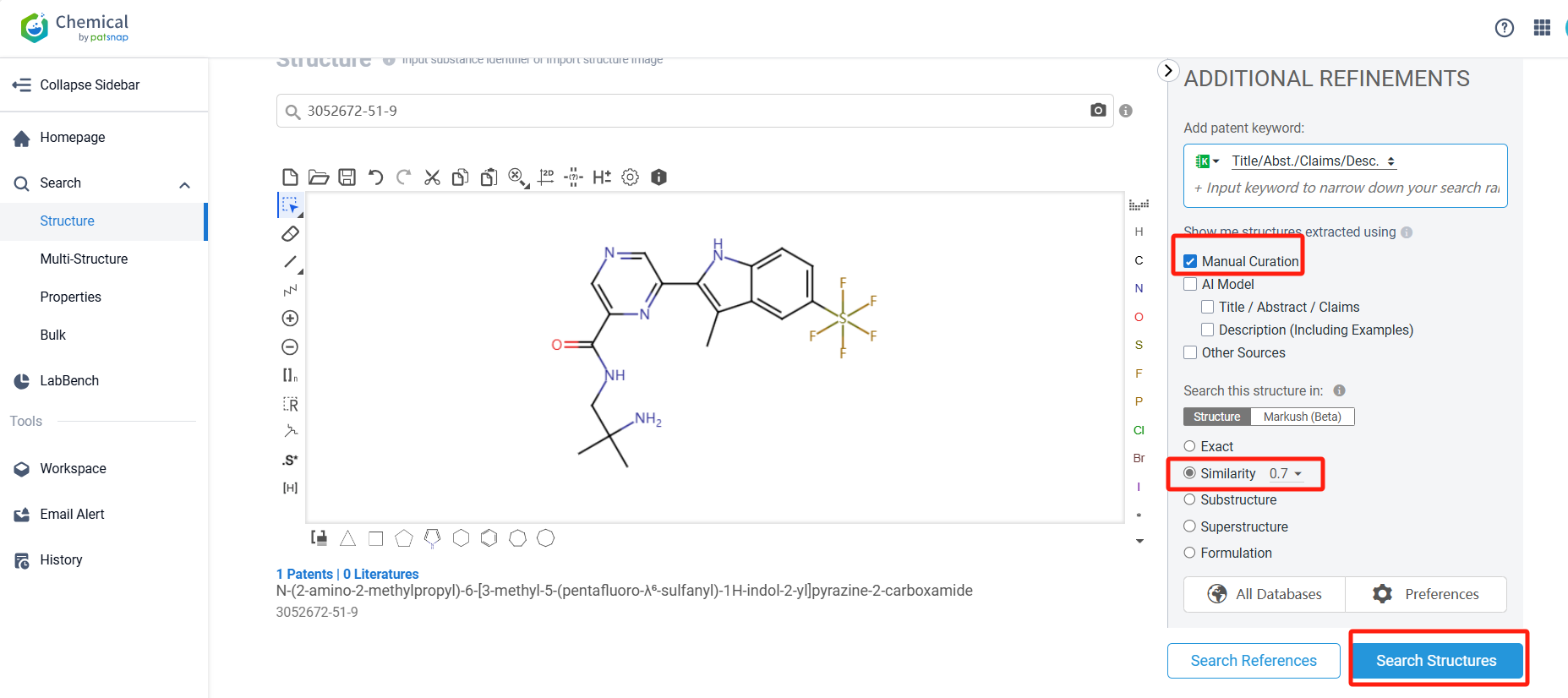
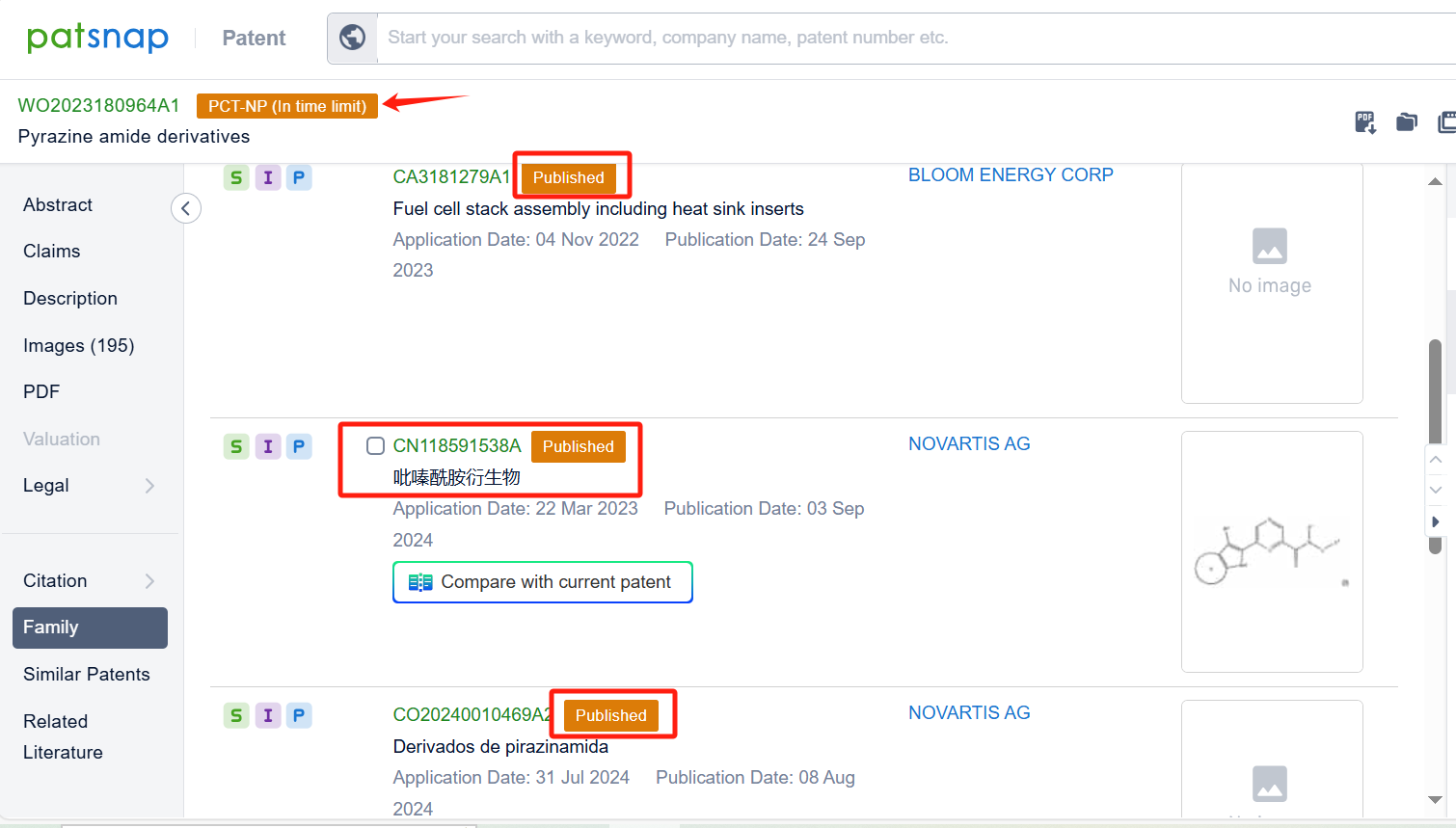
Log in to the Patsnap Chemical. Select the structural search and enter the common identity information of IWY-357(such as CAS number, generic substance name, molecular formula, SMILES file, etc.). Here, using a similarity search (setting the Tanimoto coefficient to 0.7), check the box for manual curation, click on search structures, and you can find the innovative drug IWY-357, as disclosed in the patent application with the publication number WO2023180964A1, first made public on 2023-09-28, shares its structural novelty with similar compounds that also originate from the same patent document. This highlights the novelty of the compound's structure.
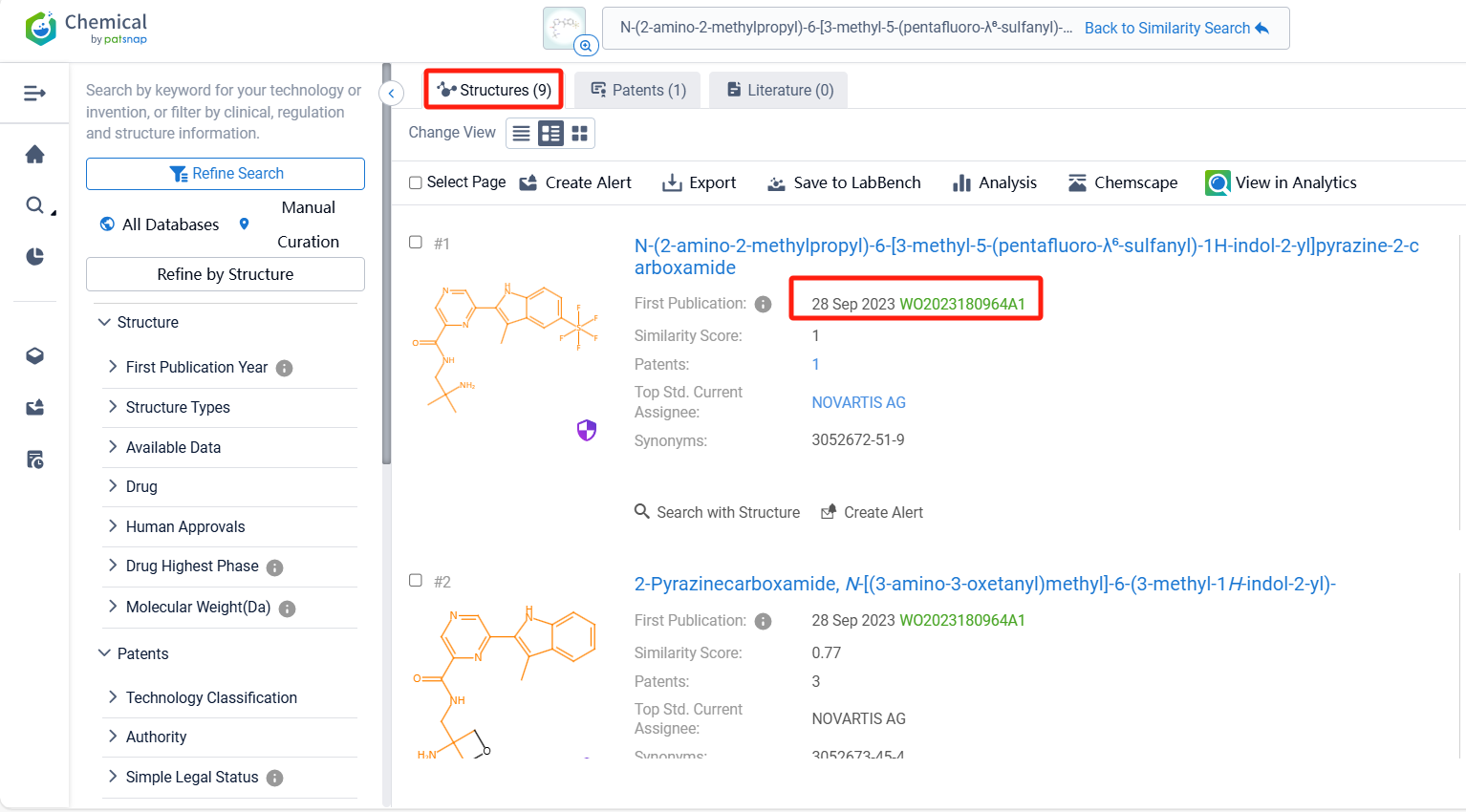
The compound is uniquely associated with a single patent application, underscoring the innovative nature of its molecular structure as detailed in the patent document WO2023180964A1. Clicking the "view in Analytics" will direct you to the Patsnap Patent.
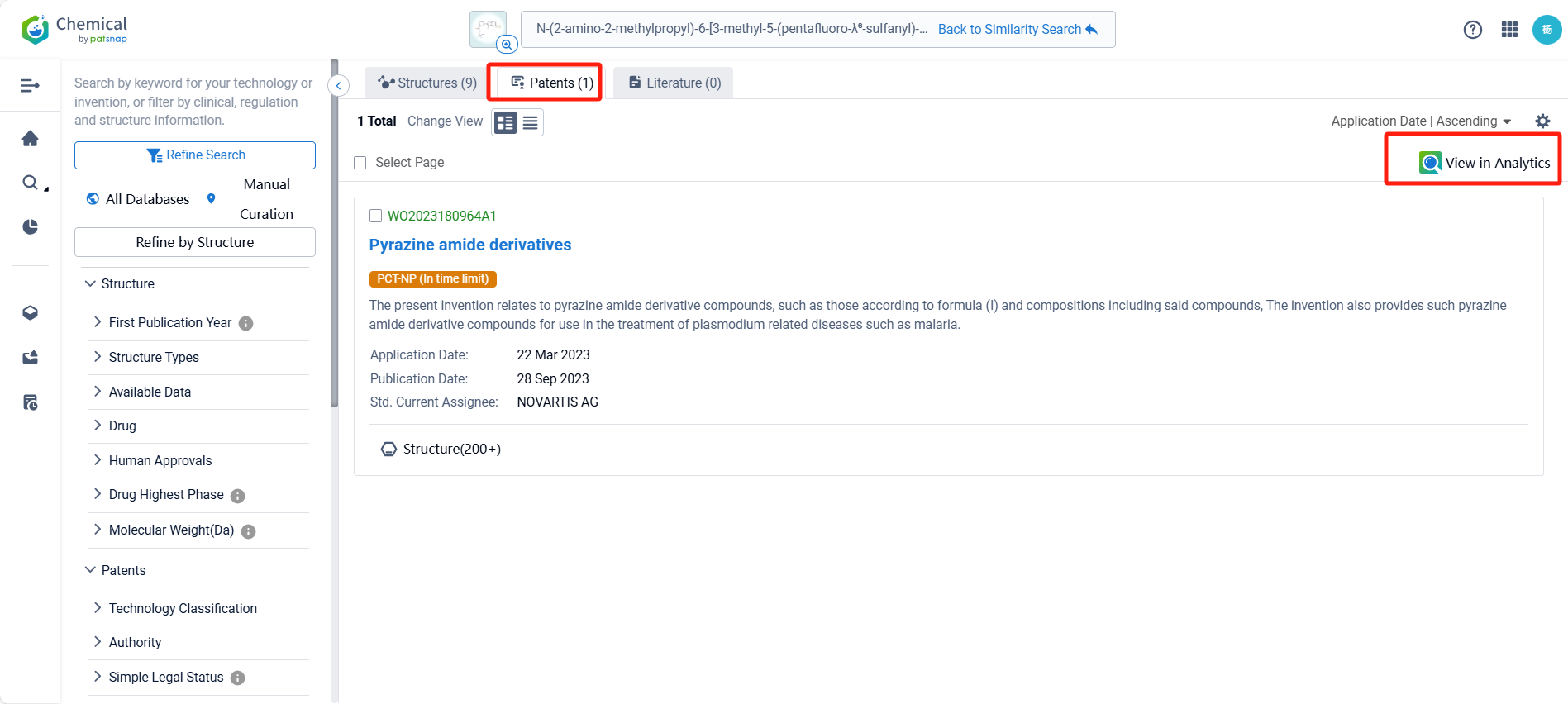
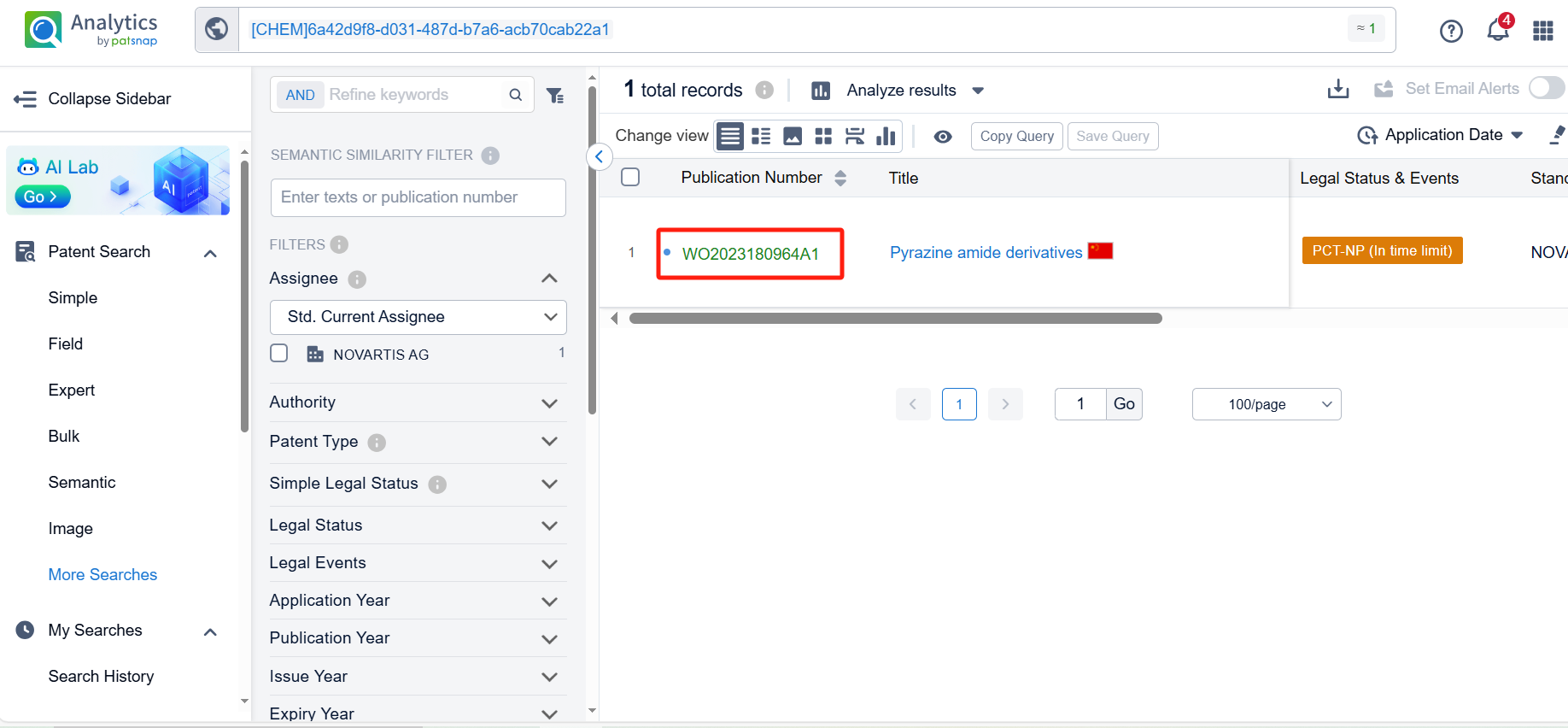
Upon reviewing the core patent, it is evident that the patent application was filed on March 22, 2023, and published on September 28, 2023. The Chinese counterpart of this international application, CN118591538A, was also published on September 3, 2024. All are currently under substantive examination. Judging from the search of the compound, there is a high likelihood that the patent application will be granted.
The fact that IWY-357 has reached Phase 1 indicates that the drug has shown promising results in preclinical studies, and its safety profile has been deemed acceptable for initial testing in humans. This milestone is a significant step forward in the drug development process and suggests that IWY-357 has the potential to advance further through clinical trials, ultimately leading to regulatory approval and commercialization.
In summary, IWY-357 is a small molecule drug developed by Novartis AG, with a specific focus on treating malaria caused by the Falciparum parasite. Its progression to Phase 1 demonstrates its potential as a novel treatment for this infectious disease, addressing an important public health concern. The drug's development represents a significant advancement in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to combat infectious diseases and improve global health outcomes.
AI built to maximize IP and R&D efficiency
Redefine chemical FTO with a range of structure retrieval options at your fingertips, from exact matches to similarity searches, all powered by deep data processing techniques and proprietary AI algorithms to eliminate the risk of omitting key results.