How to find the structure and classification of Basiliximab?
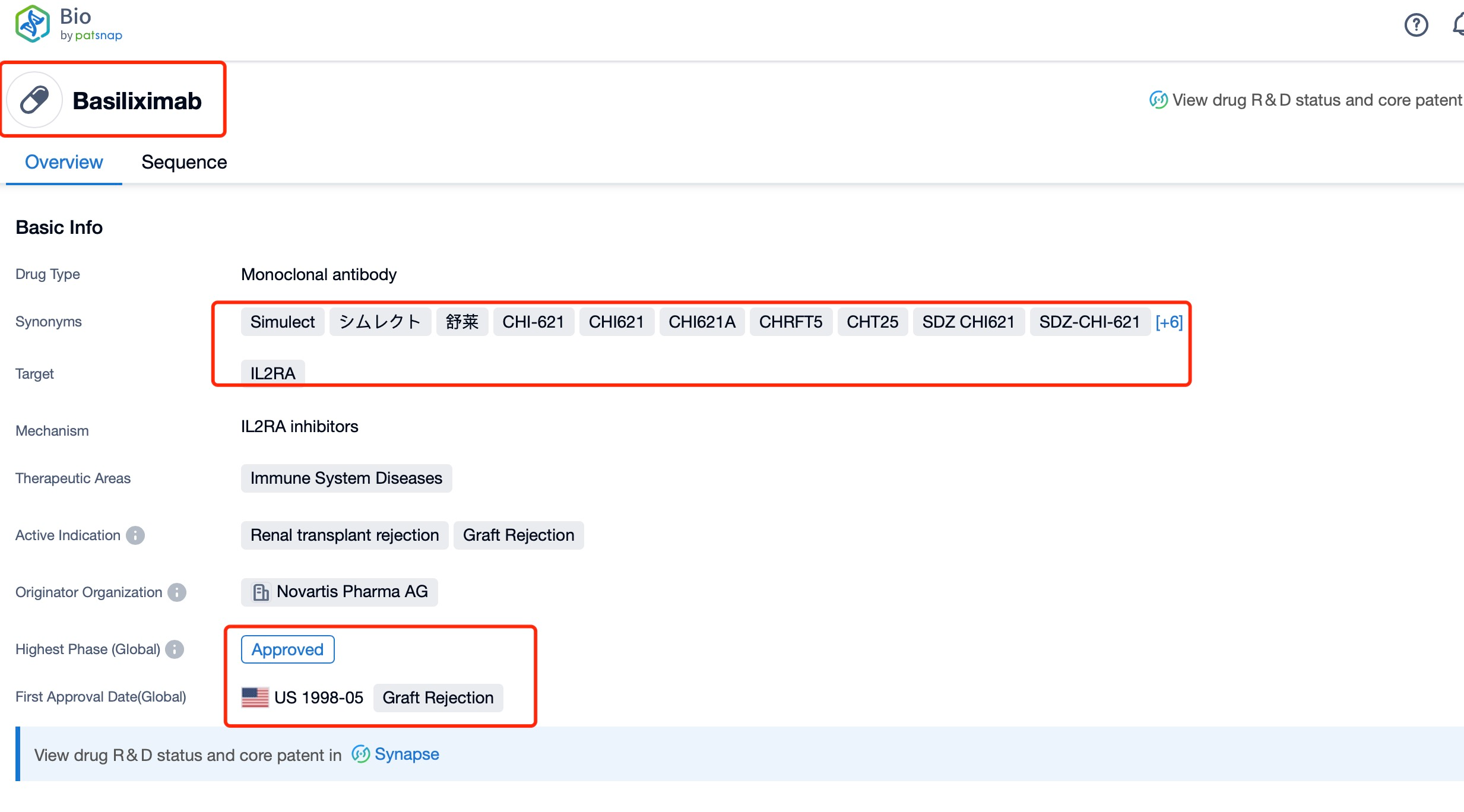
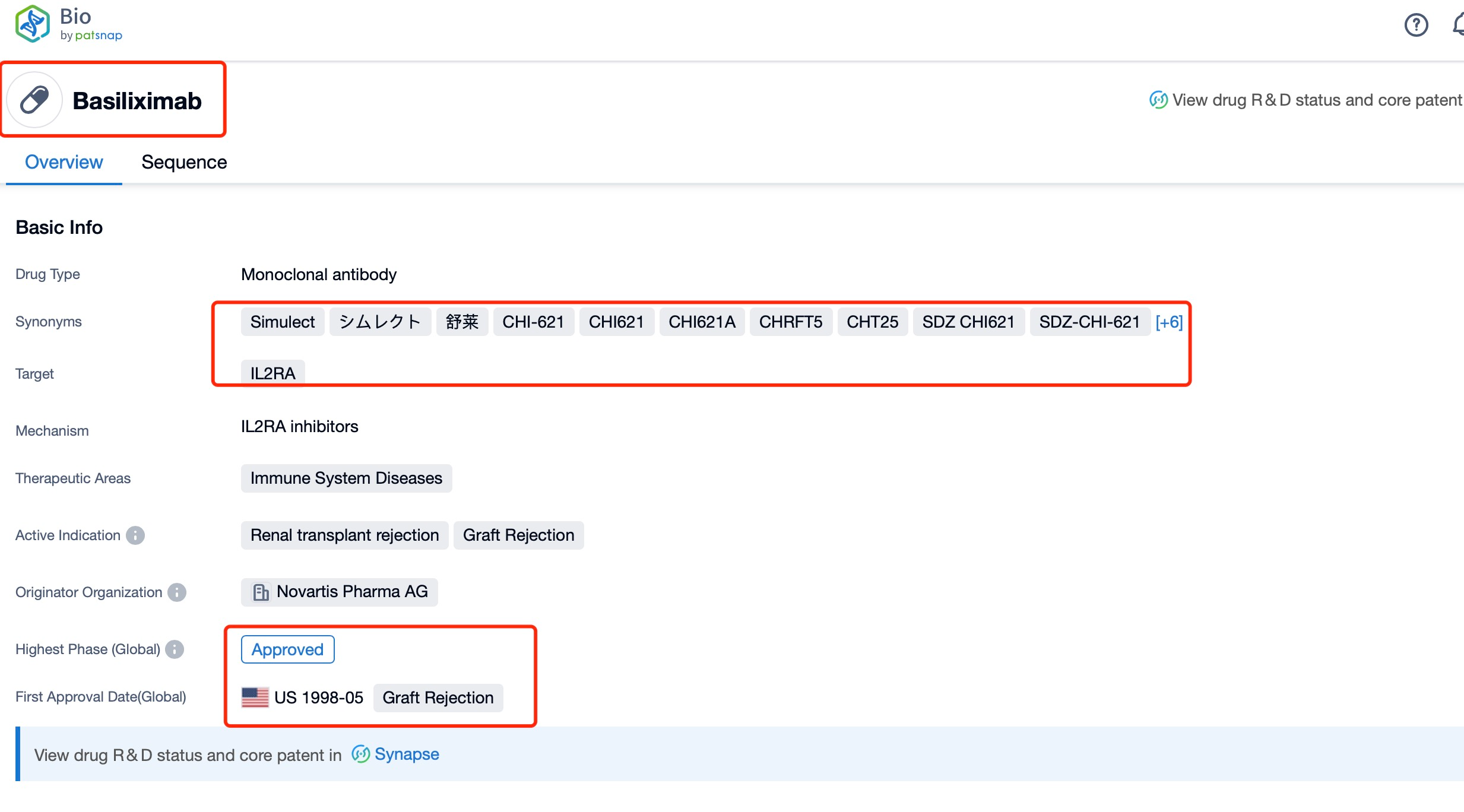
Basiliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) alpha chain, also known as CD25. Developed by Novartis, Basiliximab is classified as a therapeutic protein and is primarily indicated for the prevention of acute organ rejection in kidney transplant recipients. It is administered as part of an immunosuppressive regimen to reduce the risk of graft rejection.
Summary of Research Progress:
The research progress of Basiliximab has been significant, with extensive studies elucidating its mechanism of action and clinical efficacy. Basiliximab works by binding to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor on activated T cells, preventing the binding of IL-2 to its receptor. This inhibition blocks the proliferation and activation of T cells, which are key mediators of the immune response and organ rejection. By suppressing T cell activity, Basiliximab helps to prevent the immune system from attacking the transplanted organ.
Globally, Basiliximab has been approved in numerous countries, including the United States, Europe, and Japan. It received FDA approval in 1998 for the prevention of acute organ rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Since then, it has been widely adopted in clinical practice and has gained approvals in many other regions. The drug has also been studied for potential use in other transplant settings, such as liver and heart transplants, although its primary indication remains kidney transplantation.
The competitive landscape for Basiliximab is diverse, with several other immunosuppressive agents and biologics available. Key competitors include tacrolimus (Prograf), mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), and sirolimus (Rapamune). Despite this competition, Basiliximab has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. Clinical trials have consistently shown that Basiliximab, when used in combination with other immunosuppressive agents, can significantly reduce the incidence of acute organ rejection and improve graft survival rates.
Type of Immunoglobulin of Basiliximab
Basiliximab is a chimeric IgG1κ immunoglobulin. Chimeric antibodies are engineered to combine the antigen-binding variable regions from a mouse antibody with the constant regions from a human antibody. This design reduces the immunogenicity of the antibody while maintaining its therapeutic efficacy. The κ light chain is one of the two types of light chains found in immunoglobulins, the other being λ. The κ light chain is more common and provides stability and specificity to the antibody structure.
Light and Heavy Chains and Structural Characteristics of Basiliximab
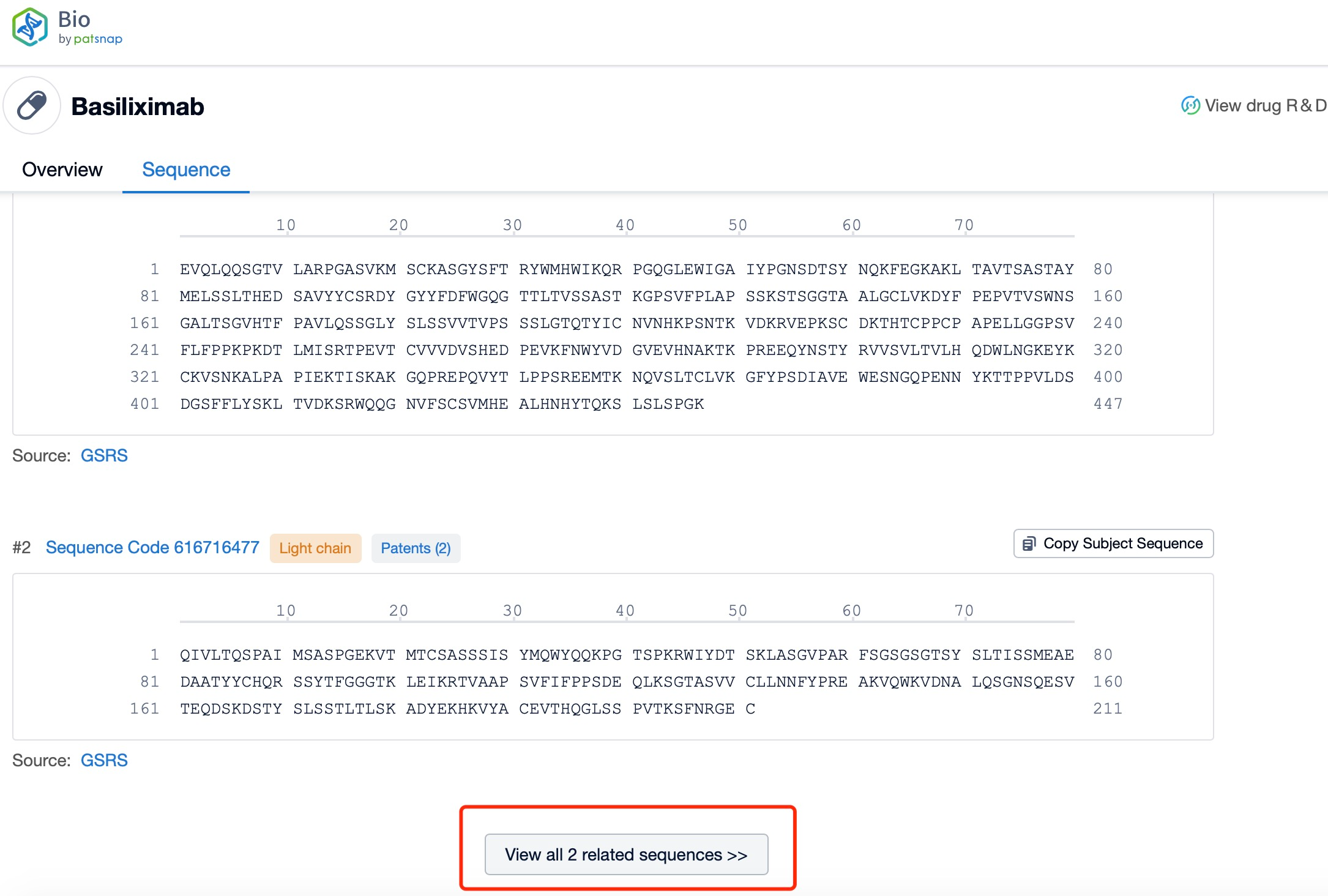
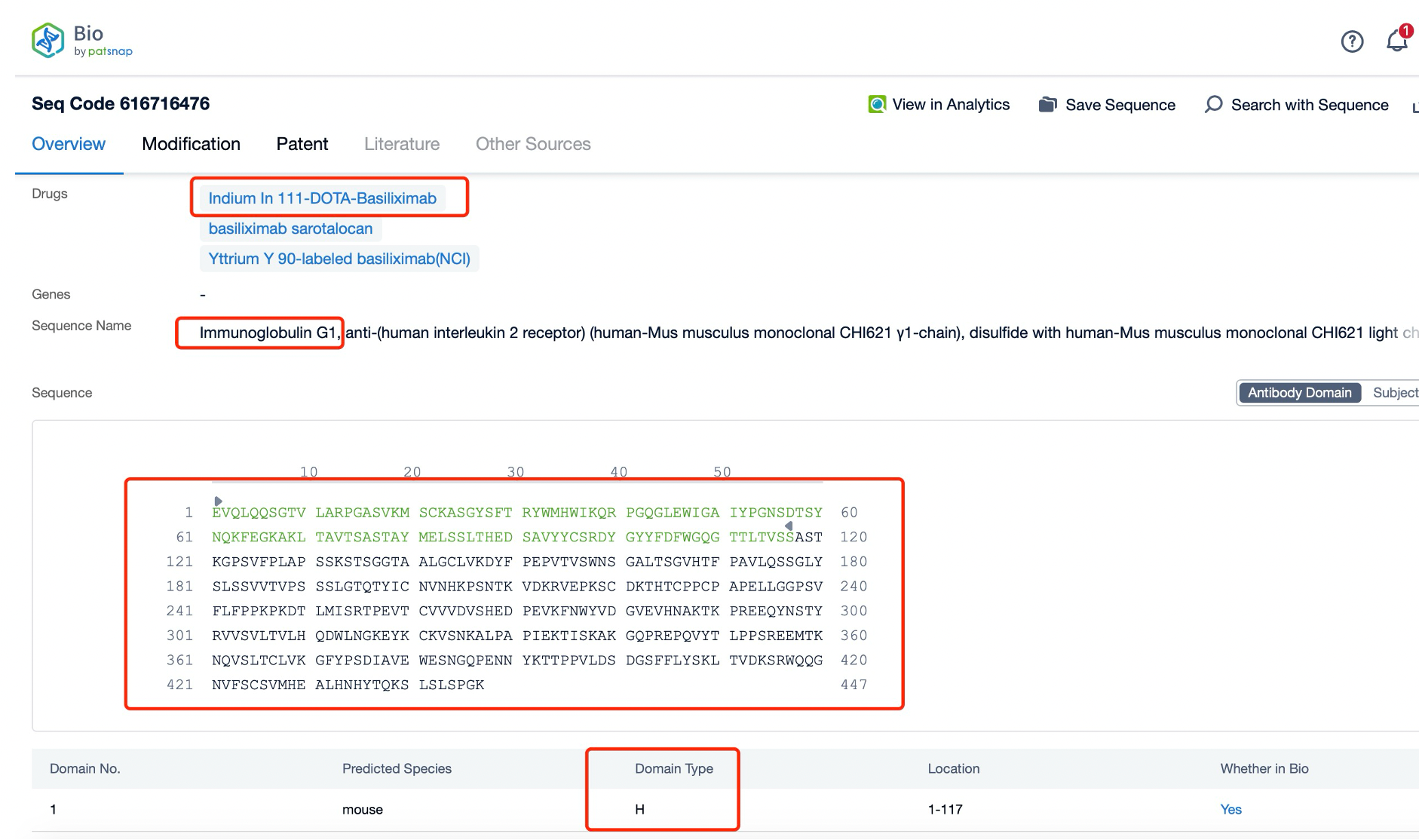
The heavy chain of Basiliximab is a chimeric IgG1 molecule, which consists of four domains: variable (VH), constant 1 (CH1), constant 2 (CH2), and constant 3 (CH3). The VH domain is responsible for antigen binding, while the CH1 domain forms part of the Fc region, which is crucial for the antibody's effector functions. The CH2 and CH3 domains are involved in the interaction with Fc receptors and complement proteins, respectively.
The light chain of Basiliximab is a κ chain, which also consists of two domains: variable (VL) and constant (CL). The VL domain pairs with the VH domain to form the antigen-binding site, ensuring high specificity and affinity for the target antigen. The CL domain, like the CH1 domain, contributes to the stability and function of the antibody.
Structurally, Basiliximab is a well-characterized and highly specific monoclonal antibody. The variable regions of both the heavy and light chains are designed to recognize and bind to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor (CD25) on activated T cells with high affinity. This binding prevents the binding of IL-2 to its receptor, effectively blocking the proliferation and activation of T cells. The constant regions of the heavy and light chains provide additional functional properties to Basiliximab. The Fc region, composed of the CH2 and CH3 domains, is capable of engaging Fc receptors on immune cells, leading to various effector functions such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). These functions enhance the therapeutic potential of Basiliximab by facilitating the clearance of targeted T cells and modulating the immune response.
Summary and Prospect
In summary, Basiliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor (CD25) on activated T cells, making it a valuable therapeutic option for the prevention of acute organ rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Its mechanism of action involves binding to CD25 and blocking the binding of IL-2 to its receptor, thereby inhibiting T cell proliferation and activation. Basiliximab has been approved globally for kidney transplantation and has maintained a strong market presence due to its well-established efficacy and safety profile. As a chimeric IgG1κ immunoglobulin, Basiliximab exhibits well-defined structural characteristics that contribute to its high specificity and efficacy. The heavy and light chains, with their respective variable and constant domains, ensure precise antigen binding and robust effector functions, making Basiliximab a valuable and effective treatment for preventing acute organ rejection. Future research and development efforts will likely focus on optimizing its delivery methods, exploring new indications, and enhancing its therapeutic benefits for patients.
How to find the structure and classification of antibody drugs?
In Patsnap Bio, you can find the sequence and latest research and development advances of all antibody drugs.
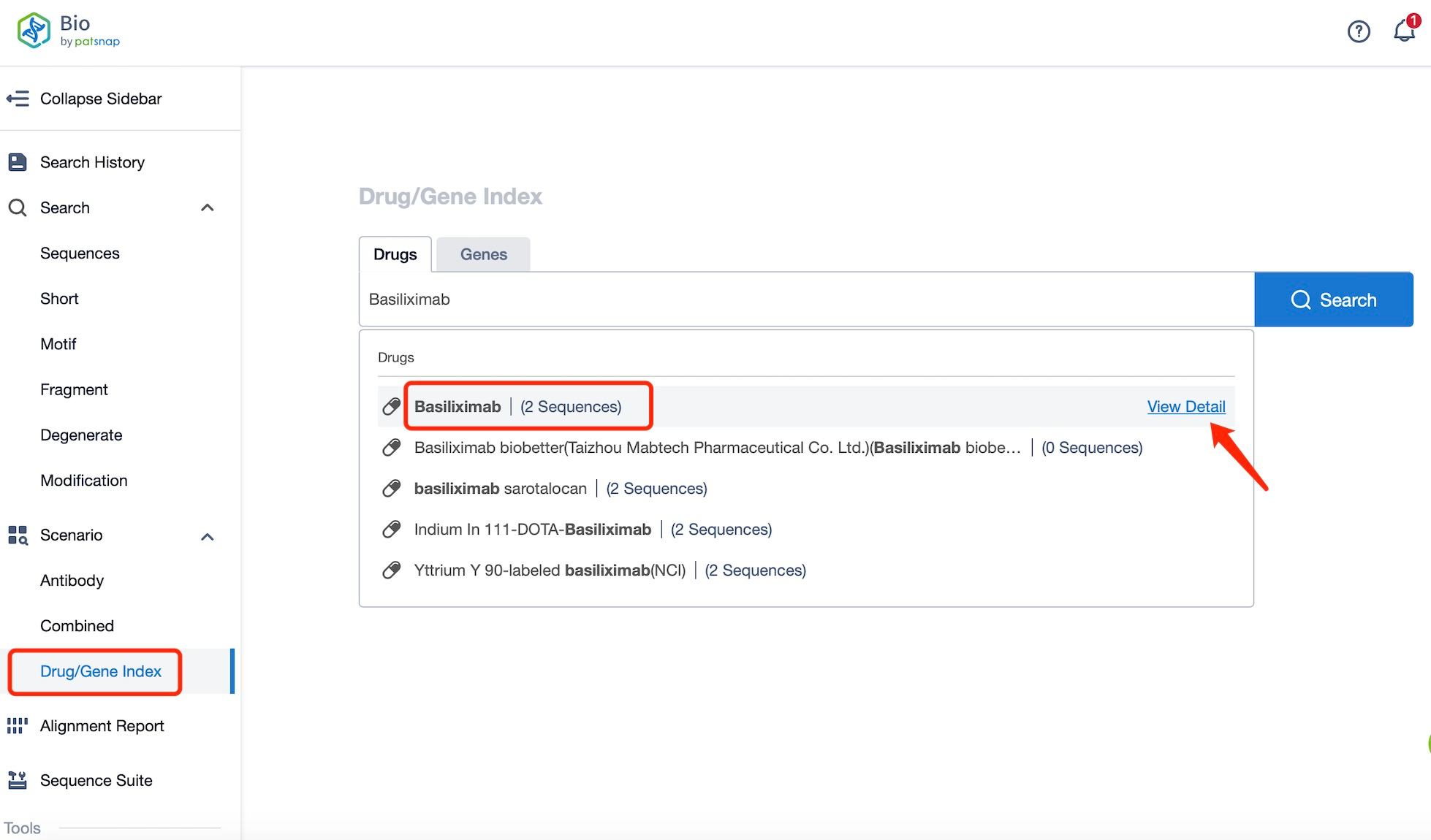
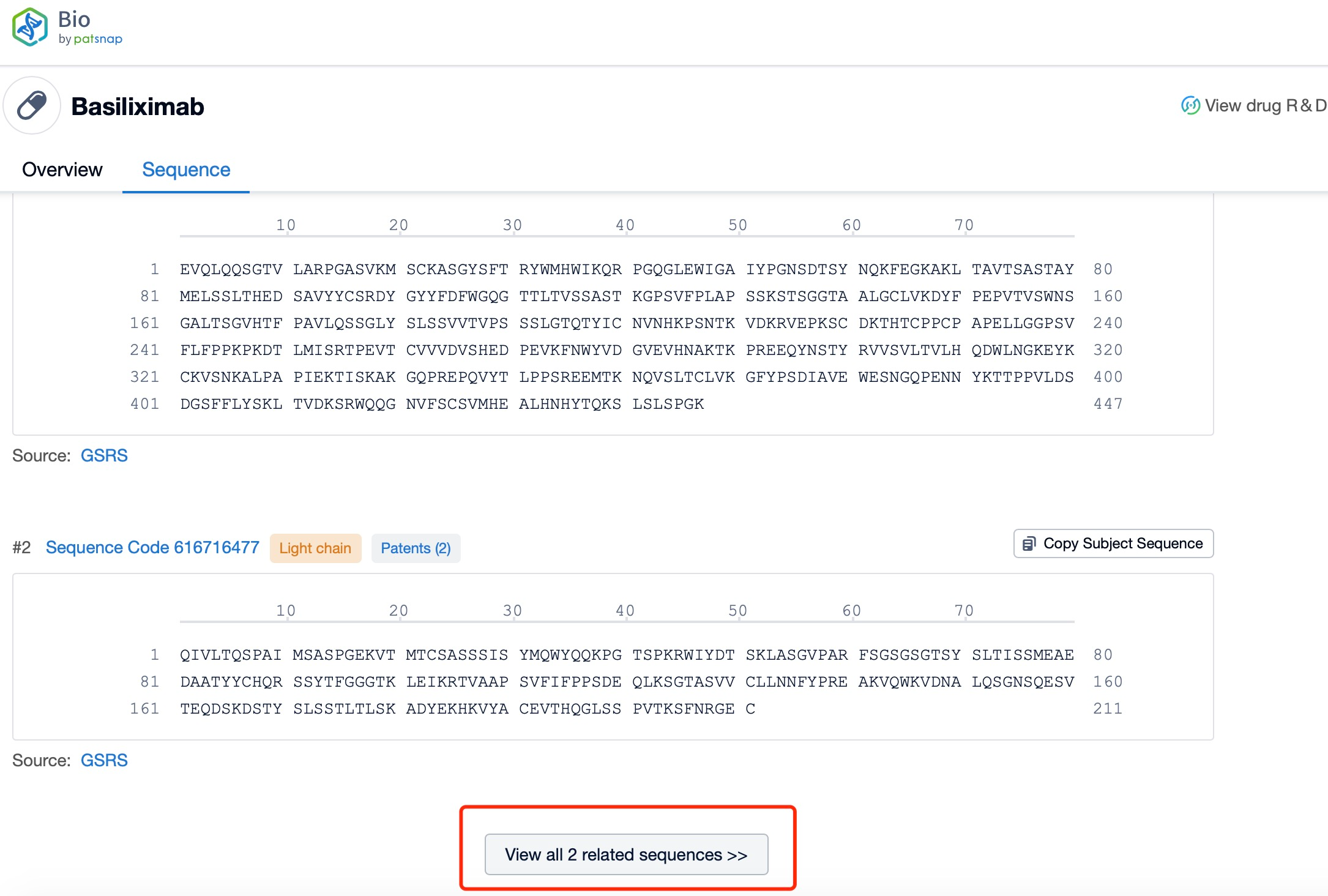
Taking Basiliximab as an example, first click on the Drug/Gene Index on the Patsnap Bio homepage. Here you can search for sequence information by drug and gene names. Enter ' Basiliximab ' in the search box and click to view the details. On the details page, you can find the basic information and research progress of Basiliximab.
Click "View all related sequences" below the sequence information to search for and retrieve all biological sequences similar to this information.
Clicking on the sequence name will provide you with all the basic information of that sequence. Here, you can easily query the sequence and action of the light and light chains of antibodies.
Patsnap Bio helps you turn weeks into minutes with cutting-edge AI-enabled tools built to master the complexities of sequence retrieval and automate IP analysis with precision and ease.