An effective method to ward off viral intrusions: Toxoid Vaccine
Toxoid Vaccine is essentially a bacterial toxin that is rendered harmless due to processing. However, it retains the characteristic of exposing the organism to the toxin to provoke the formation of antibodies. Toxoids assist humans in forming antibodies to resist bacterial infections, which requires periodic vaccinations with toxoid vaccines to ensure that the body system has adequate antibodies to resist harmful bacteria entering the body.
When a toxoid enters the body, even if it has been weakened, the body will regard it as an enemy and form antibodies. These antibodies will be retained and resist other bacteria related to this toxin that enter the body, serving to prevent bacterial infections and diseases.
"Pseudovirus" suggests that it shares characteristics remarkably similar to a real virus, particularly in structure and immunogenicity. Precisely because it is similar and not identical, it's not a virus in the true sense, thus lacking the dubbed “deadly” viral genome. Viruses lead a parasitic life and need to rely on host cells for self-replication. Their genome is a lethal weapon, disarmed and thereby posing no threat. Pseudovirus particles are like "hollowed out" viral particles, left with just the outer shell and devoid of the viral genome. Thus, on this level, pseudovirus particles are quite safe.
Virus-like particles are one of the substances that our immune system is most "sensitive" to, especially for dendritic cells. Dendritic cells are the body's most functional professional antigen presenting cells (APC), capable of efficiently ingesting, processing and presenting antigens. In the collaborative action with floating morphological virus-like particles, dendritic cells can easily be detected and recorded by the human immune system, preparing for encounters with real viruses.
Furthermore, each protein monomer has an antigen determinant site. Since there are many monomers that make up the virus-like particles, it can very effectively cross-link B cell receptors, thus inducing a strong B-cell response and further highlighting its immunogenicity. Because of this, such a vaccine usually does not require an adjuvant. Adjuvants, also known as non-specific immunity enhancers, do not have antigenicity themselves, but can enhance immunogenicity or change the type of immune response when used with antigens or pre-injected into the body. However, GSK still used an adjuvant to further enhance the immune system's response.
With the development of synthetic biology, protein monomers can be produced in a wide variety of expression systems. It is worth noting that most of these expression systems are excellent at splicing, and the 3D structure of virus-like particles can be efficiently formed within cells.
The four major platforms in genetic engineering for recombinant protein expression include the E. coli expression system, yeast expression system, insect cell-baculovirus expression system, and eukaryotic cell expression system. GSK chooses to use the Baculovirus Expression Vector System (BEVS) for mass production of vaccines. The advantages of this kind of expression system include high protein expression level, low cost, and ease of mass production. Of course, the inactivation and removal of baculoviruses is undoubtedly a key consideration and difficult operation in the downstream process of vaccine purification.
Toxoid Vaccine Competitive Landscape
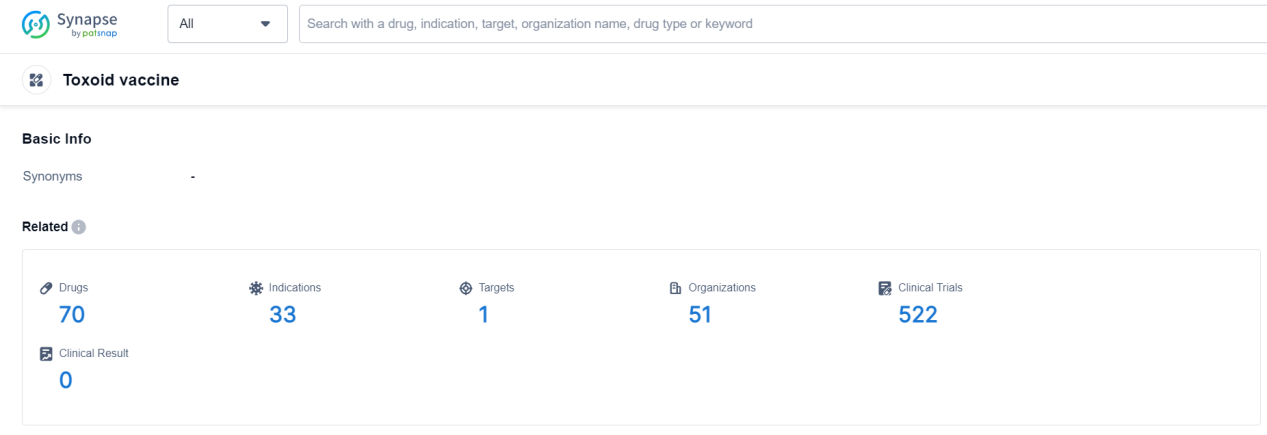
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 19 Sep 2023, there are a total of 70 Toxoid vaccine drugs worldwide, from 51 organizations, covering 1 targets, 33 indications, and conducting 522 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this drug type.
Approved Toxoid Vaccine Medicinal: Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid
The Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid is a toxoid vaccine developed by The Japan Blood Products Organization. It is specifically designed to target the tetanus toxin and is used for the treatment of tetanus, an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani.
This vaccine has been approved and is currently in the highest phase of development globally. It received its first approval in August 2006 in Japan, making it available for use in the country. The approval in Japan indicates that the drug has met the necessary regulatory requirements and has been deemed safe and effective for use in treating tetanus.
As a toxoid vaccine, Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid works by stimulating the body's immune system to produce antibodies against the tetanus toxin. By introducing a harmless form of the toxin into the body, the vaccine helps the immune system recognize and respond to the actual toxin if exposed to it in the future. This provides protection against tetanus infection and its potentially severe complications.
The Japan Blood Products Organization, the originator organization of this vaccine, is responsible for its development and production. They have likely conducted extensive research and clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the vaccine.
Tetanus is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that primarily affects the nervous system. It is commonly contracted through contaminated wounds or puncture injuries. The availability of the Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid vaccine provides an important preventive measure against tetanus, particularly for individuals at risk of exposure to the bacterium.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
In summary, the Adsorbed Tetanus Toxoid is a toxoid vaccine developed by The Japan Blood Products Organization. It is used for the treatment of tetanus, an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. The vaccine has received approval in Japan and is currently in the highest phase of development globally. By stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against the tetanus toxin, the vaccine provides protection against tetanus infection and its complications.