An In-depth Analysis of Amobarbital's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Amobarbital's R&D Progress
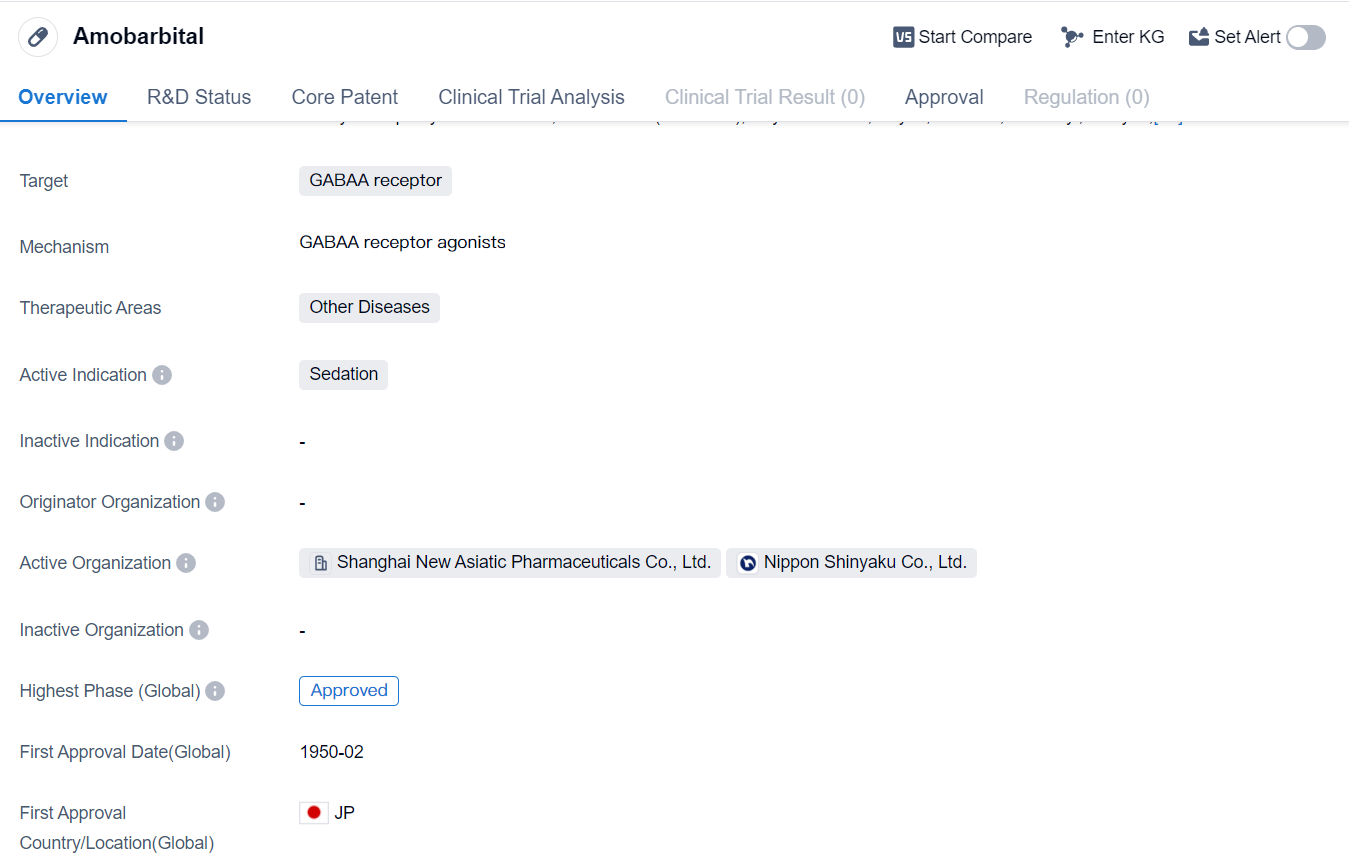
Amobarbital is a small molecule drug that acts as a sedative by targeting the GABAA receptor. It falls under the therapeutic area of Other Diseases. The drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globbally market .
Amobarbital was first approved in Japan in February 1950, making it one of the earliest drugs to receive approval. Its approval in Japan indicates its early recognition and acceptance in the medical community. Since then, it has gained approval in other countries as well, establishing its global presence.
As a small molecule drug, Amobarbital is designed to interact with the GABAA receptor, which is a key target in the central nervous system. By binding to this receptor, the drug enhances the inhibitory effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), leading to sedation. This mechanism of action makes Amobarbital effective in inducing sleep and reducing anxiety.
The therapeutic area of Other Diseases suggests that Amobarbital may have applications beyond its primary indication of sedation. However, the specific diseases or conditions within this category are not provided in the given information. Further research and clinical trials may be necessary to explore the drug's potential in treating other diseases.
The fact that Amobarbital has reached the highest phase of approval indicates its established safety and efficacy profile. This is a positive sign for the drug's market potential and its ability to meet regulatory requirements. The approval in the global market further highlights its broad acceptance and potential for commercial success.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Amobarbital: GABAA receptor agonist
GABAA receptor agonists are a type of drugs that bind to and activate the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. When GABAA receptors are activated by agonists, such as certain drugs, they enhance the inhibitory effects of GABA, leading to a decrease in neuronal excitability.
From a biomedical perspective, GABAA receptor agonists are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions related to the central nervous system, including anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and insomnia. By enhancing the inhibitory actions of GABA, these drugs can help reduce excessive neuronal activity and promote relaxation, sedation, and anticonvulsant effects.
It is important to note that the use of GABAA receptor agonists should be done under medical supervision, as they can have side effects and potential for abuse. Additionally, individual responses to these drugs may vary, and proper dosage adjustments are necessary to achieve optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse reactions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Amobarbital
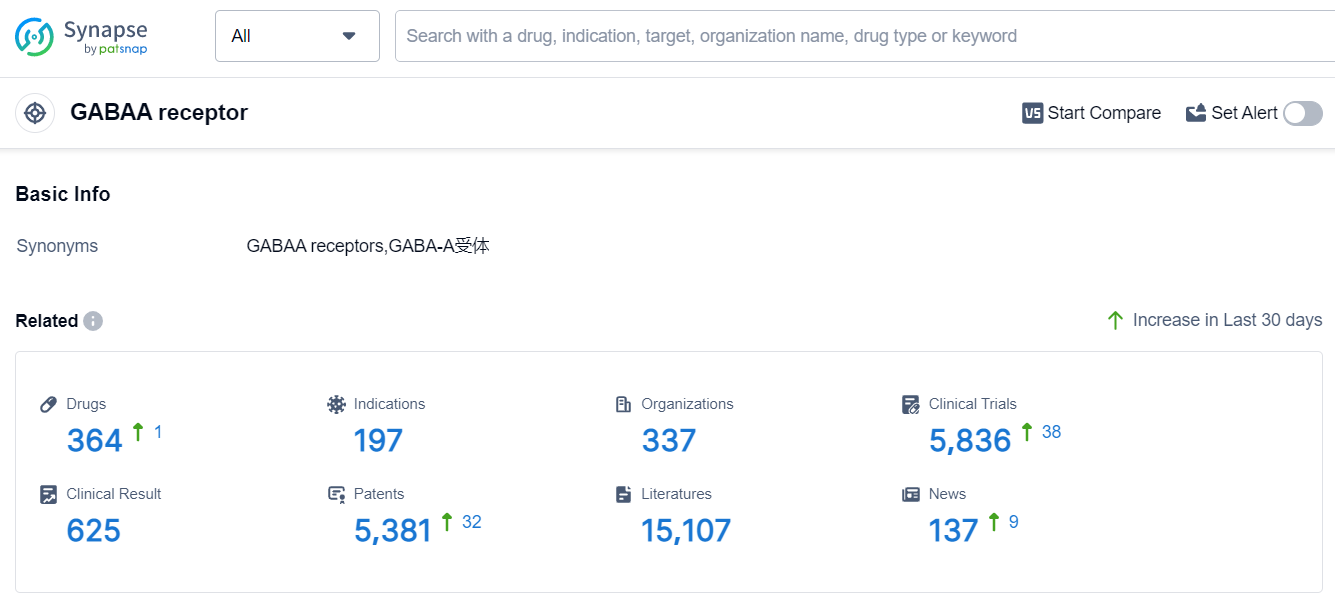
The target GABAA receptor is a highly researched area in the pharmaceutical industry. Pfizer Inc., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. are some of the companies with the highest stage of development on this target. The approved indications for drugs targeting the GABAA receptor include Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders, Anesthesia, Anxiety, Epilepsy, Seizures, Sedation, Depressive Disorder, Anxiety Disorders, Sleep Wake Disorders, Muscle Spasticity, Pain, Fever, Neurotic Disorders, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Catatonia, Panic Disorder, Status Epilepticus, Depression, Postpartum, Psychotic Disorders, and Migraine Disorders. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type under this target. China has shown significant progress in the development of drugs targeting the GABAA receptor. Overall, the competitive landscape for the target GABAA receptor is dynamic, with multiple companies and countries actively involved in research and development.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 8 Sep 2023, there are a total of 364 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 337 organizations, covering 197 indications, and conducting 5836 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Amobarbital is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor to induce sedation. It has been approved in multiple countries, with its first approval dating back to 1950 in Japan. The drug's therapeutic area is categorized as Other Diseases, suggesting potential applications beyond sedation. Its highest phase of approval and global presence make it a promising candidate in the pharmaceutical industry.