Salicylamide: Detailed Review of its Transformative R&D Success
Salicylamide's R&D Progress
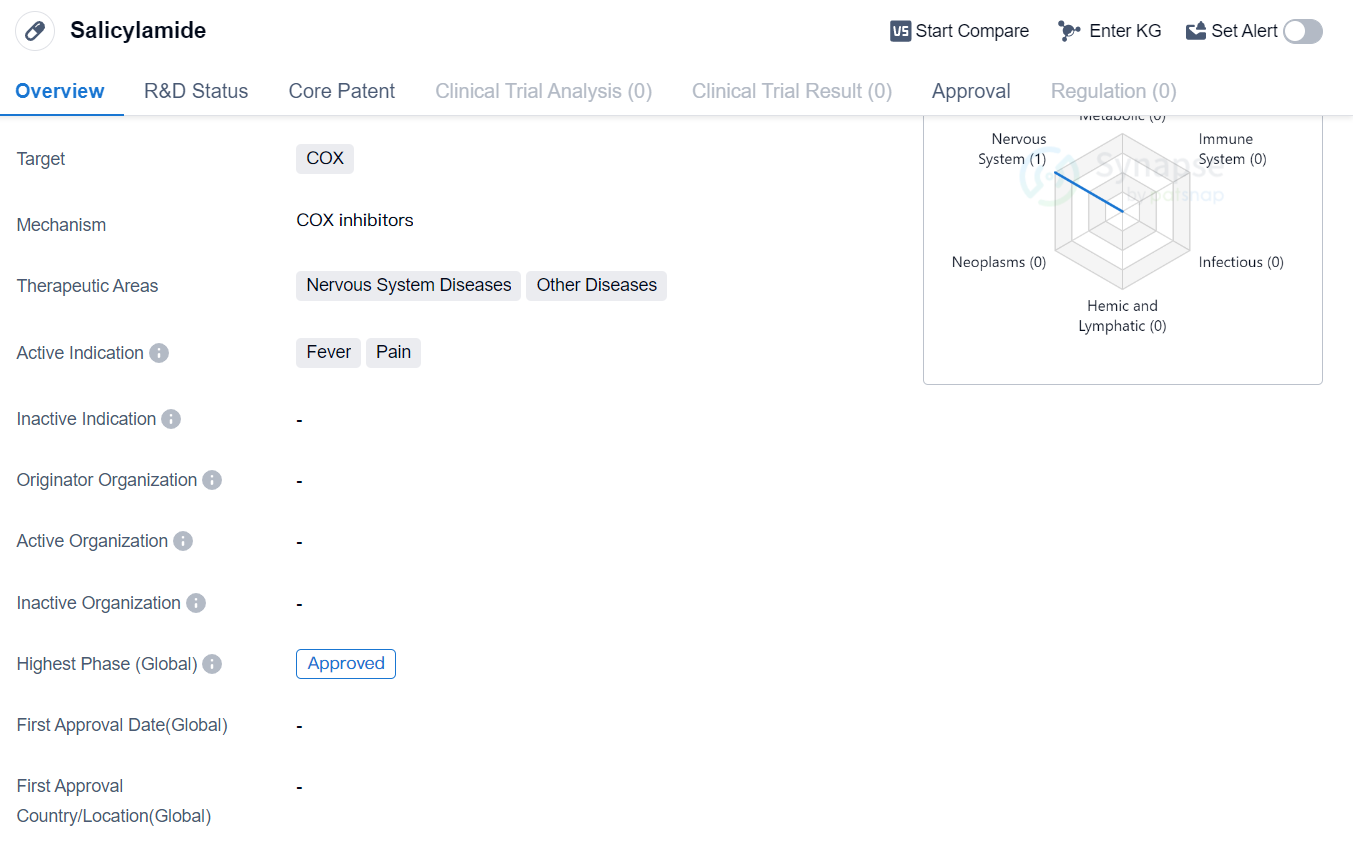
Salicylamide is a small molecule drug that primarily targets COX enzymes. It is used in the treatment of various therapeutic areas, including Nervous System Diseases and Other Diseases. The drug is specifically indicated for the management of fever and pain.
Salicylamide belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and is commonly used as an analgesic and antipyretic agent. It works by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are responsible for the production of prostaglandins, substances that play a role in inflammation, pain, and fever.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. As an approved drug, it has met the regulatory requirements of the relevant authorities and can be prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Salicylamide's therapeutic areas of focus, Nervous System Diseases and Other Diseases, suggest its potential for treating a wide range of conditions beyond fever and pain. However, without further information, it is difficult to determine the specific diseases or conditions it may target within these therapeutic areas.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Salicylamide: COX inhibitor
COX inhibitors, also known as cyclooxygenase inhibitors, are a class of drugs that work by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase. Cyclooxygenase is responsible for the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances involved in inflammation, pain, and fever. By blocking the action of cyclooxygenase, COX inhibitors reduce the production of prostaglandins, thereby relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever.
From a biomedical perspective, COX inhibitors are commonly used in the field of medicine to treat various conditions such as arthritis, menstrual cramps, headaches, and other types of pain and inflammation. They are available both as prescription medications and over-the-counter drugs. Some examples of COX inhibitors include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, as well as selective COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib.
It is important to note that COX inhibitors can have side effects, particularly on the gastrointestinal system, as they can interfere with the protective lining of the stomach and increase the risk of ulcers and bleeding. Therefore, their use should be carefully monitored, and it is recommended to take them at the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Salicylamide
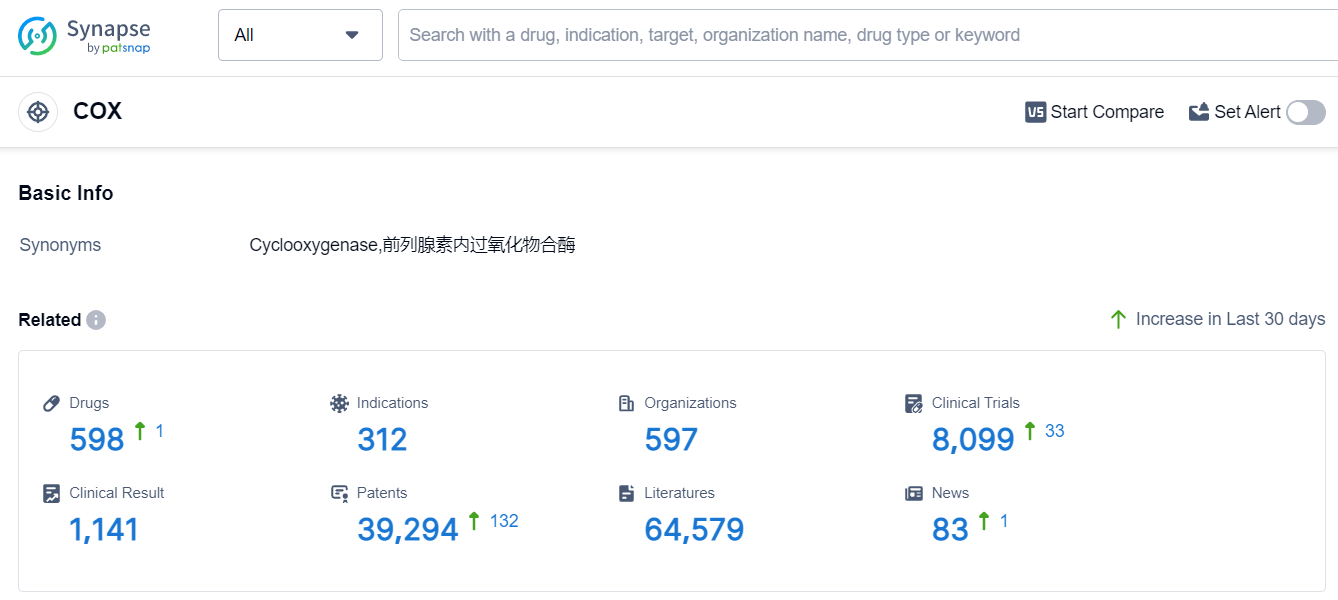
The analysis of the target COX reveals a competitive landscape with several companies vying for market dominance. GSK Plc, Viatris Inc., and Pfizer Inc. are the fastest-growing companies under the target, with a significant number of approved drugs. However, GSK Plc's high number of inactive drugs raises concerns about their R&D progress. The most common indication for drugs targeting COX is pain, followed by common cold, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type, indicating intense competition in the market. China is leading in the development of drugs targeting COX, followed by the United States, Japan, and the European Union. The future development of target COX is expected to be driven by advancements in R&D efforts, particularly in small molecule drugs, and the continued growth of the pharmaceutical industry in China and other key countries/locations.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 9 Sep 2023, there are a total of 598 COX drugs worldwide, from 597 organizations, covering 312 indications, and conducting 8099 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.
Conclusion
Overall, Salicylamide is a small molecule drug that targets COX enzymes and is approved for the treatment of fever and pain. Its highest phase of development indicates its successful evaluation and regulatory approval. While it is primarily indicated for Nervous System Diseases and Other Diseases, further information is needed to understand its specific applications within these therapeutic areas.