An In-depth Analysis of Penicillin G Procaine's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Penicillin G Procaine's R&D Progress
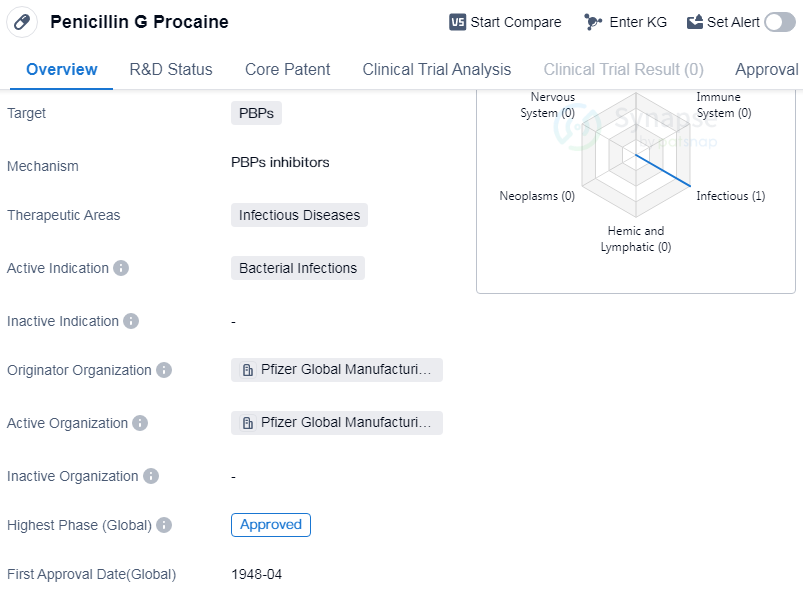
Penicillin G Procaine is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic area of infectious diseases. It is primarily used to treat bacterial infections. The drug targets penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) to inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to the destruction of the bacteria.
The originator organization of Penicillin G Procaine is Pfizer Global Manufacturing China. Pfizer is a renowned pharmaceutical company known for its contributions to the development of various drugs. The drug has been approved and is currently in the highest phase of development globally. It received its first approval in the United States in April 1948.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Penicillin G Procaine: PBPs inhibitors
PBPs inhibitors refer to a class of drugs that target and inhibit the activity of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). PBPs are enzymes found in bacterial cell walls and are involved in the synthesis and maintenance of the cell wall structure. By inhibiting PBPs, these drugs disrupt the bacterial cell wall formation, leading to cell lysis and ultimately killing the bacteria.
From a biomedical perspective, PBPs inhibitors are important in the treatment of bacterial infections. By specifically targeting PBPs, these drugs can selectively inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis without affecting human cells, as human cells do not have PBPs. This specificity makes PBPs inhibitors effective in treating various bacterial infections while minimizing harm to the human body.
It is worth noting that the term "PBPs inhibitors" does not refer to a specific drug but rather a class of drugs that inhibit PBPs. Examples of PBPs inhibitors include penicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems, which are commonly used antibiotics. These drugs bind to PBPs and prevent the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, weakening the bacterial cell wall and making it susceptible to rupture.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Penicillin G Procaine
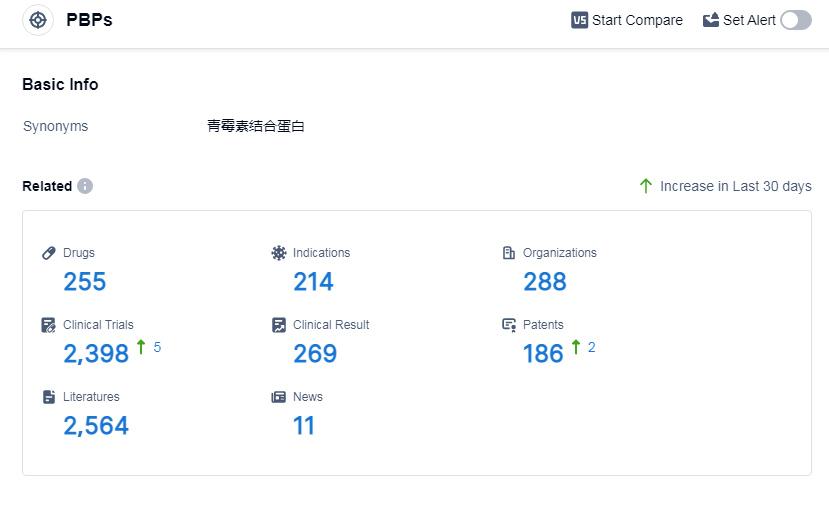
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 255 PBPs drugs worldwide, from 288 organizations, covering 214 indications, and conducting 2398 clinical trials.
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target PBPs reveals that Pfizer Inc., Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., and Merck & Co., Inc. are the companies growing fastest under this target. The R&D progress of these companies indicates their commitment to developing drugs targeting PBPs. The approved drugs under the target PBPs cover a wide range of indications, primarily focusing on bacterial infections and related diseases. Small molecule drugs and synthetic peptides are the drug types progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition around the innovative drugs. China, Japan, the United States, and the European Union are the countries/locations developing fastest under the target PBPs, with China showing significant progress. Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of drugs targeting PBPs in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Penicillin G Procaine is a small molecule drug developed by Pfizer Global Manufacturing China. It is used to treat bacterial infections and targets PBPs to inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. The drug received its first approval in the United States in 1948 and is currently in the highest phase of development globally. Its long history and approval in a major market highlight its significance in the field of infectious diseases.