An In-depth Analysis of Tolbutamide's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Tolbutamide's R&D Progress
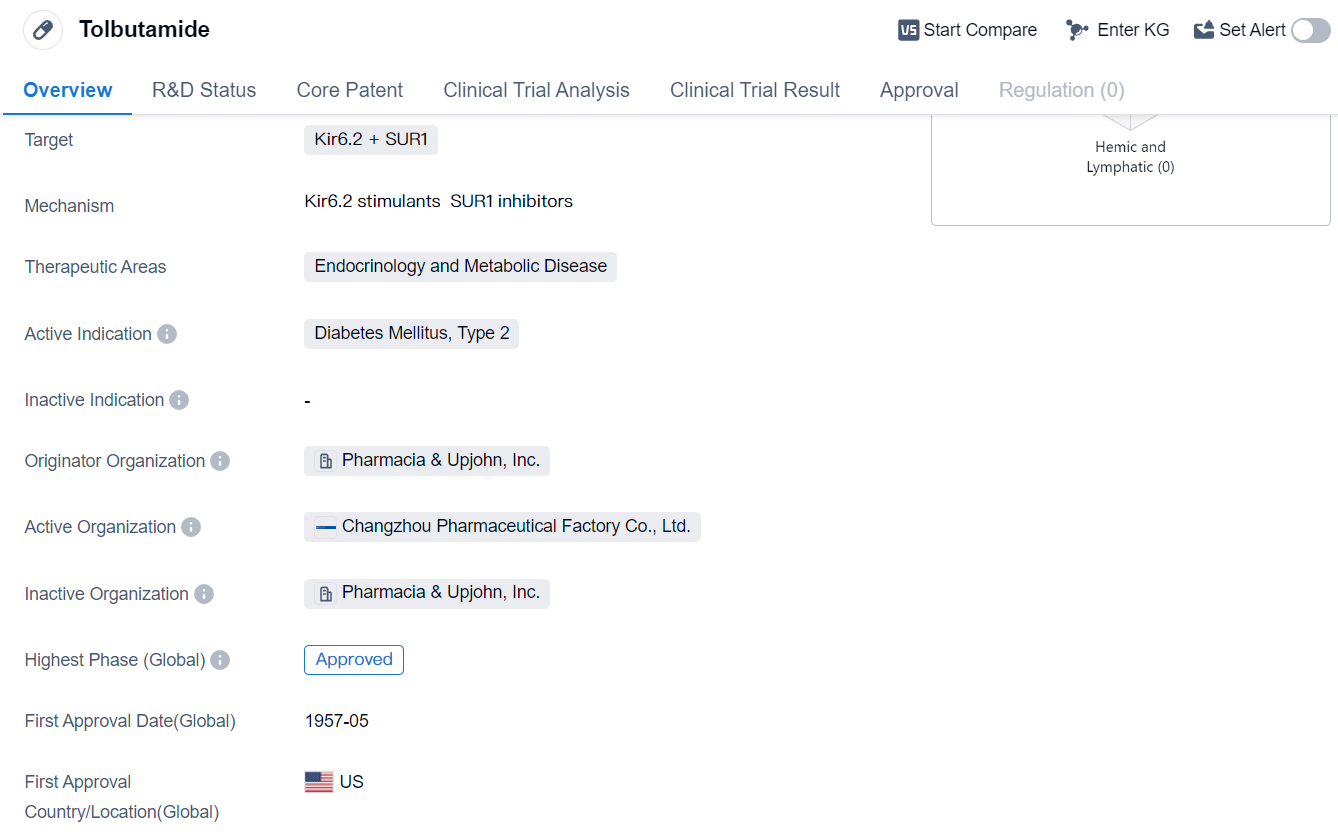
Tolbutamide is a small molecule drug that falls under the therapeutic areas of endocrinology and metabolic disease. It is primarily used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, specifically type 2 diabetes. The drug targets the Kir6.2 and SUR1 proteins, which are involved in the regulation of insulin secretion.
Tolbutamide was first approved for use in the United States in May 1957 by the originator organization, Pharmacia & Upjohn, Inc. This drug has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
As a small molecule drug, Tolbutamide is designed to interact with specific molecular targets in the body, in this case, the Kir6.2 and SUR1 proteins. By targeting these proteins, Tolbutamide helps to regulate insulin secretion, which is crucial for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The approval of Tolbutamide in 1957 marked a significant milestone in the treatment of diabetes. It provided healthcare professionals with a new tool to help patients manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Since then, Tolbutamide has been widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, both in the United States and globally.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Tolbutamide: Kir6.2 stimulant and SUR1 inhibitor
Kir6.2 stimulants and SUR1 inhibitors are terms related to biomedicine, specifically in the field of pharmacology and drug development.
Kir6.2 refers to a specific type of potassium inward rectifier channel subunit. These channels play a crucial role in regulating the movement of potassium ions across cell membranes. Kir6.2 stimulants are substances or drugs that enhance the activity or function of Kir6.2 channels. By stimulating these channels, they can increase the flow of potassium ions into the cells, leading to various physiological effects.
SUR1, on the other hand, stands for sulfonylurea receptor 1. It is a protein subunit that forms a complex with Kir6.2 channels, creating a functional ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel. SUR1 inhibitors are substances or drugs that block or inhibit the activity of SUR1, thereby affecting the function of KATP channels. These inhibitors can modulate the flow of potassium ions and influence cellular processes.
The combination of Kir6.2 stimulants and SUR1 inhibitors is of particular interest in the development of drugs for various medical conditions. By targeting these channels and receptors, researchers aim to regulate potassium ion flux and impact cellular functions. This approach has potential applications in the treatment of diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions.
In summary, Kir6.2 stimulants enhance the function of potassium inward rectifier channels, while SUR1 inhibitors block the activity of sulfonylurea receptor 1. Together, they can modulate potassium ion flow and have implications in the development of therapeutic interventions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Tolbutamide
The analysis of the current competitive landscape of target Kir6.2 + SUR1 reveals that Pfizer Inc. is the leading company with the highest number of approved drugs. The drugs under this target have been approved for indications such as Diabetes Mellitus, Alopecia, Neonatal diabetes mellitus, and various other diseases. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating potential intense competition in the market. China is showing significant progress in the development of drugs targeting Kir6.2 + SUR1, with the highest number of approved drugs among all countries/locations. The future development of this target holds promise for the treatment of various diseases and conditions.
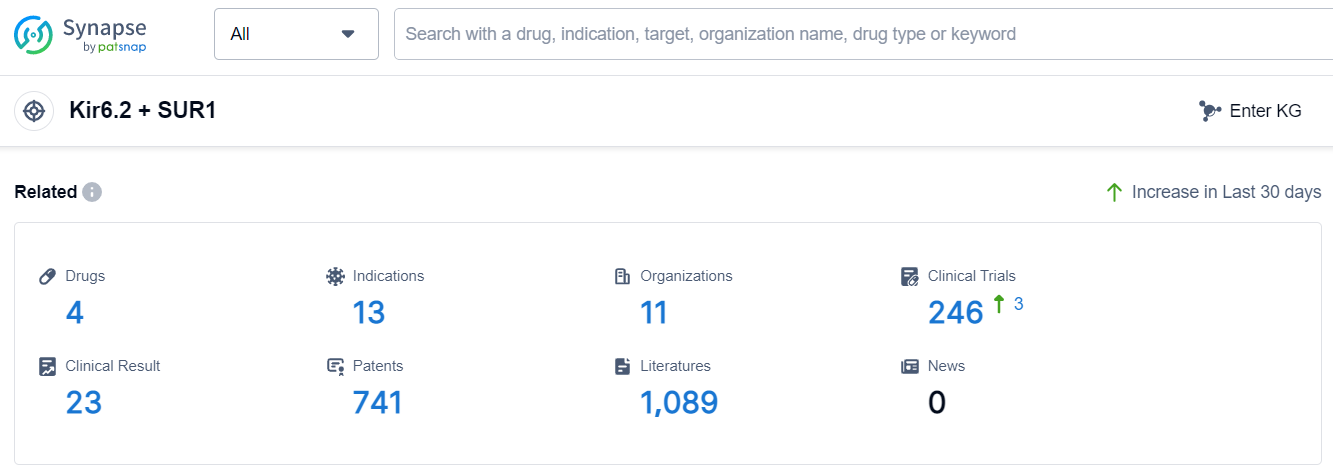
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 11 Sep 2023, there are a total of 4 Kir6.2 + SUR1 drugs worldwide, from 11 organizations, covering 13 indications, and conducting 246 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Tolbutamide is a small molecule drug used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It targets the Kir6.2 and SUR1 proteins and has been approved for use since 1957. Its approval in the global market highlights its significance in the field of endocrinology and metabolic disease.