Bluejay Therapeutics' BJT-778 Achieves 100% Virologic Response in Hepatitis D Patients
Bluejay Therapeutics, a biopharmaceutical firm in the clinical development phase specializing in innovative treatments for viral hepatitis and severe liver diseases, has revealed new findings from its Phase 2 trial of BJT-778. This investigational monoclonal antibody (mAb) is fully human and exhibits high affinity, targeting hepatitis B virus surface antigen (anti-HBsAg). The Phase 2 trial is exploring the efficacy of BJT-778 as a potential standalone treatment for adults suffering from chronic hepatitis D (CHD), the most severe variant of viral hepatitis.
👇Explore more about this drug by clicking the image below. Gain detailed insights into its R&D Status, Core Patent, Clinical Trials and Global Approval Status. Stay informed and updated.
Detailed data will be unveiled during an oral presentation on November 19 at The Liver Meeting® 2024, hosted by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). The company will also share findings from its development program focusing on the functional cure for chronic hepatitis B (CHB), encompassing preclinical investigations into the uptake and T cell activation prompted by BJT-778, along with the preclinical evaluation of cavrotolimod, a spherical TLR9 agonist that may serve as a potential partner for BJT-778.
"For the over 12 million individuals worldwide suffering from chronic hepatitis D, which represents the most severe and aggressive variant of viral hepatitis, there are few treatment alternatives available," stated Kosh Agarwal, MD, a Consultant Hepatologist and Transplant Physician at the Institute of Liver Studies at King’s College Hospital in London, UK. "We must improve patient care. The phase 2 results of BJT-778 indicate that this monotherapy could represent a significant therapeutic advancement in chronic hepatitis D (CHD)."
Findings from the BJT-778 CHD Phase 2 Study
In this phase 2 trial, participants with measurable hepatitis D virus (HDV) RNA and hepatitis B virus (HBV) controlled by nucleos(t)ide therapies were allocated to one of three dosing regimens of BJT-778: 300 mg once weekly (QW) (n=18); 600 mg weekly for 12 weeks followed by biweekly dosing (Q2W) (n=11); and 900 mg every four weeks following a loading dose at week two (Q4W) (n=18). Inclusion criteria permitted patients with compensated cirrhosis and those with well-managed HIV.
The primary endpoints of the trial included safety and tolerability, virological response (characterized as a reduction of ≥2 log10 HDV RNA IU/mL from baseline or HDV RNA target not detected [TND]); normalization of ALT levels in participants who exhibited elevated ALT at baseline; and the composite endpoint that combines virological response with ALT normalization. Following FDA guidelines, this composite measure is deemed a reliable indicator of clinical advantage and supports the approval of new treatments for CHD.
BJT-778 demonstrated a 100% virological response across all dosing groups, with nearly 78% of participants achieving the composite endpoint of combined virological response and ALT normalization. This simultaneous reduction in HDV viral load and ALT levels was observed in all dosing cohorts, suggesting an advantageous impact on liver inflammation as a result of the decrease in viral load.
👇Explore the most recent advancements in drug research, indications, organizations, clinical trials, results, and patents related to this target by clicking the image link below. Dive in to gain deeper insights!
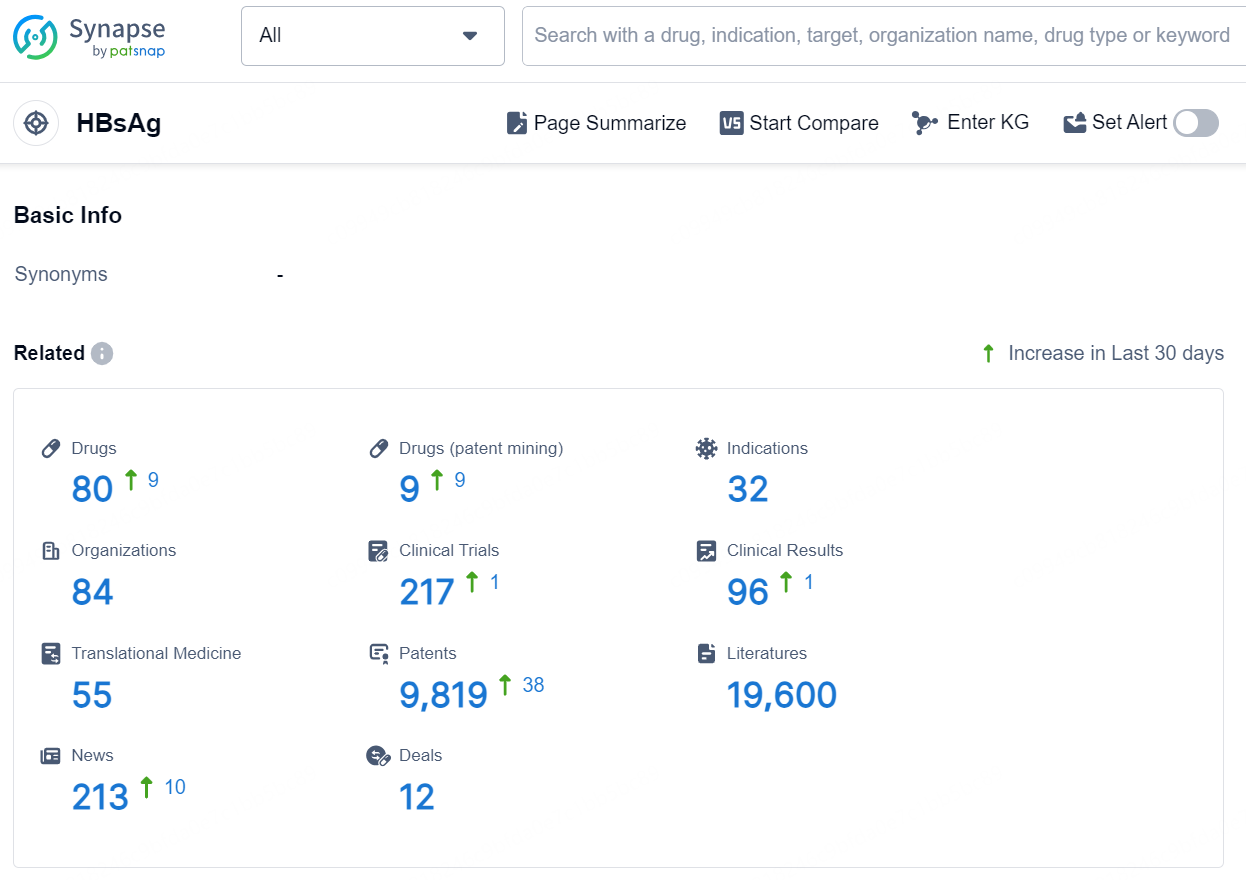
According to the data provided by the Synapse Database, As of November 19, 2024, there are 80 investigational drugs for the HBsAg target, including 32 indications, 84 R&D institutions involved, with related clinical trials reaching 217, and as many as 9819 patents.
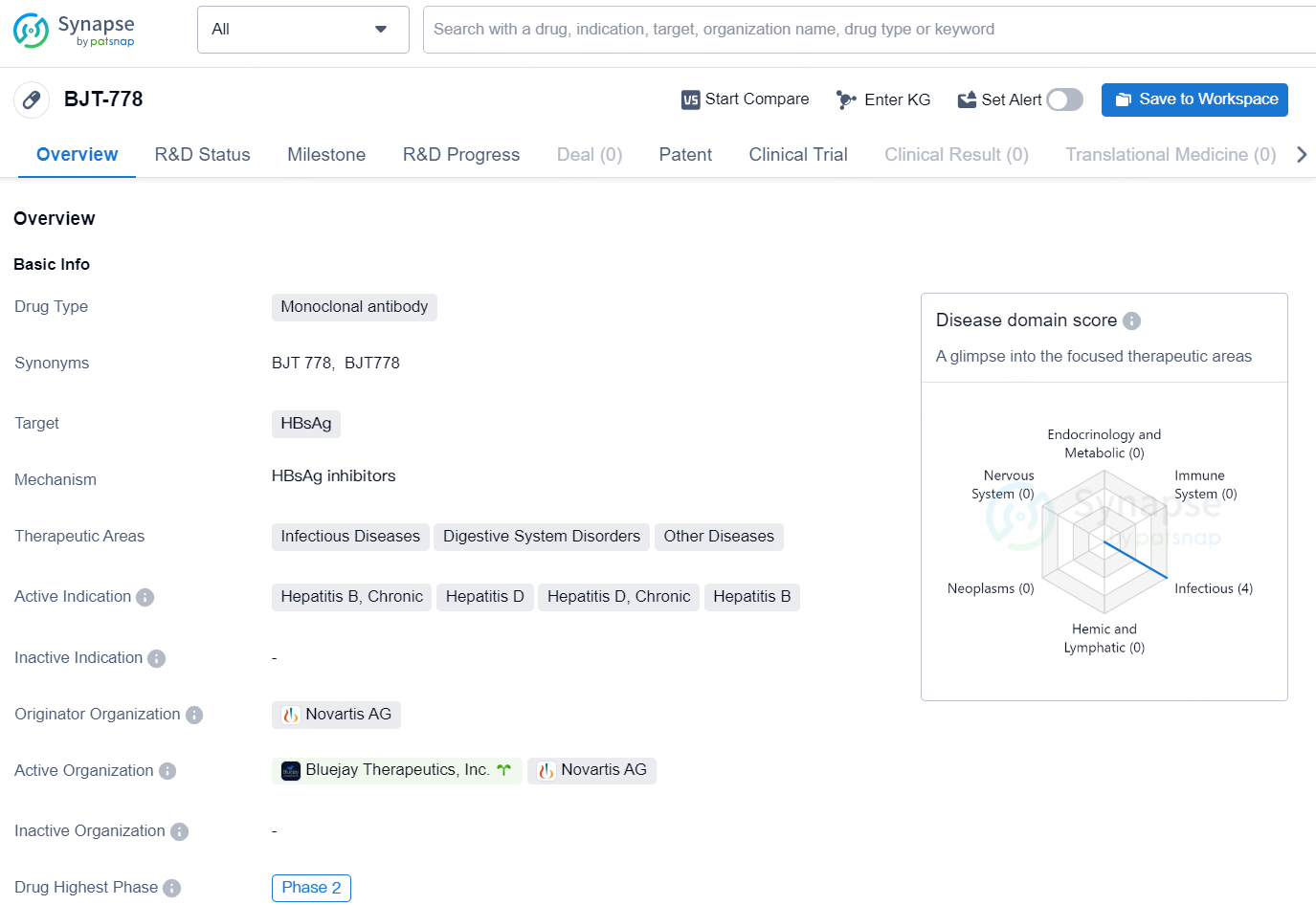
BJT-778 is a monoclonal antibody drug designed to target HBsAg, with primary therapeutic areas including Infectious Diseases, Digestive System Disorders, and Other Diseases. The drug is indicated for the treatment of Hepatitis B, Chronic, Hepatitis D, and Chronic Hepatitis D.