How to find the structure and classification of Retifanlimab?
Retifanlimab, a groundbreaking therapeutic agent, is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody developed by Incyte Corporation. This innovative medication targets the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor, a key protein involved in the immune checkpoint pathway, and is specifically indicated for the treatment of metastatic or recurrent locally advanced Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). MCC is a rare and aggressive form of skin cancer with a high mortality rate, and effective treatments are crucial for improving patient outcomes and survival rates.
Summary of Research Progress:
The research progress of Retifanlimab has been marked by significant advancements and milestones. Mechanistically, Retifanlimab operates through the inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, a key checkpoint in the immune system. PD-1 is expressed on the surface of T-cells, and its ligand, PD-L1, is often overexpressed on tumor cells. When PD-1 binds to PD-L1, it sends an inhibitory signal that suppresses T-cell activation and proliferation, allowing tumors to evade immune detection and destruction. By blocking this interaction, Retifanlimab enhances T-cell activation and restores the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. This targeted approach addresses the underlying immune evasion mechanisms of MCC, offering a more comprehensive and sustainable treatment option compared to traditional therapies.
Retifanlimab has achieved significant regulatory milestones. In March 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval for Retifanlimab, marketed as Zynyz, for the treatment of adults with metastatic or recurrent locally advanced MCC. This approval was based on the results of the Phase II PODIUM-201 trial, which demonstrated a high objective response rate (ORR) of 52% in patients who had not previously received chemotherapy. Among these patients, 18% achieved complete responses, and 34% achieved partial responses. The median duration of response (DOR) ranged from 1.1 to 24.9 months, with 76% of responders maintaining their response for more than 6 months and 62% for more than 12 months. These results highlight the efficacy and durability of Retifanlimab in treating MCC.
Globally, the competition in the MCC treatment market is limited but growing. Traditional treatments for MCC include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, which are often used in combination but have limitations in terms of efficacy and side effects, especially in advanced stages of the disease. Retifanlimab, with its novel mechanism of action and targeted delivery, offers a unique and potentially superior treatment option. The drug's ability to achieve sustained responses with a manageable safety profile makes it an attractive alternative for patients and healthcare providers. Other PD-1 inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have also been approved for MCC, but Retifanlimab's high affinity and potent binding to PD-1 set it apart.
Type of Immunoglobulin of Retifanlimab
Retifanlimab is classified as an immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody. IgG4 is one of the four subclasses of IgG, the most abundant type of antibody in human serum. IgG4 antibodies have unique properties that make them suitable for therapeutic applications. They have a lower affinity for Fcγ receptors and complement proteins, which reduces the risk of adverse immune reactions such as cytokine release syndrome and infusion-related reactions. Additionally, IgG4 antibodies have a higher degree of glycosylation, which enhances their stability and prolongs their half-life in the circulation. These characteristics contribute to the favorable safety profile and prolonged therapeutic effect of Retifanlimab.
Light and Heavy Chains and Structural Characteristics of Retifanlimab
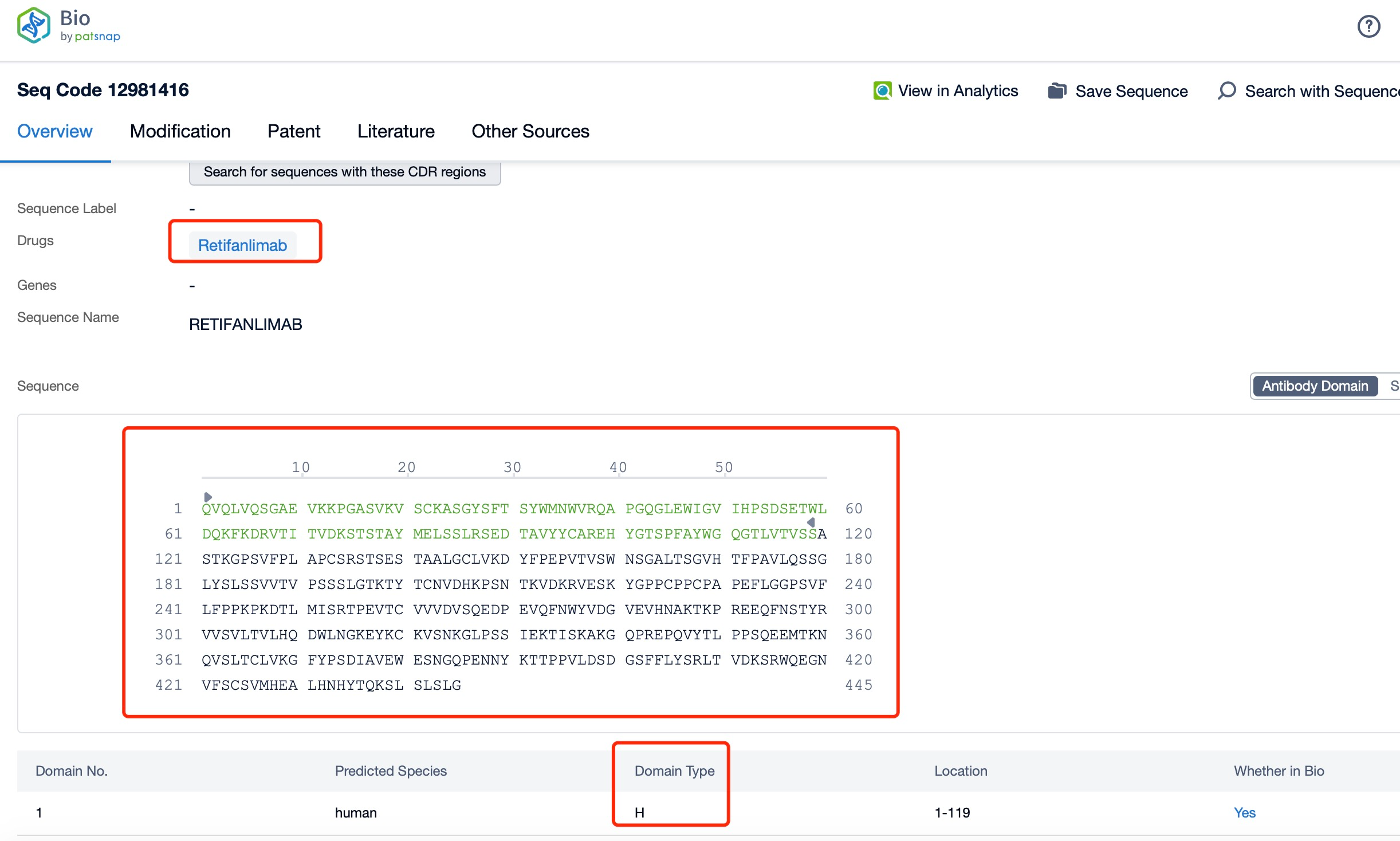
The light and heavy chains of Retifanlimab are critical components of its structure and function. Each Retifanlimab molecule consists of two heavy chains and two light chains, forming a Y-shaped structure. The heavy chains are approximately 450 amino acids long and contain variable (VH) and constant (CH) regions. The light chains are approximately 214 amino acids long and also contain variable (VL) and constant (CL) regions. The variable regions of the heavy and light chains form the antigen-binding sites, which are responsible for recognizing and binding to the PD-1 protein on T-cells. The constant regions of the heavy chains form the Fc region, which interacts with Fc receptors on immune cells and mediates various effector functions.
The structural characteristics of Retifanlimab are optimized for its therapeutic application. The variable regions of the heavy and light chains are engineered to ensure high specificity and affinity for the PD-1 protein, minimizing off-target effects and maximizing therapeutic efficacy. The Fc region is modified to reduce the affinity for Fcγ receptors and complement proteins, which helps to minimize adverse immune reactions. Additionally, the heavy and light chains are linked by disulfide bonds, which stabilize the structure and enhance the overall stability and bioavailability of the antibody. These modifications contribute to the high affinity and potent binding of Retifanlimab to PD-1, making it an effective therapeutic agent.
Summary and Prospect
In summary, Retifanlimab represents a significant breakthrough in the treatment of metastatic or recurrent locally advanced Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Its targeted mechanism of action, involving the inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, offers a novel and effective approach to managing this condition. The drug's favorable safety profile, combined with its convenient dosing schedule of once-every-four-weeks intravenous infusions, makes it an attractive option for patients with MCC. With ongoing Phase III trials and strong preclinical and early-phase clinical data, Retifanlimab is poised to play a crucial role in the future of MCC treatment. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to further optimize the drug's therapeutic potential and explore its use in other related conditions, opening up new possibilities for patients suffering from rare and aggressive cancers. The success of Retifanlimab not only highlights the potential of monoclonal antibody therapy but also paves the way for the development of similar therapies for a wide range of cancers. As the field of immuno-oncology continues to evolve, Retifanlimab stands as a testament to the innovative approaches being developed to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes.
How to find the structure and classification of antibody drugs?
In Patsnap Bio, you can find the sequence and latest research and development advances of all antibody drugs.
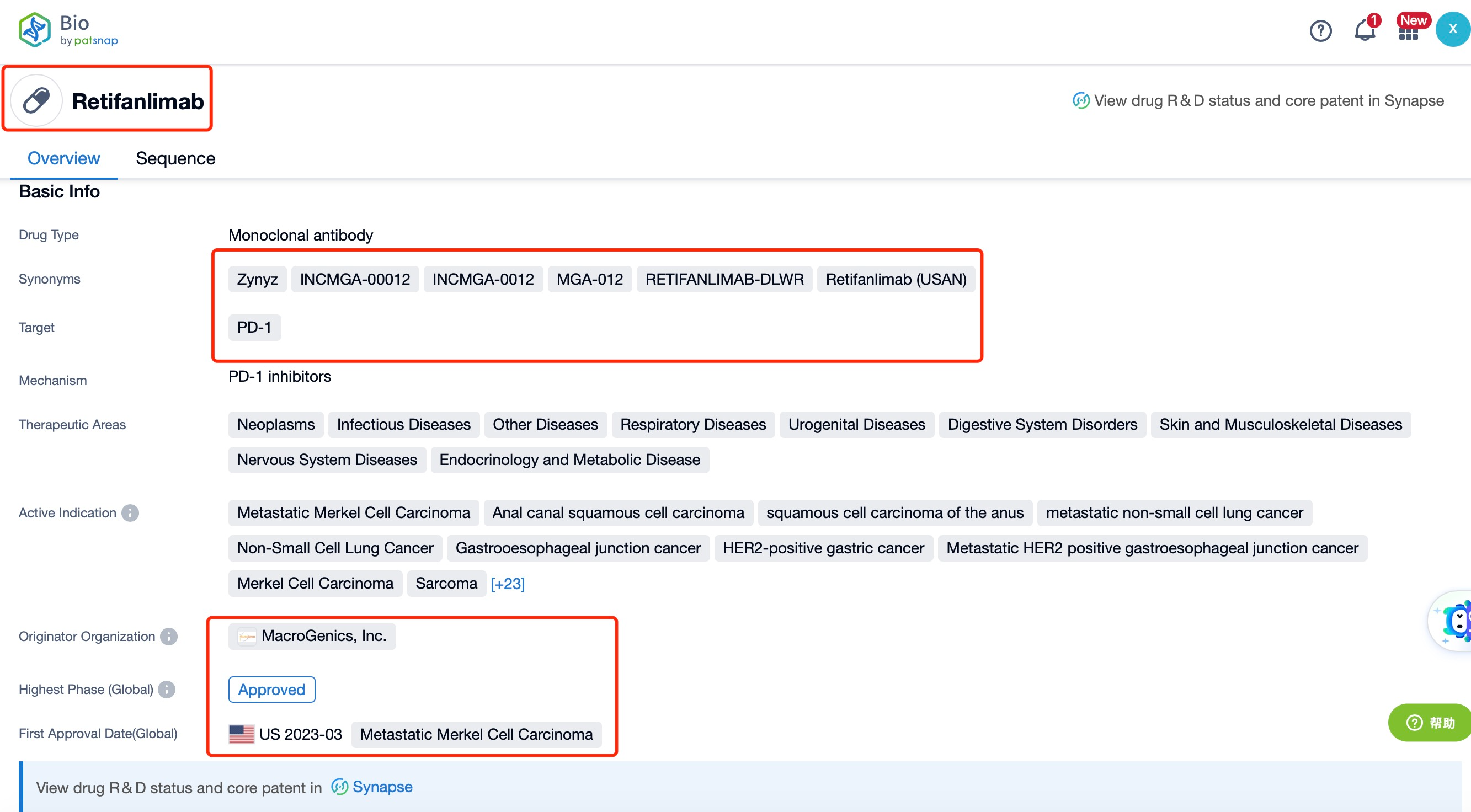
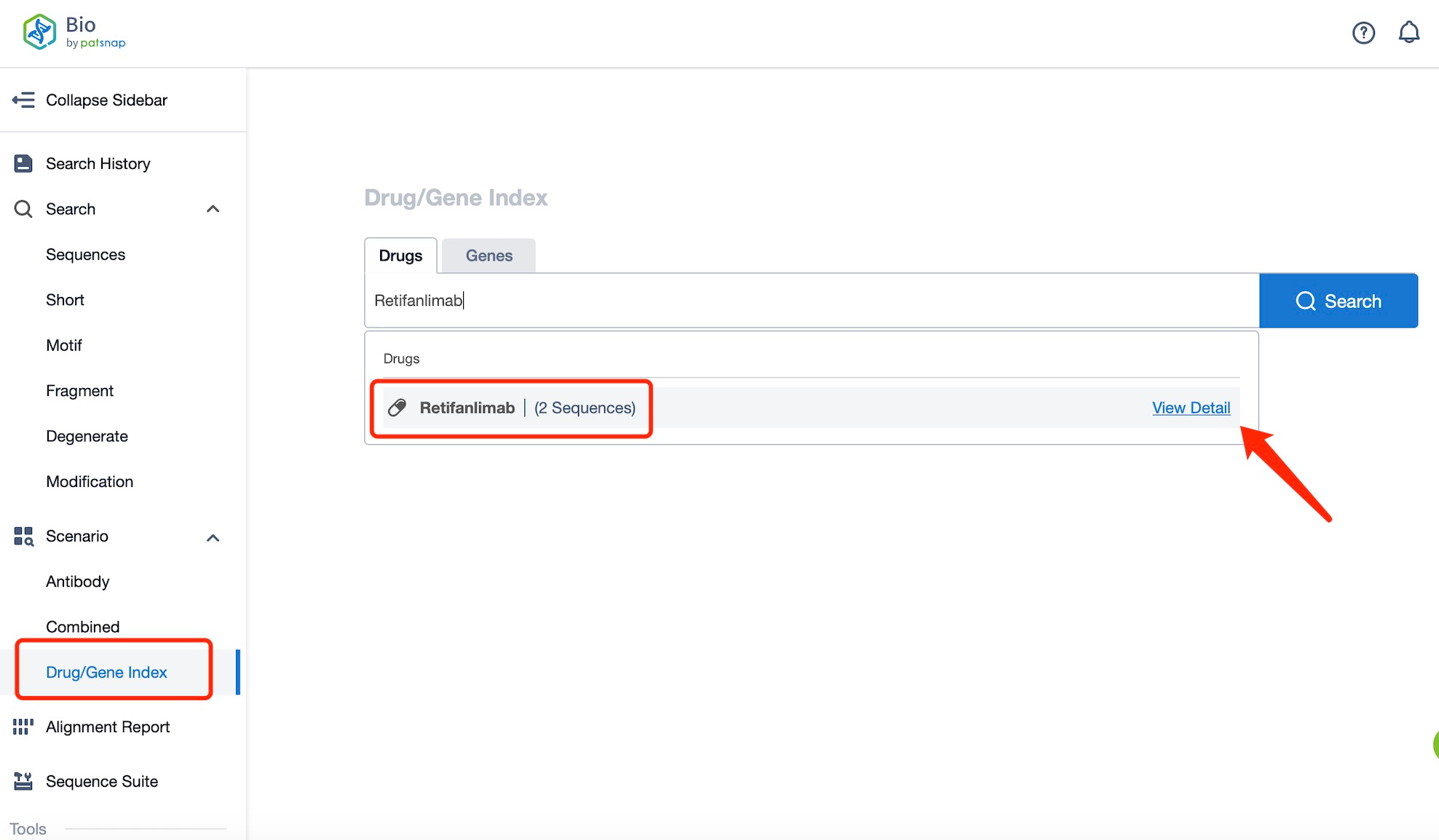
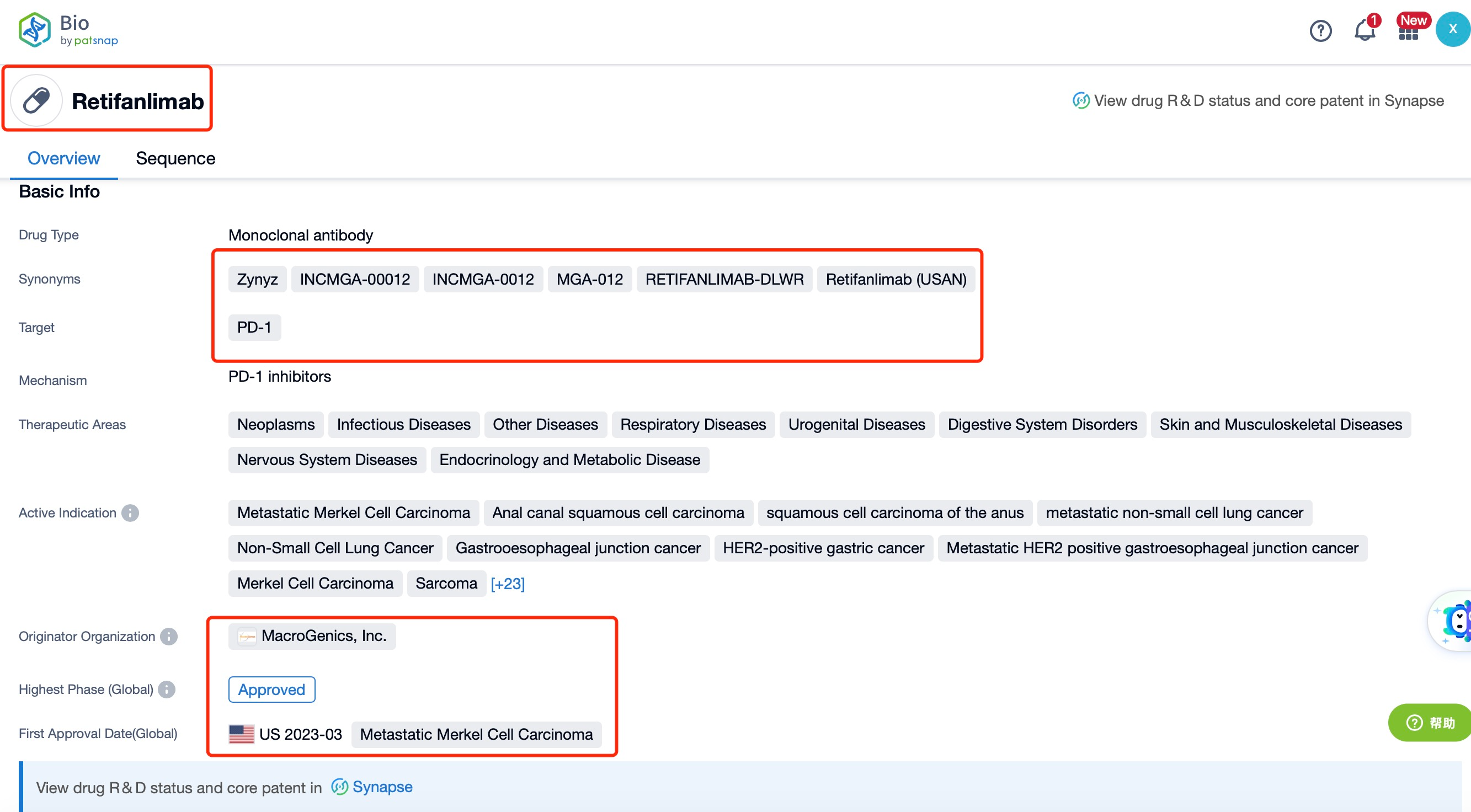
Taking Retifanlimab as an example, first click on the Drug/Gene Index on the Patsnap Bio homepage. Here you can search for sequence information by drug and gene names. Enter ' Retifanlimab ' in the search box and click to view the details. On the details page, you can find the basic information and research progress of Retifanlimab.
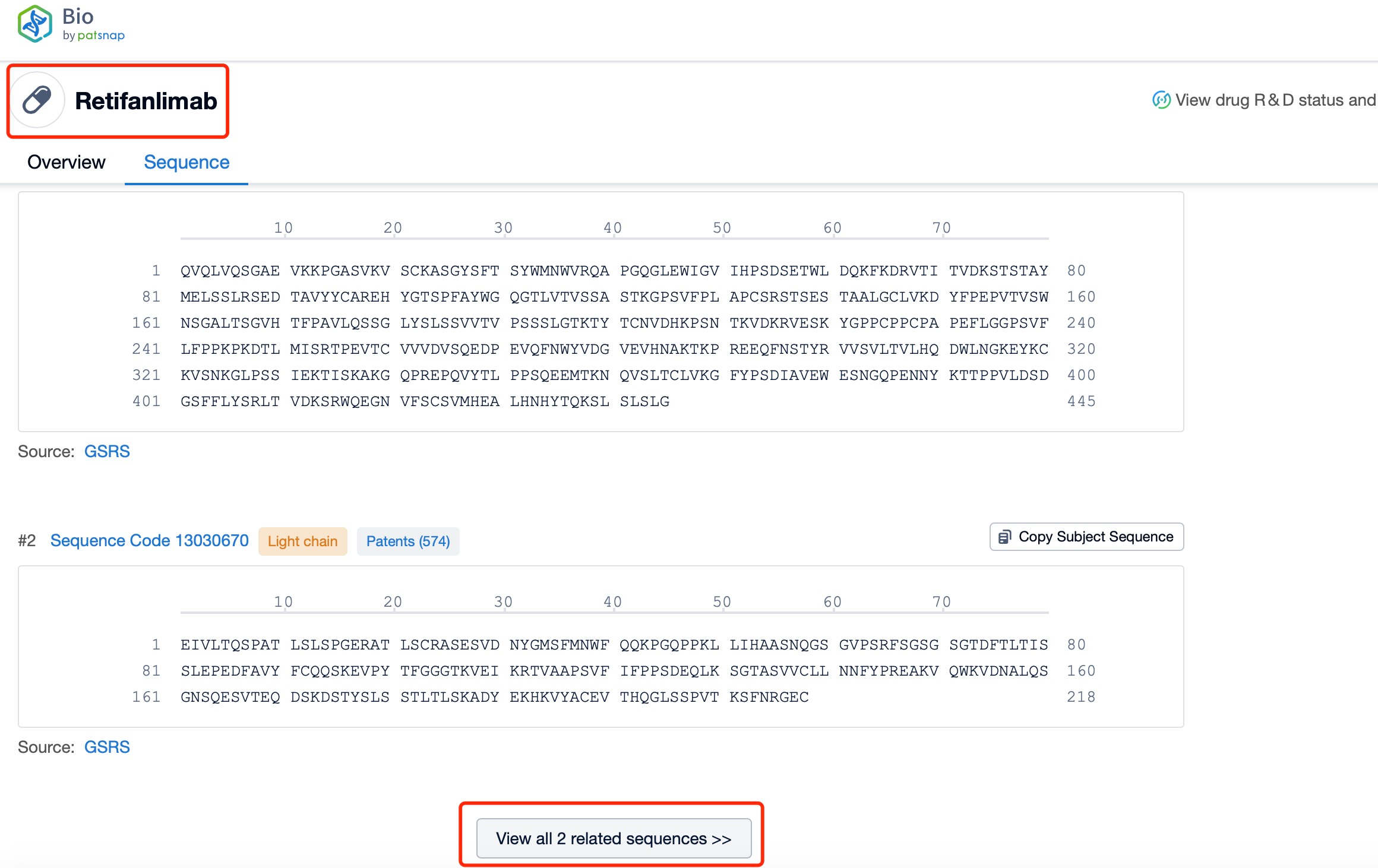
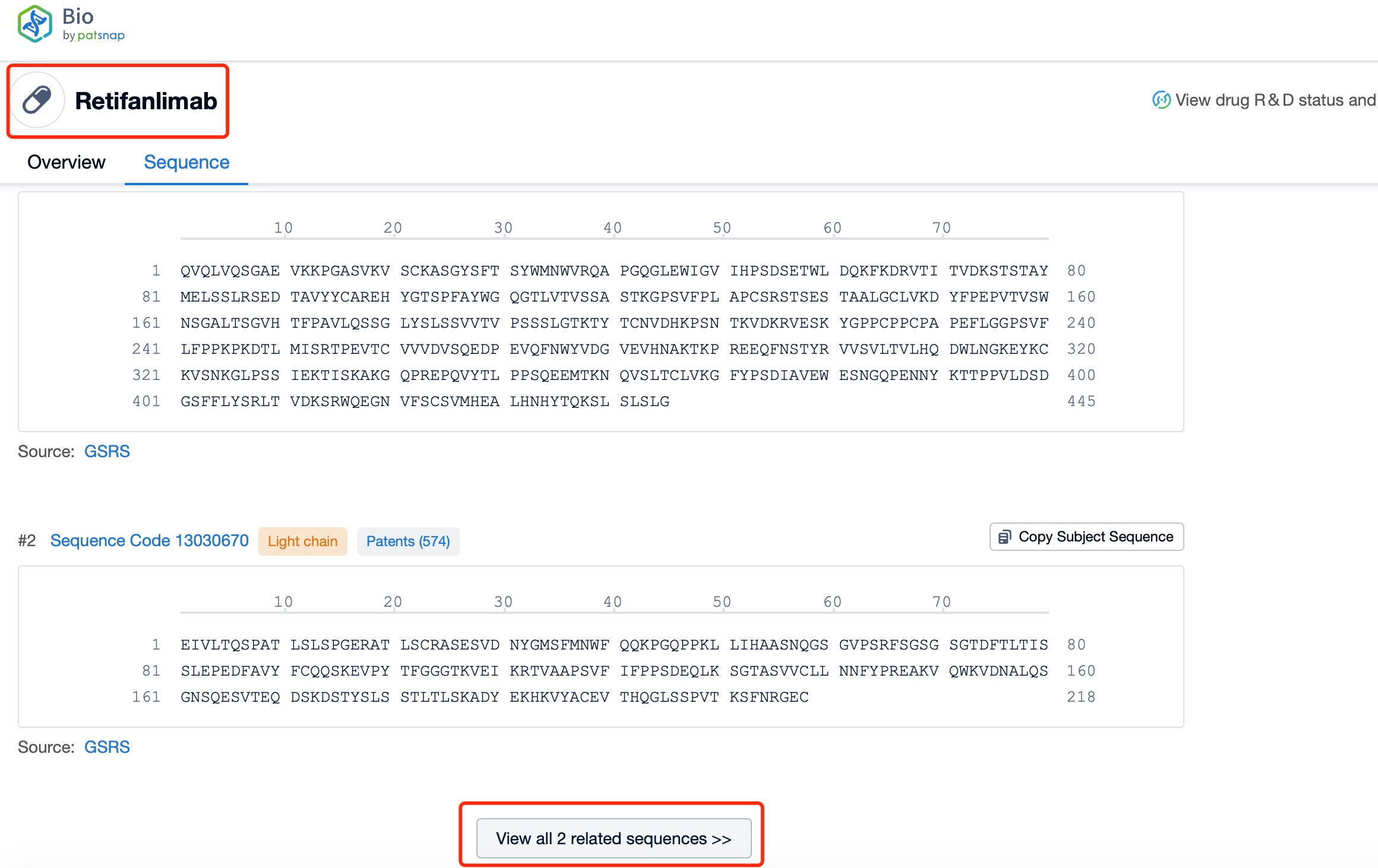
Click "View all related sequences" below the sequence information to search for and retrieve all biological sequences similar to this information.
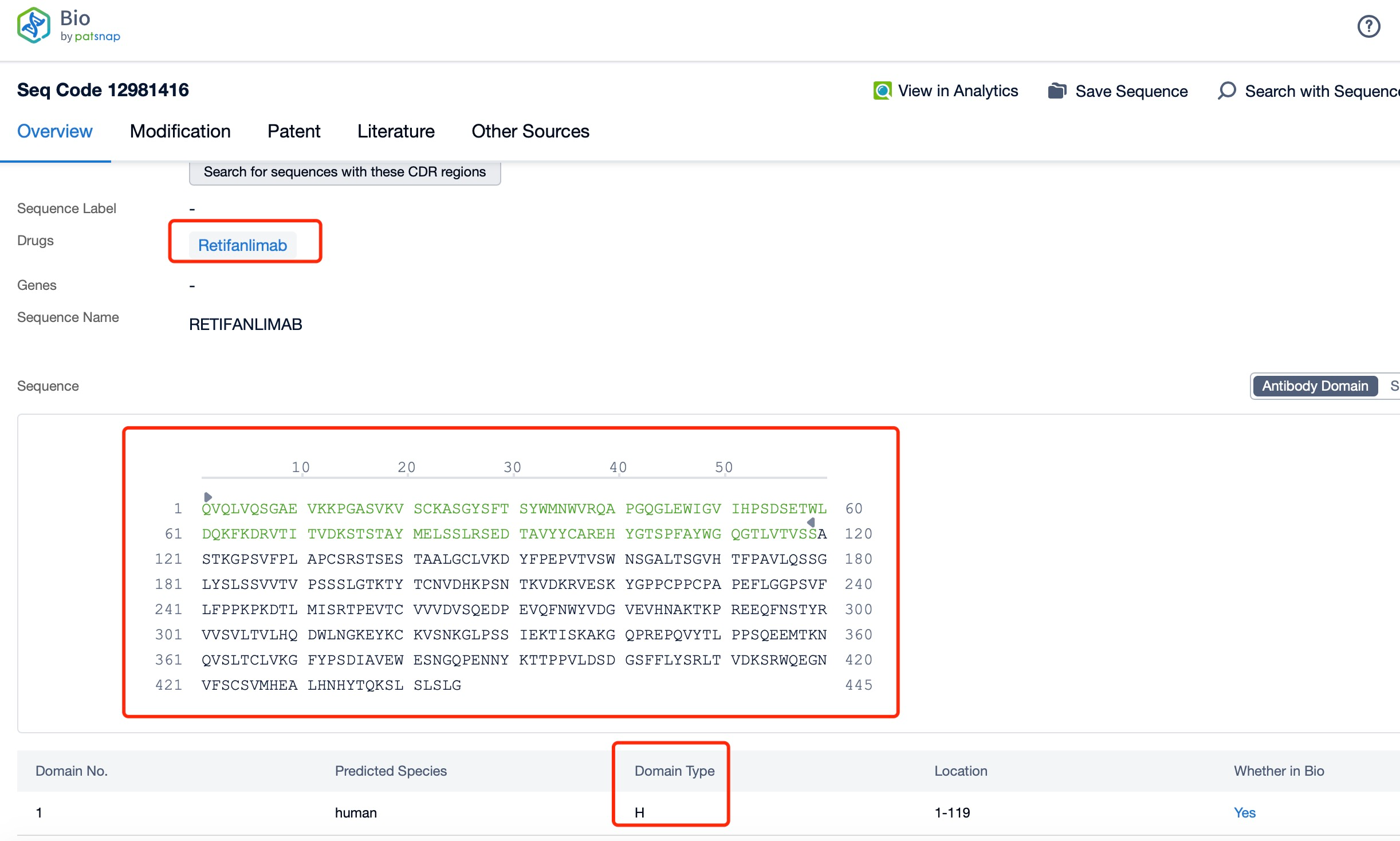
Clicking on the sequence name will provide you with all the basic information of that sequence. Here, you can easily query the sequence and action of the light and light chains of antibodies.
Patsnap Bio helps you turn weeks into minutes with cutting-edge AI-enabled tools built to master the complexities of sequence retrieval and automate IP analysis with precision and ease.