Broad-spectrum anti-cancer drugs - RET inhibitors
RET is a proto-oncogene initially discovered in 1985, it is located on chromosome 10q11.2, encoding a transmembrane glycoprotein: receptor tyrosine kinase, which interacts with ligands (GFRα1-4) of the glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family.
RET plays a significant role in the development and function of the enteric nervous system and the kidney system. RET can be activated by binding with GFRα and GDNF ligands on the cell membrane, forming RET homodimers, triggering downstream signals through the phosphorylation of the intracellular structure domain, activating cell proliferation pathways such as MAPK, JAK-STAT and PI3K-AKT-mTOR.
Therefore, once RET abnormalities (fusion, rearrangement or mutation, etc.) occur, causing RET protein to overactivate without depending on ligands, it will lead to abnormal cell proliferation and induce cancer. According to statistics, RET abnormalities can be detected in 2% of human cancers, commonly in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), thyroid cancer, etc.
RET Competitive Landscape
According to the data provided by Patsnap Synapse-Global Drug Intelligence Database: the following figure shows that as of 25 Sep 2023, there are a total of 55 RET drugs worldwide, from 96 organizations, covering 103 indications, and conducting 2420 clinical trials.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or login directly if you have freemium accounts, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs , indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target.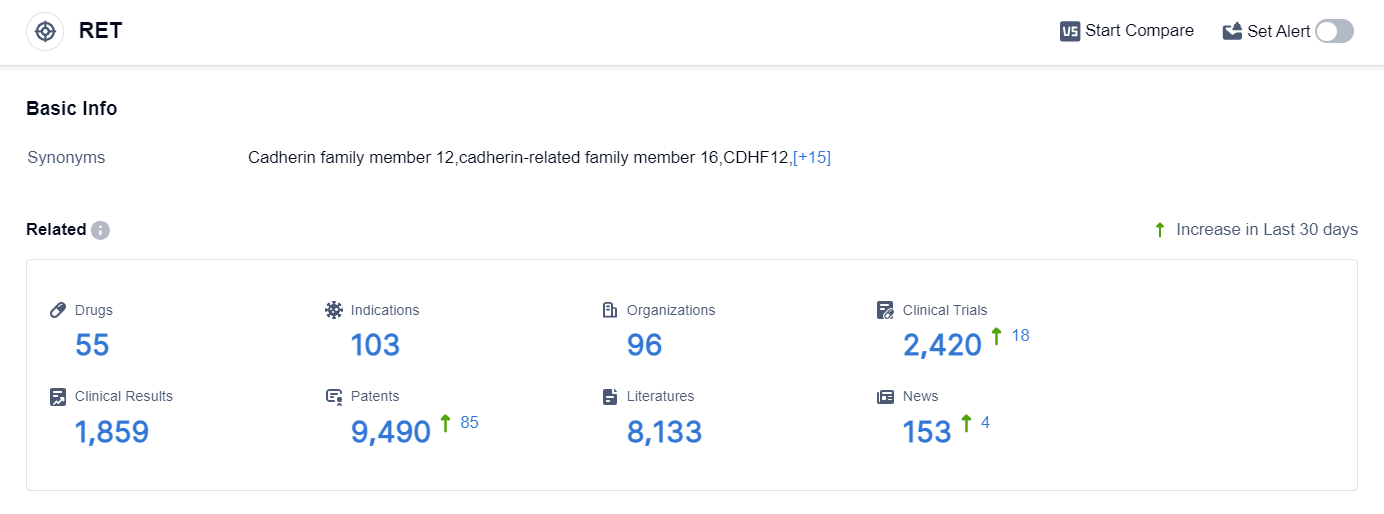
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target RET reveals a strong focus and investment in this area by various pharmaceutical companies. Roche Holding AG and Bayer AG are leading the way with the highest number of drugs in advanced stages of development.
The indications of Thyroid Cancer, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and NSCLC have seen the most drug approvals, indicating a significant need for effective treatments in these areas.
The dominance of small molecule drugs suggests intense competition and innovation in this field. China has shown significant progress in the development of drugs targeting RET, indicating the growing presence and contribution of Chinese pharmaceutical companies.
Overall, the analysis highlights the importance of target RET in the pharmaceutical industry and the ongoing efforts to develop effective treatments for associated diseases.
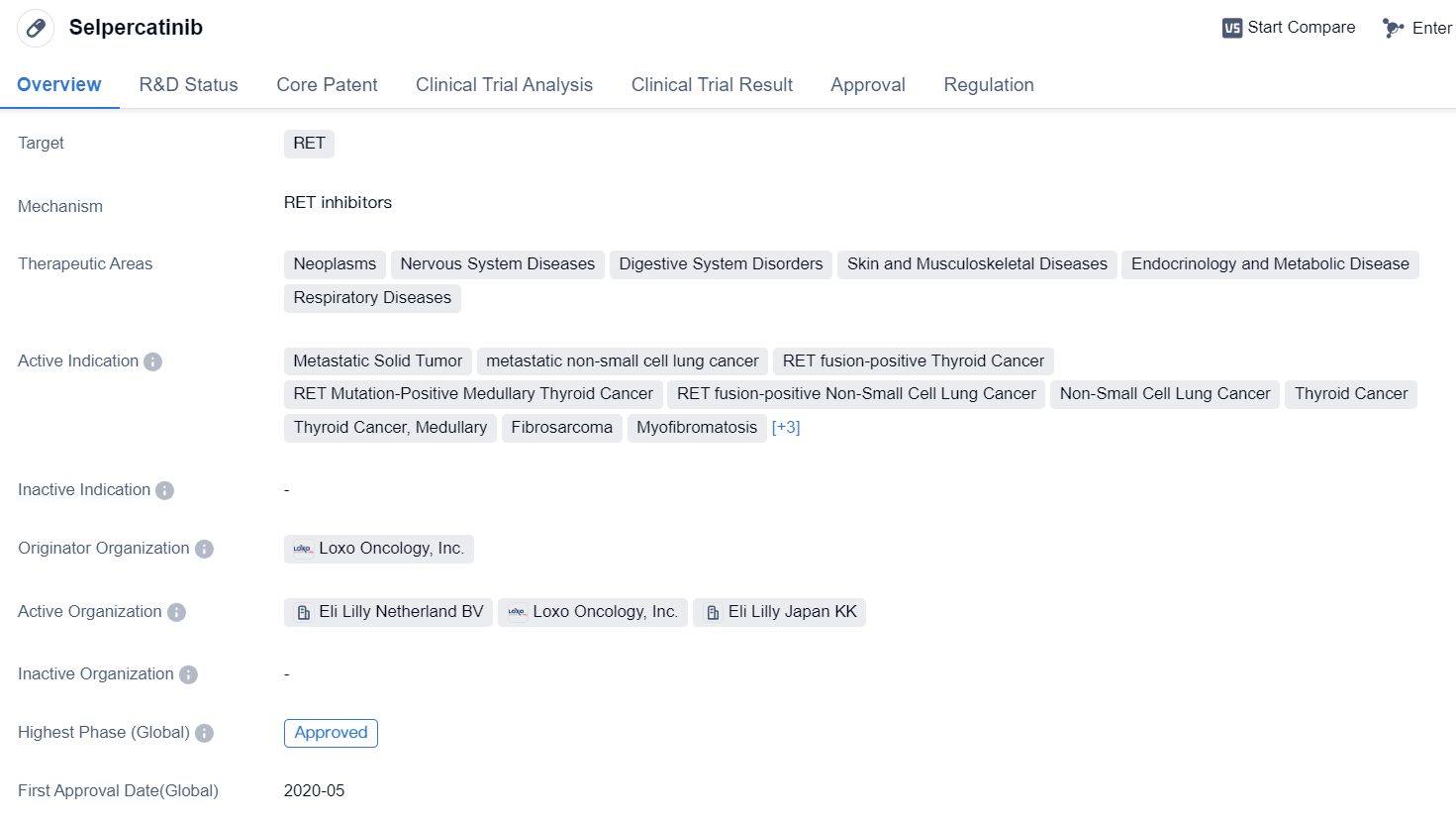
Highly Selective RET Inhibitors: Selpercatinib
Selpercatinibis a small molecule drug that falls under the category of biomedicine. It specifically targets the RET protein, which is involved in various diseases. The drug has shown potential therapeutic benefits in multiple therapeutic areas, including neoplasms, nervous system diseases, digestive system disorders, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, endocrinology and metabolic diseases, and respiratory diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Selpercatinib has been indicated for the treatment of several conditions, including metastatic solid tumors, metastatic NSCLC, RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer, RET mutation-positive medullary thyroid cancer, RET fusion-positive NSCLC, NSCLC, thyroid cancer (medullary and papillary), fibrosarcoma, myofibromatosis, colonic cancer, and central nervous system neoplasms.
The drug was developed by Loxo Oncology, Inc., an originator organization in the pharmaceutical industry. It has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials and has received approval both globally and in China. Selpercatinib obtained its first approval in the United States in May 2020.
In terms of regulation, Selpercatinib has undergone priority review, accelerated approval, and has been designated as an orphan drug. It has also been recognized as a breakthrough therapy, indicating its potential to provide significant advantages over existing treatment options.
In summary, Selpercatinib is a small molecule drug developed by Loxo Oncology, Inc. It targets the RET protein and has shown promising results in various therapeutic areas, including neoplasms and nervous system diseases. The drug has received approval in the United States and China, and its regulatory status includes priority review, accelerated approval, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough therapy designation.
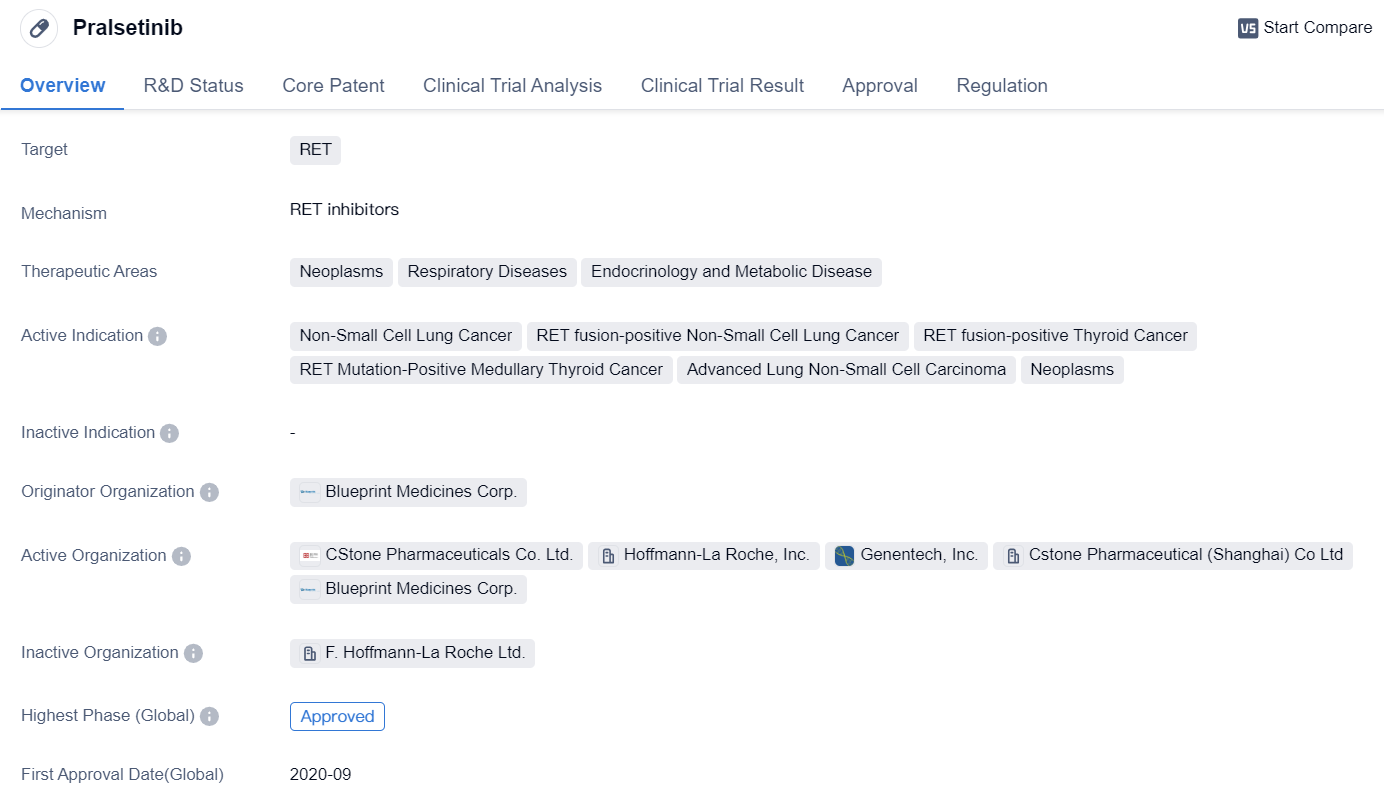
Pralsetinib
Pralsetinib is a small molecule drug that falls under the category of biomedicine. It specifically targets the RET protein, making it a promising therapeutic option for various medical conditions. The drug has shown potential in treating neoplasms, respiratory diseases, and endocrinology and metabolic diseases.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Pralsetinib has been approved for several indications, including NSCLC and RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer. It has also been found effective in treating RET mutation-positive medullary thyroid cancer and advanced lung non-small cell carcinoma. These approvals highlight the drug's versatility and potential to address different types of cancers.
The originator organization of Pralsetinib is Blueprint Medicines Corp., a pharmaceutical company known for its innovative approaches in drug development. The drug has reached the highest phase of approval globally and in China, indicating its advanced stage of development and potential for widespread use.
Pralsetinib received its first approval in the United States in September 2020. This signifies the drug's successful completion of clinical trials and meeting the necessary regulatory requirements for market authorization. The approval was granted after undergoing priority review, accelerated approval, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough therapy designation. These regulatory designations highlight the drug's potential to address unmet medical needs and expedite its availability to patients.
In summary, Pralsetinib is a small molecule drug developed by Blueprint Medicines Corp. It targets the RET protein and has shown promise in treating various types of cancers, including NSCLC and RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer. The drug has received approvals in the United States and China, with its first approval granted in September 2020. Pralsetinib has undergone priority review, accelerated approval, orphan drug designation, and breakthrough therapy designation, emphasizing its potential as an innovative and effective treatment option in the field of biomedicine.