Decoding Baicalin: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Baicalin's R&D Progress
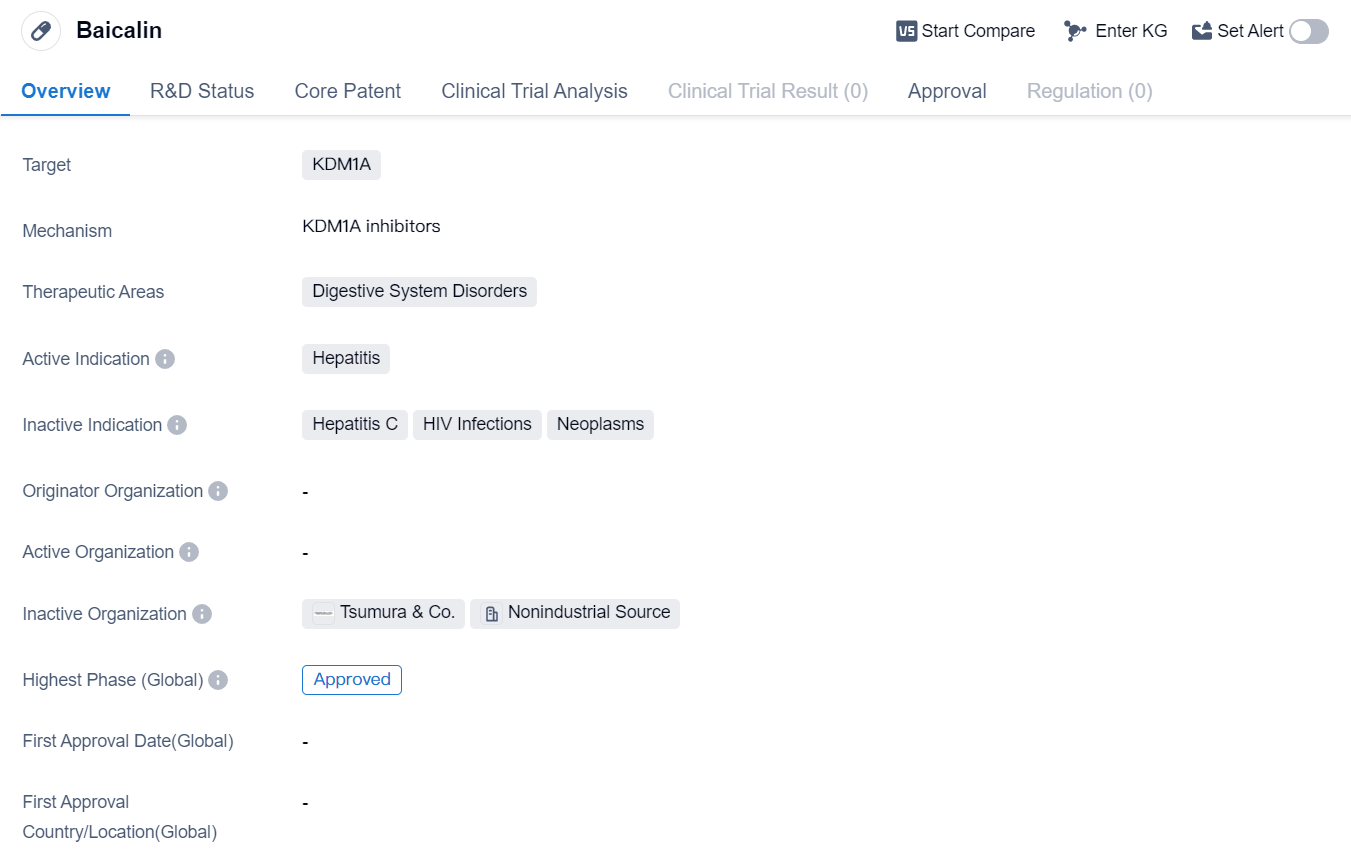
Baicalin is a small molecule drug that targets KDM1A and is primarily used in the treatment of digestive system disorders. Its active indication is hepatitis. Baicalin has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.
Baicalin is a small molecule drug, which means it is composed of low molecular weight compounds. This characteristic allows it to easily penetrate cell membranes and interact with specific targets within the body. In the case of Baicalin, its target is KDM1A, a protein involved in the regulation of gene expression. By targeting KDM1A, Baicalin may modulate gene expression and potentially provide therapeutic benefits in the treatment of digestive system disorders.
The therapeutic areas in which Baicalin is primarily used are digestive system disorders. This broad category encompasses a range of conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, including liver diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, and gastrointestinal infections. However, the active indication for Baicalin is specifically hepatitis, which refers to inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis can be caused by various factors, such as viral infections, alcohol abuse, or autoimmune diseases. Baicalin may be used to alleviate the symptoms of hepatitis and potentially improve liver function.
The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. This approval applies globally, suggesting that Baicalin has met the necessary regulatory requirements in both regions. The approval of Baicalin in China is particularly noteworthy, as it indicates recognition and acceptance of its efficacy and safety by the Chinese regulatory authorities.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Baicalin: KDM1A inhibitor
KDM1A inhibitors are a type of drug that target and inhibit the activity of the enzyme known as KDM1A. KDM1A, also called lysine-specific demethylase 1A, is an important enzyme involved in the regulation of gene expression through the removal of specific chemical groups called methyl groups from histone proteins. Histone proteins play a crucial role in packaging DNA and controlling gene activity. By inhibiting KDM1A, these inhibitors can modulate gene expression and potentially have therapeutic effects.
From a biomedical perspective, KDM1A inhibitors are being studied for their potential in cancer treatment. Abnormal gene expression is a hallmark of cancer, and targeting KDM1A can help regulate the expression of genes involved in tumor growth and progression. By inhibiting KDM1A, these inhibitors can potentially slow down or halt cancer cell growth.
It is important to note that KDM1A inhibitors are still under investigation and have not been widely approved for clinical use. Further research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness and safety profile.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Baicalin
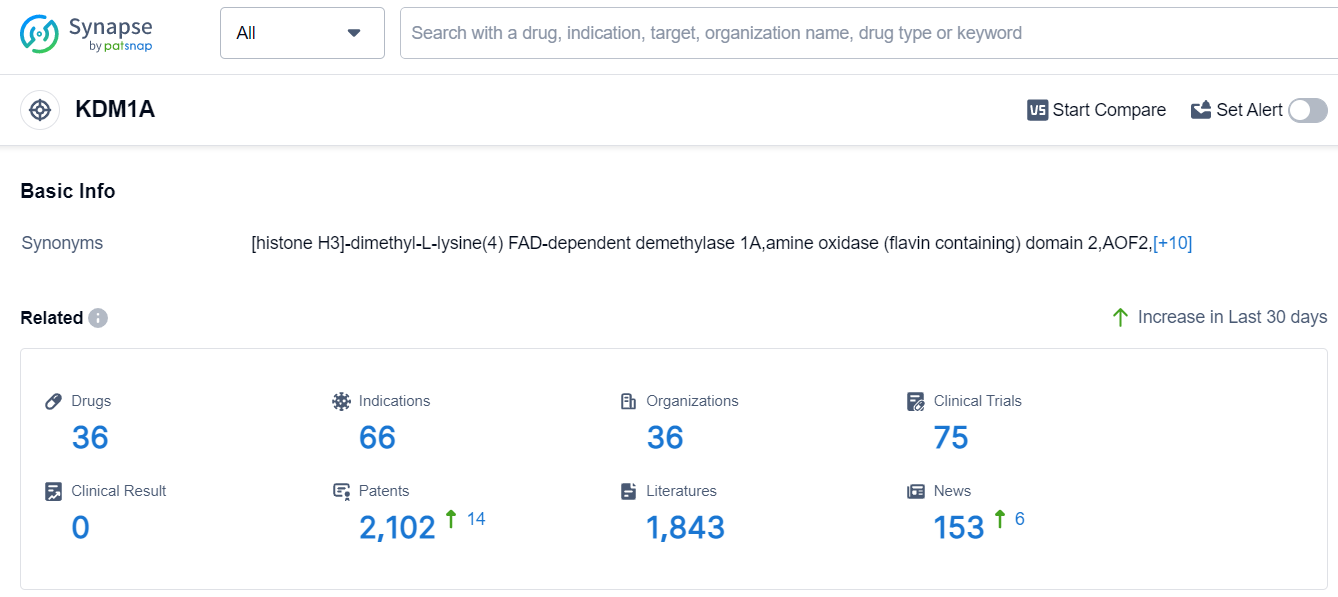
The analysis of the target KDM1A reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies actively involved in its development. Oryzon Genomics SA, Salarius Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Incyte Corp., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GSK Plc, Merck & Co., Inc., 4SC AG, Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Roche Holding AG, and other companies are growing rapidly in this field. The highest stage of development is Phase 2, indicating promising progress in clinical trials for various indications, including Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Small Cell Lung Cancer, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Neoplasms, and others. Small molecule drugs are the most rapidly progressing drug type, with a focus on Approved, Preclinical, and Inactive stages. The countries/locations developing fastest include China, United States, European Union, Spain, United Kingdom, and others. The progress in China suggests potential future developments in the country's pharmaceutical industry. Overall, the target KDM1A shows a promising competitive landscape and potential for future advancements in the pharmaceutical industry.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 9 Sep 2023, there are a total of 36 KDM1A drugs worldwide, from 36 organizations, covering 66 indications, and conducting 75 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Baicalin is a small molecule drug that targets KDM1A and is primarily used in the treatment of digestive system disorders, with a specific active indication for hepatitis. It has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally.Baicalin's approval in China highlights its potential significance in the Chinese pharmaceutical market. Further research and development may explore its efficacy in other therapeutic areas within the digestive system disorders category.