Deep Scientific Insights on Artesunate's R&D Progress
Artesunate's R&D Progress
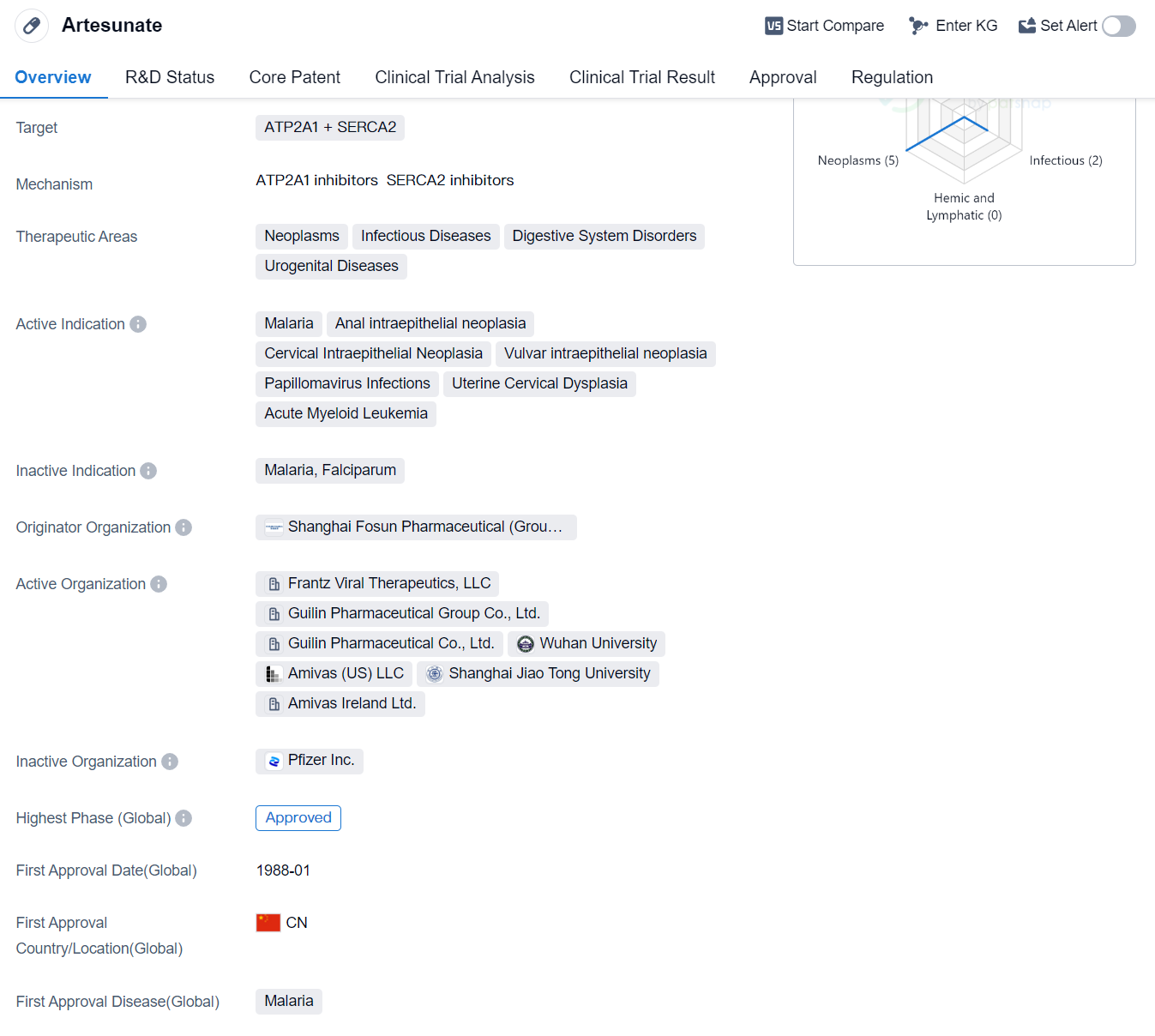
Artesunate is a small molecule drug that targets ATP2A1 and SERCA2. It has shown potential therapeutic benefits in various areas, including neoplasms, infectious diseases, digestive system disorders, and urogenital diseases. The drug has been indicated for the treatment of malaria, anal intraepithelial neoplasia, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, papillomavirus infections, uterine cervical dysplasia, and acute myeloid leukemia.
Artesunate was developed by Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical (Group) Co., Ltd., a prominent organization in the pharmaceutical industry. The drug has successfully completed the highest phase of development which is approved globally. Its first approval was granted in China in January 1988.
Regulatory authorities have recognized the potential of Artesunate and have granted it special designations, including Fast Track, Orphan Drug, and Breakthrough Therapy. These designations aim to expedite the development and approval process for drugs that address unmet medical needs or show significant advantages over existing treatments.
Artesunate's approval for the treatment of malaria is particularly noteworthy, as malaria is a major global health concern, especially in developing countries. The drug's effectiveness in combating malaria has made it an essential tool in the fight against this infectious disease.
In addition to its antimalarial properties, Artesunate has shown promise in the treatment of various neoplasms and urogenital diseases. Its potential to target ATP2A1 and SERCA2 opens up possibilities for further research and development in these therapeutic areas.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Artesunate:ATP2A1 inhibitor and SERCA2 inhibitor
ATP2A1 inhibitors, also known as SERCA2 inhibitors, are a type of drugs that target the ATP2A1 gene or the SERCA2 protein. ATP2A1 (ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 1) is a gene that encodes for the SERCA2 protein, which plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels within cells.
SERCA2 inhibitors work by blocking the activity of the SERCA2 protein, which is responsible for pumping calcium ions from the cytoplasm back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum or endoplasmic reticulum. By inhibiting SERCA2, these drugs disrupt the normal calcium cycling process, leading to an increase in cytoplasmic calcium levels.
In a biomedical perspective, ATP2A1 inhibitors or SERCA2 inhibitors have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications in various diseases. For example, in cardiac diseases such as heart failure, SERCA2 function is impaired, leading to calcium dysregulation and compromised cardiac muscle contraction. By inhibiting ATP2A1 or SERCA2, these inhibitors aim to restore calcium homeostasis and improve cardiac function.
Furthermore, ATP2A1 inhibitors have also been investigated as potential treatments for cancer. Calcium signaling pathways are involved in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. By targeting SERCA2, these inhibitors may disrupt calcium-dependent signaling pathways in cancer cells, potentially inhibiting tumor growth.
It is important to note that the use of ATP2A1 inhibitors or SERCA2 inhibitors is still under research and development, and their clinical applications are not yet fully established. Further studies are needed to determine their efficacy, safety, and potential side effects in different disease contexts.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Artesunate
The analysis of the current competitive landscape and future development of target ATP2A1 + SERCA2 reveals that Novartis AG, Shinpoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and China Resources Pharmaceutical Group Ltd. are the companies growing fastest under this target. The highest stage of development is seen in Novartis AG, with drugs in Phase 3 and Approved stages. The most common indication for drugs targeting ATP2A1 + SERCA2 is Malaria. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, indicating their potential effectiveness. China is actively involved in the development of drugs for this target, with the highest number of drugs in the Approved stage. Overall, the analysis suggests a promising future for the development of drugs targeting ATP2A1 + SERCA2, particularly in the treatment of Malaria and other relevant indications.
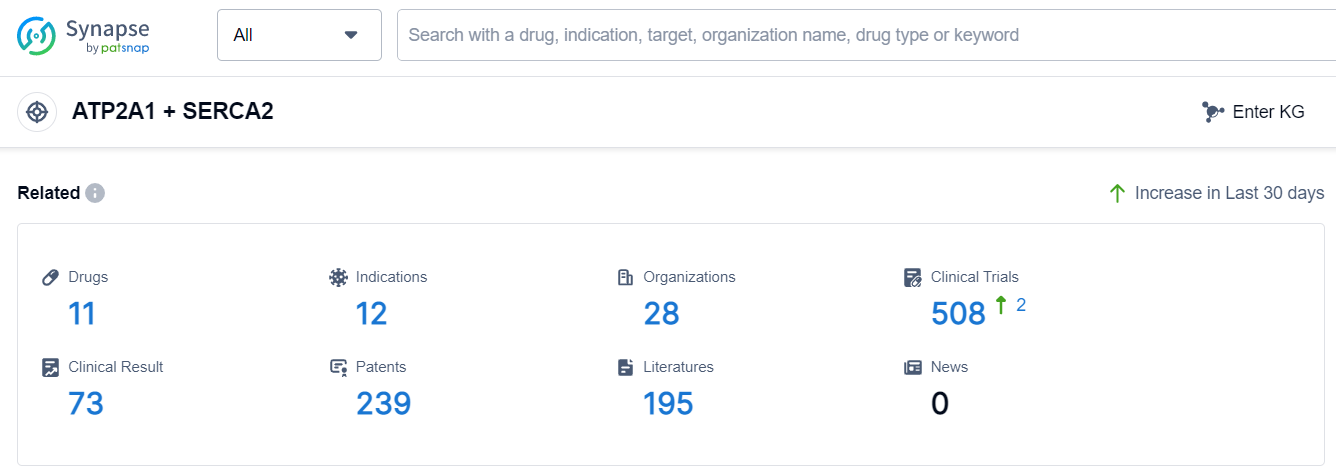
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 11 ATP2A1 + SERCA2 drugs worldwide, from 28 organizations, covering 12 indications, and conducting 508 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Artesunate's approval, its multiple indications, and the recognition it has received from regulatory authorities highlight its potential as a valuable drug in the field of biomedicine. Its success in treating malaria and its potential in addressing other diseases make it an important asset in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to improve global health outcomes.