An In-depth Analysis of Labetalol Hydrochloride's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Labetalol Hydrochloride's R&D Progress
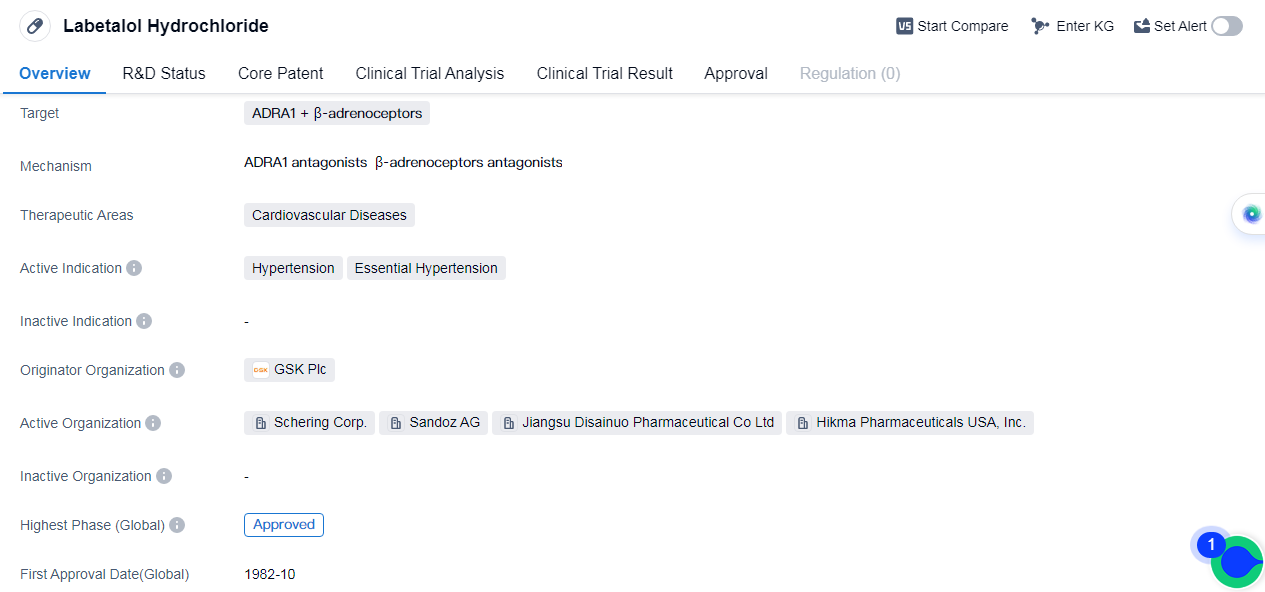
Labetalol Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors. It is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, specifically hypertension and essential hypertension. The drug was first approved in Japan in October 1982 and has since received approval globally.
The originator organization of Labetalol Hydrochloride is GSK Plc, a renowned pharmaceutical company. The drug has reached the highest phase of development, this indicates that it has successfully undergone rigorous testing and clinical trials to demonstrate its safety and efficacy.
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects a significant portion of the global population. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Labetalol Hydrochloride works by blocking the action of certain receptors, namely ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors. By doing so, it helps to relax and widen the blood vessels, reducing the pressure exerted on the arterial walls and ultimately lowering blood pressure.
Essential hypertension refers to high blood pressure that has no identifiable cause. It is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. Labetalol Hydrochloride has been proven effective in treating essential hypertension, providing patients with a reliable option to control their blood pressure and reduce the associated risks.
The approval of Labetalol Hydrochloride in Japan in 1982 marked a significant milestone in the treatment of hypertension. Since then, it has gained approval in other countries.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Labetalol Hydrochloride: ADRA1 antagonists and β-adrenoceptors antagonists
ADRA1 antagonists are drugs that block the activity of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. These receptors are found in various tissues and organs including blood vessels, smooth muscles, and the central nervous system. By blocking the action of these receptors, ADRA1 antagonists can inhibit the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine, which are neurotransmitters that bind to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors.
From a biomedical perspective, ADRA1 antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. By blocking the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in blood vessels, these drugs can cause vasodilation, leading to a decrease in blood pressure. In the case of benign prostatic hyperplasia, ADRA1 antagonists can relax the smooth muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, relieving urinary symptoms.
β-adrenoceptor antagonists, also known as beta blockers, are drugs that block the activity of beta-adrenergic receptors. These receptors are found in various tissues, including the heart, lungs, and blood vessels. By blocking the action of these receptors, β-adrenoceptor antagonists can inhibit the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are neurotransmitters that bind to beta-adrenergic receptors.
From a biomedical perspective, β-adrenoceptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as hypertension, angina, and certain heart rhythm disorders. By blocking the beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart, these drugs can reduce heart rate, decrease contractility, and lower blood pressure. This can help in managing conditions where excessive sympathetic nervous system activity is detrimental.
In summary, ADRA1 antagonists and β-adrenoceptor antagonists are drugs that block the activity of specific receptors in the body. ADRA1 antagonists target alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, while β-adrenoceptor antagonists target beta-adrenergic receptors. These drugs have various clinical applications, particularly in the treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Labetalol Hydrochloride
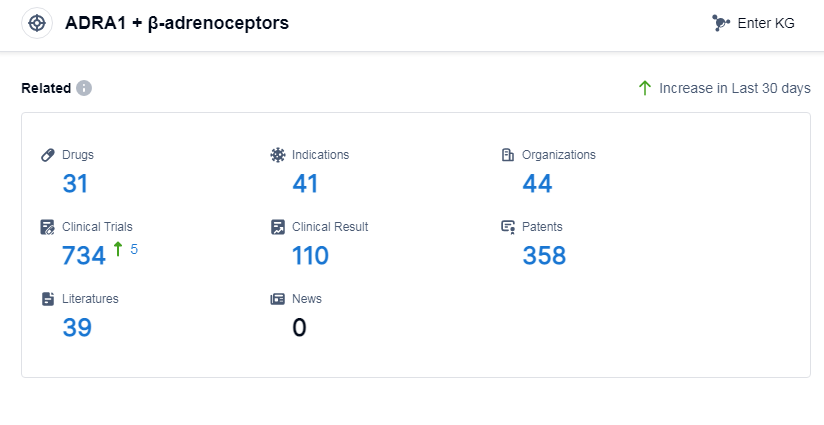
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 6 Sep 2023, there are a total of 31 ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors drugs worldwide, from 44 organizations, covering 41 indications, and conducting 734 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the data provided, the current competitive landscape of drugs targeting ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors is characterized by the involvement of multiple companies, with Merck & Co., Inc., Sanofi, GSK Plc, Novartis AG, and Organon & Co. leading in terms of R&D progress. The most common indications for approved drugs include hypertension, nasal obstruction, atrial fibrillation, and essential hypertension. Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types progressing rapidly under this target. China leads the way in terms of drug development, and get significant progress. Overall, the target ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors presents a competitive landscape with potential for future development and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Labetalol Hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by GSK Plc that targets ADRA1 and β-adrenoceptors. It is primarily used in the treatment of hypertension and essential hypertension. With its approval in multiple countries, it has become a widely recognized and effective medication for managing cardiovascular diseases.