Decoding Metyrosine: A Comprehensive Study of its R&D Trends and Mechanism on Drug Target
Metyrosine's R&D Progress
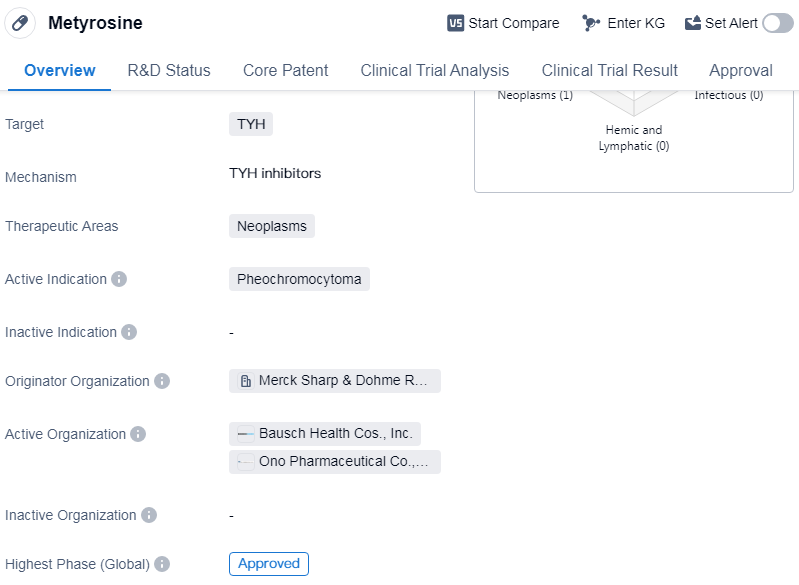
Metyrosine is a small molecule drug that targets the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TYH). It is primarily used in the treatment of neoplasms, specifically pheochromocytoma. Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor that develops in the adrenal glands, causing the release of excessive amounts of adrenaline and noradrenaline, leading to high blood pressure and other symptoms.
Metyrosine was first approved for use in the United States in October 1979. It was developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Research Laboratories, a renowned pharmaceutical organization. The drug has since received approval in other countries as well, although the specific dates and locations of these approvals are not provided.
As a small molecule drug, metyrosine is designed to interact with specific molecular targets in the body, in this case, TYH. By inhibiting the activity of TYH, metyrosine reduces the production of adrenaline and noradrenaline, helping to control the symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma.
The approval of metyrosine for the treatment of pheochromocytoma highlights its efficacy and safety profile. The fact that it has reached the highest phase of development, which is approved, suggests that it has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation to demonstrate its therapeutic benefits and minimal side effects.
Since its approval, metyrosine has likely been prescribed to patients with pheochromocytoma to help manage their condition. It is important to note that the information provided does not specify whether metyrosine is still actively marketed or if there are any generic versions available.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Metyrosine: TYH inhibitors
TYH inhibitors are a type of drug that inhibit the activity of the enzyme TYH. Tyrosine hydroxylase is an important enzyme involved in the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. By inhibiting TYH, these inhibitors can reduce the production of these neurotransmitters.
From a biomedical perspective, TYH inhibitors are primarily used in the treatment of conditions associated with excessive neurotransmitter production or activity, such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and certain types of hypertension. By reducing the levels of neurotransmitters, TYH inhibitors can help alleviate the symptoms of these conditions.
It is important to note that TYH inhibitors should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can have potential side effects and interactions with other medications. The specific mechanism of action and dosage of TYH inhibitors may vary depending on the specific drug and the condition being treated.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Metyrosine
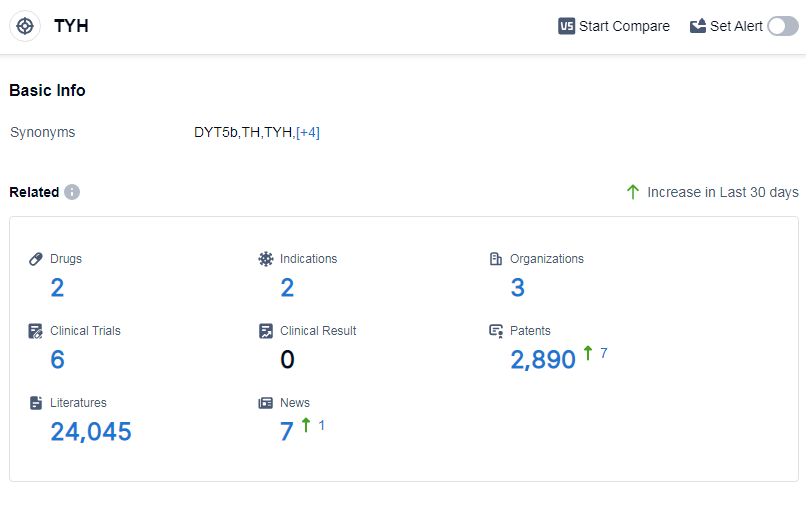
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 2 TYH drugs worldwide, from 3 organizations, covering 2 indications, and conducting 6 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape for target TYH shows that Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bausch Health Cos., Inc., and Yamo Pharmaceuticals LLC are the key players in terms of growth and development. Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Bausch Health Cos., Inc. have already received approval for their drugs, indicating successful R&D progress. The indications that have been approved under the target TYH include pheochromocytoma and autistic disorder. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, suggesting intense competition in the market. The United States and Japan are the leading countries/locations in terms of development for this target. However, there is no specific information provided regarding progress in China for target TYH. Overall, the analysis indicates a promising competitive landscape and future development potential for target TYH in the pharmaceutical industry.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Metyrosine is a small molecule drug developed by Merck Sharp & Dohme Research Laboratories. It is approved for the treatment of pheochromocytoma, a rare tumor that affects the adrenal glands. By targeting TYH, metyrosine helps regulate the production of adrenaline and noradrenaline, providing relief from the symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma. Its approval in 1979 in the United States signifies its efficacy and safety in treating this condition.