Deep Scientific Insights on Mexazolam's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Mexazolam's R&D Progress
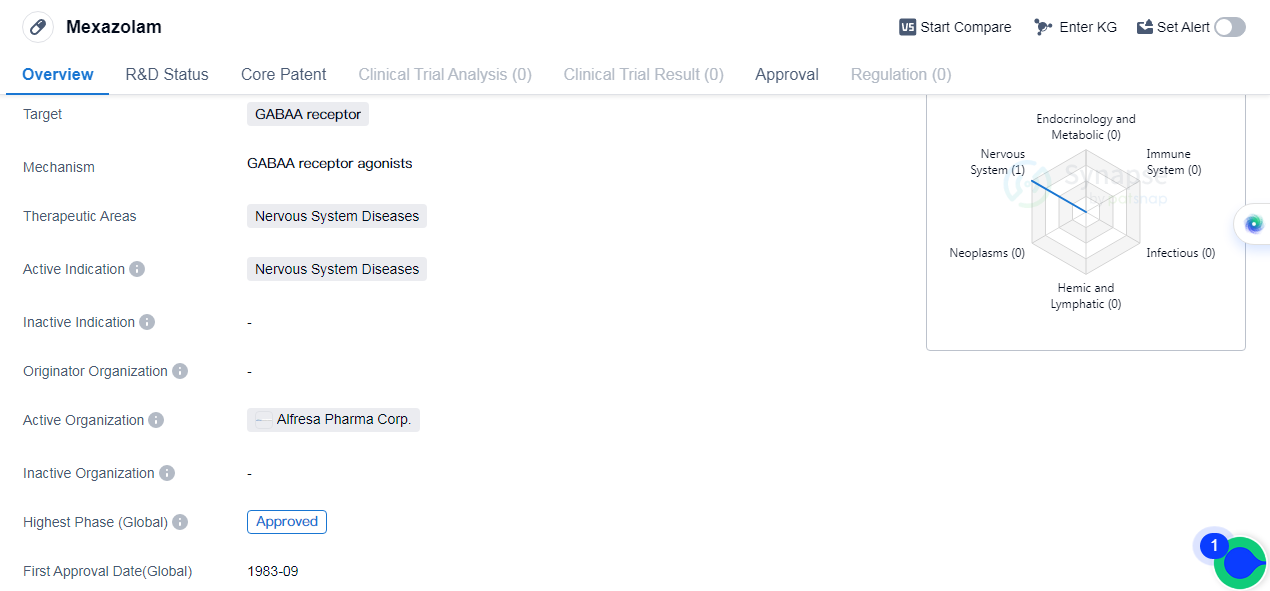
Mexazolam is a small molecule drug that targets the gamma-aminobutyric acid type-A (GABAA)receptor and is primarily used in the treatment of nervous system diseases. It was first approved in Japan in September 1983 and has since received global approval.
As a small molecule drug, Mexazolam is composed of low molecular weight compounds that can easily penetrate cell membranes. This allows for efficient absorption and distribution throughout the body, making it an effective treatment option for nervous system diseases.
The drug's primary target is the GABAA receptor, which is a type of receptor found in the central nervous system. Activation of this receptor leads to an increase in inhibitory neurotransmission, resulting in sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant effects. Mexazolam's ability to target this receptor makes it particularly useful in the treatment of nervous system diseases.
Nervous system diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Examples of such diseases include anxiety disorders, insomnia, epilepsy, and muscle spasms. Mexazolam's approval for use in nervous system diseases suggests that it has demonstrated efficacy and safety in treating these conditions.
The fact that Mexazolam has reached the highest phase of approval indicates that it has undergone extensive clinical trials and has been deemed safe and effective for use in patients. This is a significant milestone in the drug development process and demonstrates the drug's potential therapeutic value.
It is worth noting that Mexazolam's first approval was in Japan, indicating that it was initially developed and tested in this country. This suggests that the drug may have been specifically tailored to address the needs of the Japanese population or that the Japanese pharmaceutical market was the primary target for its commercialization.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Mexazolam: GABAA Receptor Agonists
GABAA receptor agonists are a type of drug that binds to and activates the GABAA receptors in the brain. GABAA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. When GABAA receptors are activated by agonists, such as certain drugs, they enhance the inhibitory effects of GABA, leading to a decrease in neuronal excitability.
From a biomedical perspective, GABAA receptor agonists are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, seizures, and muscle spasms. By enhancing the inhibitory actions of GABA, these drugs help to reduce excessive neuronal activity and promote relaxation and sedation.
It's important to note that the use of GABAA receptor agonists should be done under medical supervision, as they can have sedative and potentially addictive effects. Additionally, different GABAA receptor agonists may have varying selectivity and affinity for different subtypes of GABAA receptors, which can influence their specific therapeutic effects and potential side effects.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Mexazolam
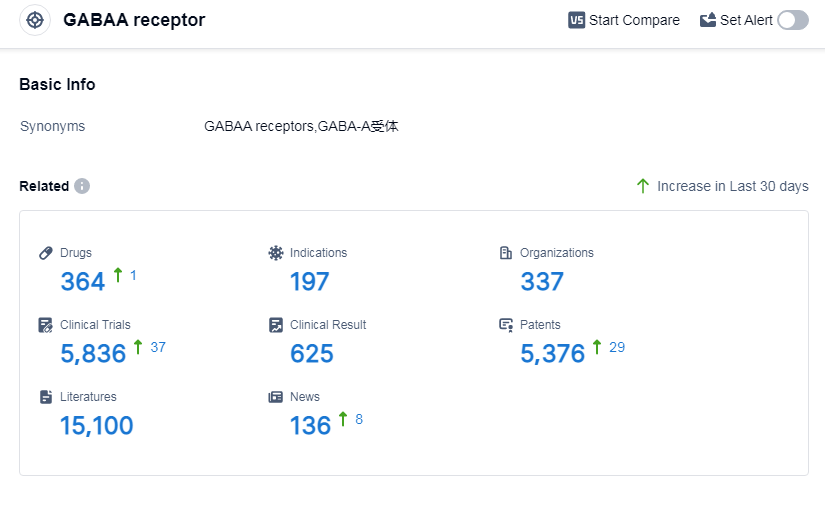
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 7 Sep 2023, there are a total of 364 GABAA receptor drugs worldwide, from 337 organizations, covering 197 indications, and conducting 5836 clinical trials.
The target GABAA receptor in the pharmaceutical industry has seen significant growth and development. Pfizer Inc., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. are some of the companies growing fastest under this target. The highest stage of development is the approved phase, with drugs targeting indications such as sleep initiation and maintenance disorders, anesthesia, anxiety, epilepsy, and seizures. Small molecule drugs are progressing most rapidly, indicating intense competition in the market. China has shown significant progress in the development of drugs targeting the GABAA receptor. Overall, the competitive landscape for the target GABAA receptor is dynamic, with potential for future growth and innovation.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Mexazolam is a small molecule drug that targets the GABAA receptor and is approved for use in nervous system diseases. Its approval in Japan in 1983 marked its first global approval, indicating its efficacy and safety in treating these conditions. Mexazolam's development and approval highlight its potential as a therapeutic option for patients suffering from nervous system diseases.