Deep Scientific Insights on Carbidopa/Levodopa's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Carbidopa/Levodopa's R&D Progress
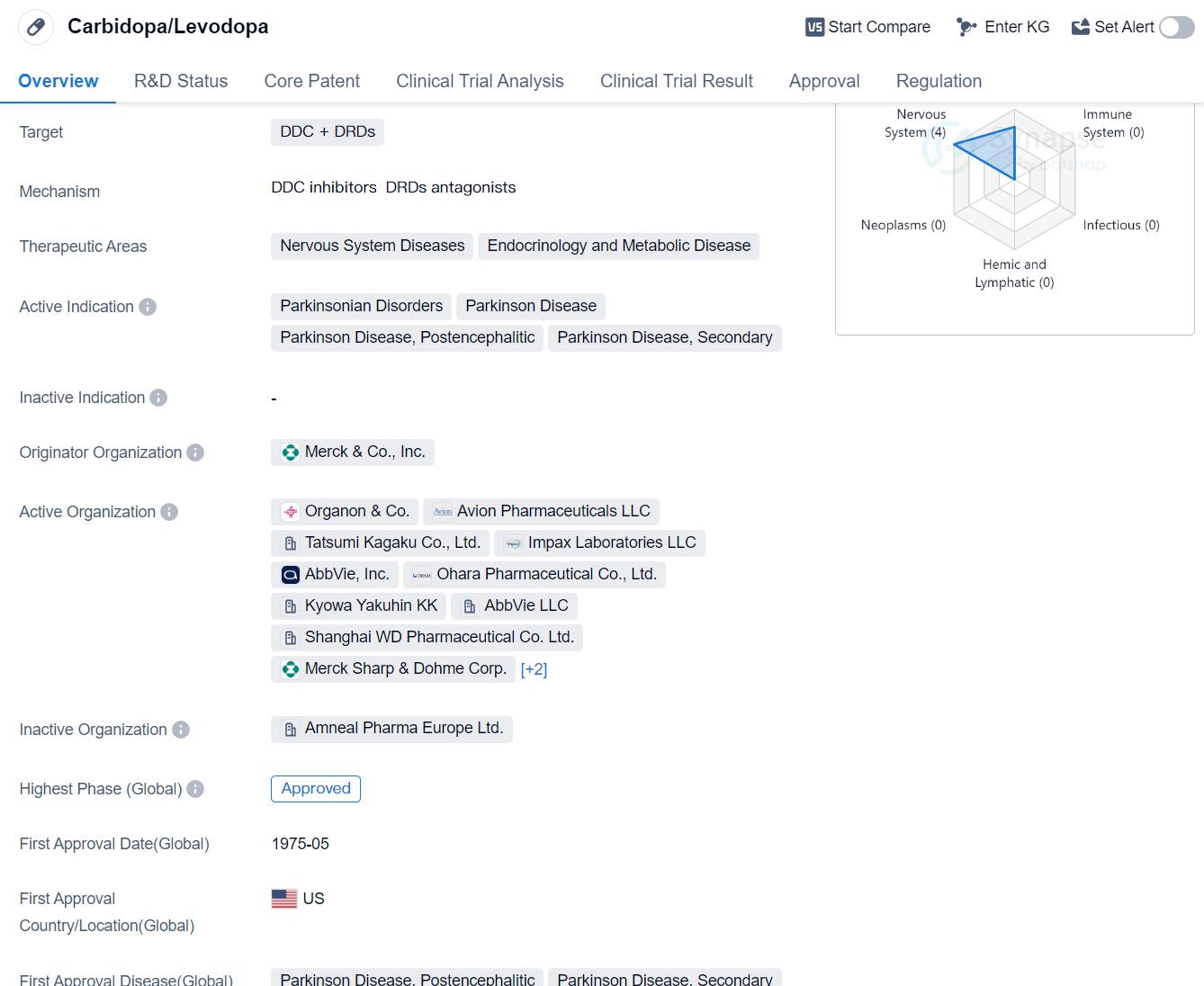
Carbidopa/Levodopa is a small molecule drug used in the treatment of various nervous system diseases, particularly Parkinson's disease. It targets two key components, DDC (dopa decarboxylase) and DRDs (dopamine receptors), to alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. The drug has been approved for use in the global market.
The therapeutic areas in which Carbidopa/Levodopa is primarily used include nervous system diseases, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases. Parkinsonian disorders, Parkinson's disease, Parkinson's disease postencephalitic, and secondary Parkinson's disease are the active indications for this drug. These conditions are characterized by the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain, leading to motor and non-motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and impaired balance.
Merck & Co., Inc. is the originator organization of Carbidopa/Levodopa. The drug received its first approval in the United States in May 1975, making it a well-established treatment option for Parkinson's disease and related disorders. It has since gained global recognition and approval.
Carbidopa/Levodopa has been regulated under the Fast Track designation, which expedites the development and review process for drugs addressing unmet medical needs. Additionally, it has been designated as an orphan drug, indicating its use in the treatment of rare diseases or conditions.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Carbidopa/Levodopa: DDC inhibitor and DRDs antagonist
DDC inhibitors and DRDs antagonists are terms related to biomedicine, specifically to the field of pharmacology and neuroscience.
DDC inhibitors refer to drugs or compounds that inhibit the activity of the enzyme DOPA decarboxylase (DDC). DDC is responsible for the conversion of the amino acid L-DOPA to dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in various physiological processes. By inhibiting DDC, these inhibitors can reduce the production of dopamine, which can be beneficial in certain conditions such as Parkinson's disease, where excessive dopamine levels contribute to symptoms. DDC inhibitors are commonly used in combination with L-DOPA therapy to enhance its effectiveness and reduce side effects.
DRDs antagonists, on the other hand, refer to drugs or compounds that block the activity of dopamine receptors (DRDs). Dopamine receptors are proteins located on the surface of cells that bind to dopamine and mediate its effects. By antagonizing or blocking these receptors, DRDs antagonists can inhibit the actions of dopamine in the body. This can be useful in various conditions where excessive dopamine signaling is problematic, such as schizophrenia or certain movement disorders. DRDs antagonists are commonly used as antipsychotic medications to alleviate symptoms associated with excessive dopamine activity.
In summary, DDC inhibitors inhibit the enzyme responsible for dopamine production, while DRDs antagonists block the receptors that mediate dopamine's effects. Both these approaches are utilized in biomedicine to modulate dopamine levels and activity for therapeutic purposes.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Carbidopa/Levodopa
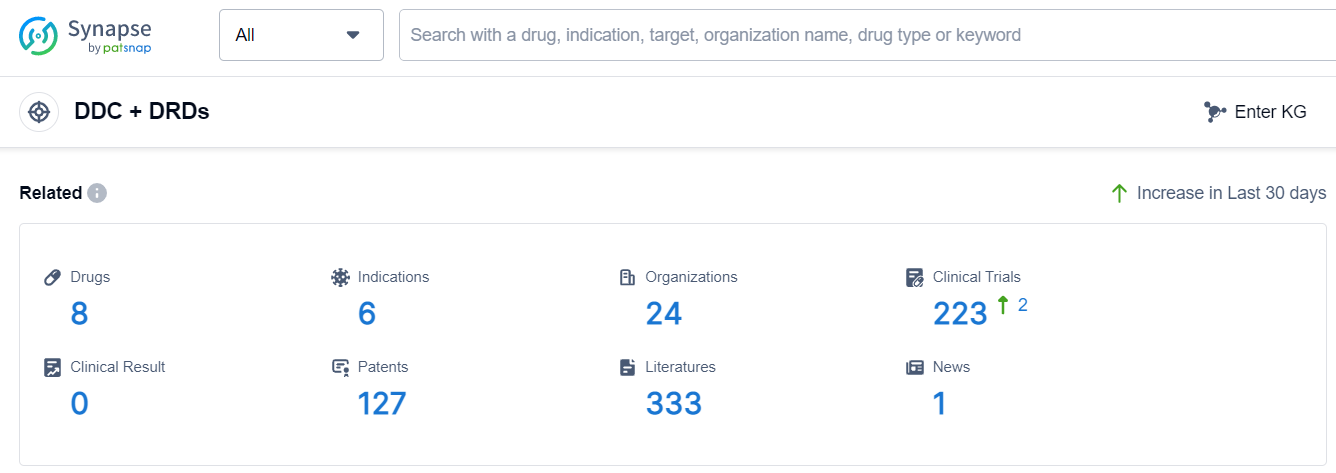
The current competitive landscape of the target DDC + DRDs is characterized by multiple companies actively involved in R&D and clinical trials. Novartis AG, Orion Pharma Ltd., Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Inc., AbbVie, Inc., and other companies are leading in terms of growth and development. The highest stage of development is the Approved phase, indicating that several drugs are close to commercial availability. The indications with approved drugs include Parkinson Disease, Parkinson Disease, Postencephalitic, Parkinsonian Disorders, Parkinson Disease, Secondary, Spinal Cord Injuries, and Multiple Sclerosis. Small molecule drugs are progressing rapidly, with a significant number of drugs in the Approved phase. The United States, China, European Union, and Japan are the countries/locations with the highest number of approved drugs, with China showing notable progress. Overall, the target DDC + DRDs present a promising future for the pharmaceutical industry, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on addressing unmet medical needs in various indications.
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 16 Sep 2023, there are a total of 8 DDC + DRDs drugs worldwide, from 24 organizations, covering 6 indications, and conducting 223 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Carbidopa/Levodopa is a small molecule drug developed by Merck & Co., Inc. It targets DDC and DRDs to treat various nervous system diseases, including Parkinson's disease. The drug has been approved in the global market,with its first approval dating back to 1975 in the United States. Carbidopa/Levodopa is regulated under Fast Track and orphan drug designations, highlighting its importance in addressing unmet medical needs and rare conditions.