Deep Scientific Insights on Dopamine hydrochloride's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Dopamine hydrochloride's R&D Progress
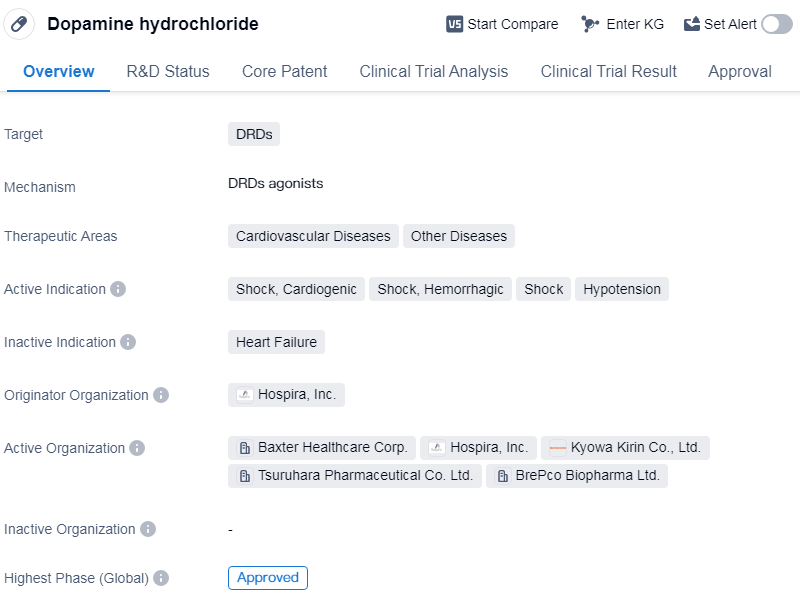
Dopamine hydrochloride is a small molecule drug that targets dopamine receptors(DRDs). It is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and other related conditions. The active indications for this drug include shock, specifically cardiogenic shock, hemorrhagic shock, and hypotension.
The drug was developed by Hospira, Inc., a pharmaceutical company. It has reached the highest phase of approval globally, indicating its established safety and efficacy profile. The first approval for dopamine hydrochloride was granted in February 1974 in the United States.
Dopamine hydrochloride is classified as an orphan drug, which means it is intended to treat rare diseases or conditions that affect a small number of patients. This regulatory designation provides certain incentives to pharmaceutical companies to develop drugs for these specific indications.
The therapeutic areas of cardiovascular diseases and shock highlight the importance of dopamine hydrochloride in managing critical conditions that affect the heart and blood circulation. Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, while hemorrhagic shock is caused by severe blood loss. Hypotension refers to low blood pressure, which can lead to inadequate blood flow to vital organs.
As a small molecule drug, dopamine hydrochloride is likely to have a well-defined chemical structure and can be easily synthesized. This characteristic may contribute to its widespread availability and use in clinical practice.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Dopamine hydrochloride: DRDs Agonists
DRDs agonists refer to drugs or compounds that act as agonists at the DRDs. Dopamine receptors are a class of G-protein coupled receptors found in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. They play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including motor control, reward, mood regulation, and hormone release.
DRDs agonists are substances that bind to and activate these dopamine receptors, mimicking the effects of dopamine. By stimulating the receptors, these agonists can modulate dopamine signaling pathways and exert their pharmacological effects. The specific subtype of dopamine receptor targeted by the agonist determines the physiological response produced.
In the field of biomedicine, DRDs agonists are of particular interest in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. For example, in Parkinson's disease, which is characterized by a deficiency of dopamine, DRDs agonists can help alleviate motor symptoms by compensating for the reduced dopamine levels. They can also be used in the management of conditions like restless leg syndrome and schizophrenia.
It's important to note that different DRDs subtypes have distinct functions and distributions in the brain and body. Therefore, the choice of a specific DRDs agonist depends on the desired therapeutic outcome and the receptor subtype involved. The development and use of DRDs agonists require careful consideration of their pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and potential side effects to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Dopamine hydrochloride
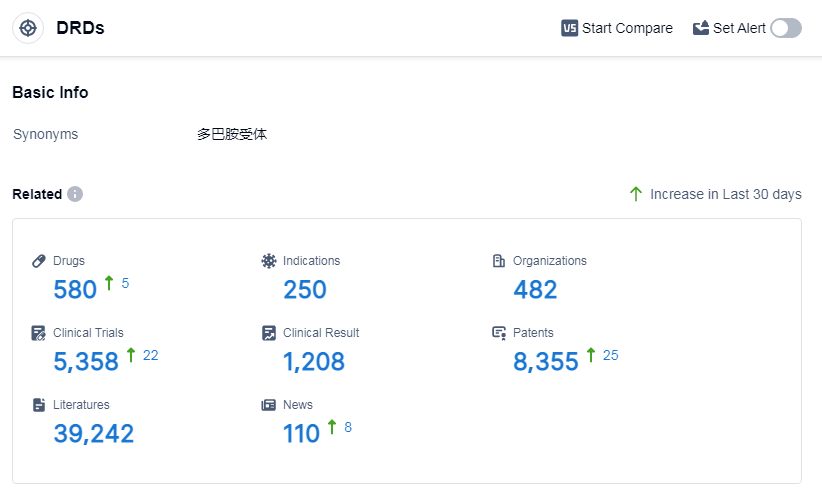
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 14 Sep 2023, there are a total of 580 DRDs drugs worldwide, from 482 organizations, covering 250 indications, and conducting 5358 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape of target DRDs is characterized by the presence of several leading pharmaceutical companies, such as Johnson & Johnson, Novartis AG, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corp., and Sanofi. These companies have shown significant progress in the development of drugs, with a focus on indications like schizophrenia, Parkinson'sdisease, bipolar disorder, and depressive disorder.
Small molecule drugs dominate the drug types progressing most rapidly under the current targets, indicating their continued importance in the pharmaceutical industry. Biosimilars do not appear to be ranking high, suggesting less intense competition around innovative biological drugs.
China, the United States, and Japan are the countries/locations developing fastest under the current targets. China, in particular, has shown significant progress with the highest number of approved drugs.
Overall, the target DRDs present a competitive landscape with diverse companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations. The future development of target DRDs will likely continue to focus on these areas, with an emphasis on innovation, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In summary, Dopamine hydrochloride is a small molecule drug developed by Hospira, Inc. It targets DRDs and is primarily used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and shock. It was first approved in the United States in 1974 and has received approval in the global markets. The drug's orphan drug status indicates its potential to address rare conditions, and its active indications include cardiogenic shock, hemorrhagic shock, and hypotension.