An In-depth Analysis of Doravirine's R&D Progress and Mechanism of Action on Drug Target
Doravirine's R&D Progress
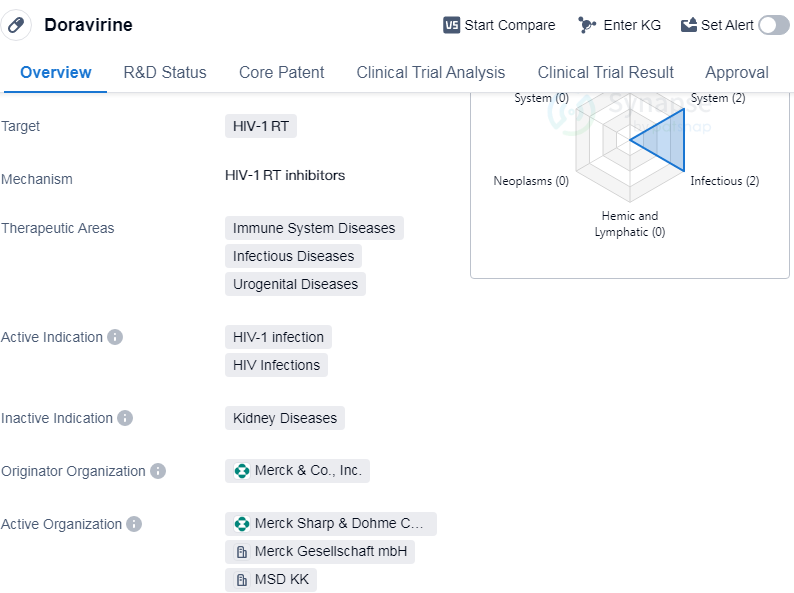
Doravirine is a small molecule drug that targets HIV-1 RT, making it a potential treatment for HIV-1 infection and HIV infections. It falls under the therapeutic areas of immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and urogenital diseases. The drug was developed by Merck & Co., Inc., a renowned pharmaceutical company.
Doravirine has successfully completed the highest phase of clinical trials and has received approval globally. The drug was first approved in the United States in August 2018, marking a significant milestone in the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
As a small molecule drug, Doravirine is designed to inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme of the HIV-1 virus. By targeting this enzyme, the drug aims to prevent the replication of the virus and reduce its impact on the immune system. This mechanism of action makes Doravirine a promising option for patients suffering from HIV-1 infection.
The approval of Doravirine signifies its safety and efficacy in treating HIV-1 infection. It provides healthcare professionals and patients with an additional treatment option to manage the disease. The therapeutic areas of immune system diseases, infectious diseases, and urogenital diseases encompass a wide range of conditions. Doravirine's approval in these areas suggests its potential to address not only HIV-1 infection but also other related diseases within these therapeutic categories.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Doravirine: HIV-1 RT inhibitors
HIV-1 RT inhibitors are a class of drugs used in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. HIV-1 refers to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1, which is the most common and pathogenic strain of the virus. RT stands for reverse transcriptase, which is an enzyme produced by the virus that plays a crucial role in its replication process.
HIV-1 RT inhibitors are designed to inhibit the activity of reverse transcriptase, thereby preventing the virus from replicating and spreading in the body. These inhibitors can be classified into two main types: nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs).
NRTIs are structurally similar to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. When incorporated into the viral DNA chain during replication, they disrupt the normal structure and function of the DNA, preventing further replication. Examples of NRTIs include zidovudine (AZT), lamivudine (3TC), and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF).
NNRTIs, on the other hand, bind directly to the reverse transcriptase enzyme and inhibit its activity. Unlike NRTIs, they do not require activation by cellular enzymes. Examples of NNRTIs include efavirenz, nevirapine, and rilpivirine.
By targeting reverse transcriptase, HIV-1 RT inhibitors help to reduce the viral load in the body and slow down the progression of HIV infection. They are often used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs as part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) to effectively manage HIV-1 infection and improve the patient's immune function.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Doravirine
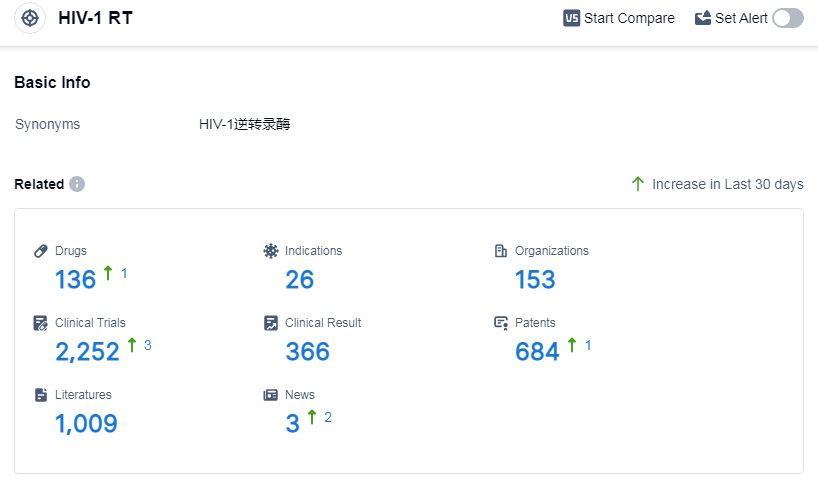
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 13 Sep 2023, there are a total of 136 HIV-1 RT drugs worldwide, from 153 organizations, covering 26 indications, and conducting 2252 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the data provided, Gilead Sciences, Inc. is the company with the highest number of drugs under the target HIV-1 RT. The indications of HIV Infections and HIV-1 infection have the highest number of approved drugs. Small molecule drugs are the most common drug type under development. The European Union, United States, China, and Japan are the countries/locations with the highest number of drugs under development. Overall, the target HIV-1 RT has a competitive landscape with multiple companies, indications, drug types, and countries/locations involved in research and development.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Doravirine's approval as a small molecule drug targeting HIV-1 RT marks a significant advancement in the field of biomedicine.