Deep Scientific Insights on interferon beta-1b's R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Target
Interferon beta-1b's R&D Progress
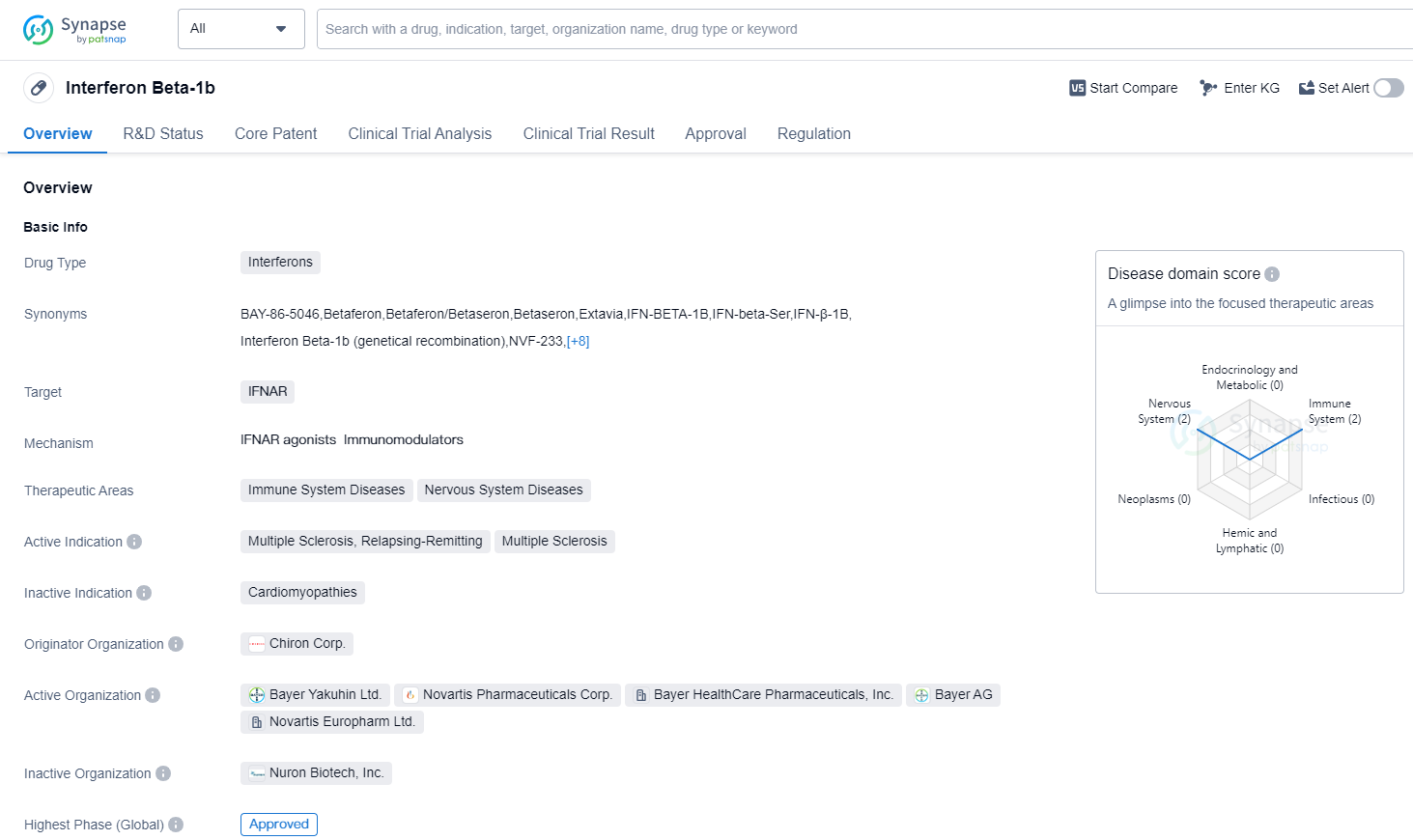
Interferon Beta-1b is a drug classified under the category of Interferons, which are proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system's response to viral infections and other diseases. The drug specifically targets IFNAR, which stands for Interferon Alpha and Beta Receptor Subunit 1. This receptor is involved in the signaling pathway that activates the immune response mediated by interferons.
The therapeutic areas in which Interferon Beta-1b is used are immune system diseases and nervous system diseases. It has been primarily indicated for the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS), specifically the relapsing-remitting form of the disease. MS is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, leading to inflammation and damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers.
Interferon Beta-1b was developed by Chiron Corp., a pharmaceutical company that has been involved in the research and development of various biopharmaceutical products. The highest R&D phase of this drug is approved. It received its first approval in the United States in July 1993, making it one of the early treatments available for MS patients.
👇Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for interferon beta-1b: IFNAR agonists Immunomodulators
IFNAR agonists are a type of immunomodulator. Immunomodulators are substances that can modify or regulate the immune system's response. In the case of IFNAR agonists, they specifically target and activate the IFNAR (interferon alpha/beta receptor) on immune cells.
The IFNAR is a receptor found on the surface of various immune cells, including dendritic cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells. When IFNAR agonists bind to this receptor, they trigger a signaling cascade that leads to the production and release of interferon-alpha and interferon-beta.
Interferons are signaling proteins that play a crucial role in immune responses. They can enhance the activity of immune cells, promote the production of other immune molecules, and help regulate inflammation. By activating the IFNAR, IFNAR agonists can amplify the immune response and promote antiviral, antitumor, and immunomodulatory effects.
IFNAR agonists have shown potential in the treatment of various diseases, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain types of cancer. By modulating the immune system, these agonists can enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms and potentially improve disease outcomes.
It's important to note that the specific mechanisms and effects of IFNAR agonists may vary depending on the context and the specific disease being targeted. Further research and clinical studies are necessary to fully understand their therapeutic potential and optimize their use in biomedicine.
Drug Target R&D Trends for interferon beta-1b
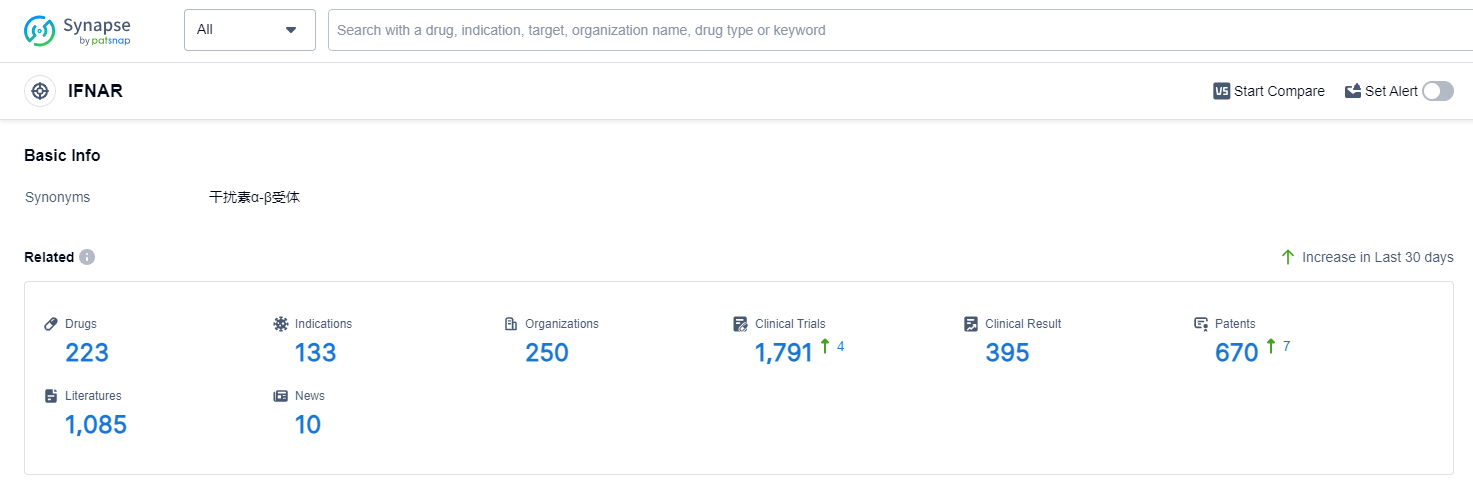
IFNAR, or interferon alpha/beta receptor, plays a crucial role in the human body's immune response. It is a receptor protein found on the surface of cells and is responsible for binding to interferon-alpha and interferon-beta, which are important signaling molecules involved in antiviral defense. When IFNAR binds to these interferons, it triggers a cascade of cellular responses that help to inhibit viral replication, activate immune cells, and enhance the body's ability to fight off infections. Understanding the role of IFNAR is essential in developing therapies that target the immune system and combat viral diseases. According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 12 Sep 2023, there are a total of 223 IFNAR drugs worldwide, from 250 organizations, covering 133 indications, and conducting 1791 clinical trials.
Overall, the target IFNAR presents a competitive landscape with promising growth opportunities. The advancements in R&D, approved indications, and country/location development indicate a positive future for the treatment options targeting IFNAR.
👇Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Interferon Beta-1b is a drug that has been approved for treating relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis. It belongs to the Interferon class and specifically targets the IFNAR receptor. The drug was developed by Chiron Corp and received its first approval in the US in 1993. It has also been approved in other countries, such as China. Interferon Beta-1b has been granted accelerated approval and orphan drug status, which highlights its significance in addressing the medical needs of MS patients.