Demystifying H2 receptor antagonists: A Comprehensive Guide and How to Keep Up with the Latest Developments
The H2 receptor, also known as the histamine H2 receptor, plays a crucial role in the human body. It is primarily found in the stomach lining and is responsible for regulating the production of gastric acid. Activation of the H2 receptor by histamine leads to an increase in acid secretion, which aids in the digestion of food. However, excessive acid production can lead to conditions like gastric ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Therefore, pharmaceutical companies have developed H2 receptor antagonists, commonly known as H2 blockers, to inhibit the receptor's activity and reduce acid secretion, providing relief from acid-related disorders.
Looking forward, the future of H2 receptor antagonists appears promising. Recent studies suggest that H2 receptor antagonists show significant promise as radioprotective agents. They could potentially be used for providing partial protection against radiation injury. Furthermore, there is ongoing research into repurposing H2 receptor antagonists for other uses. The global H2-receptor antagonists market is anticipated to grow at a substantial CAGR in the upcoming years. These developments suggest that H2 receptor antagonists could play a significant role in the treatment of various diseases in the future.
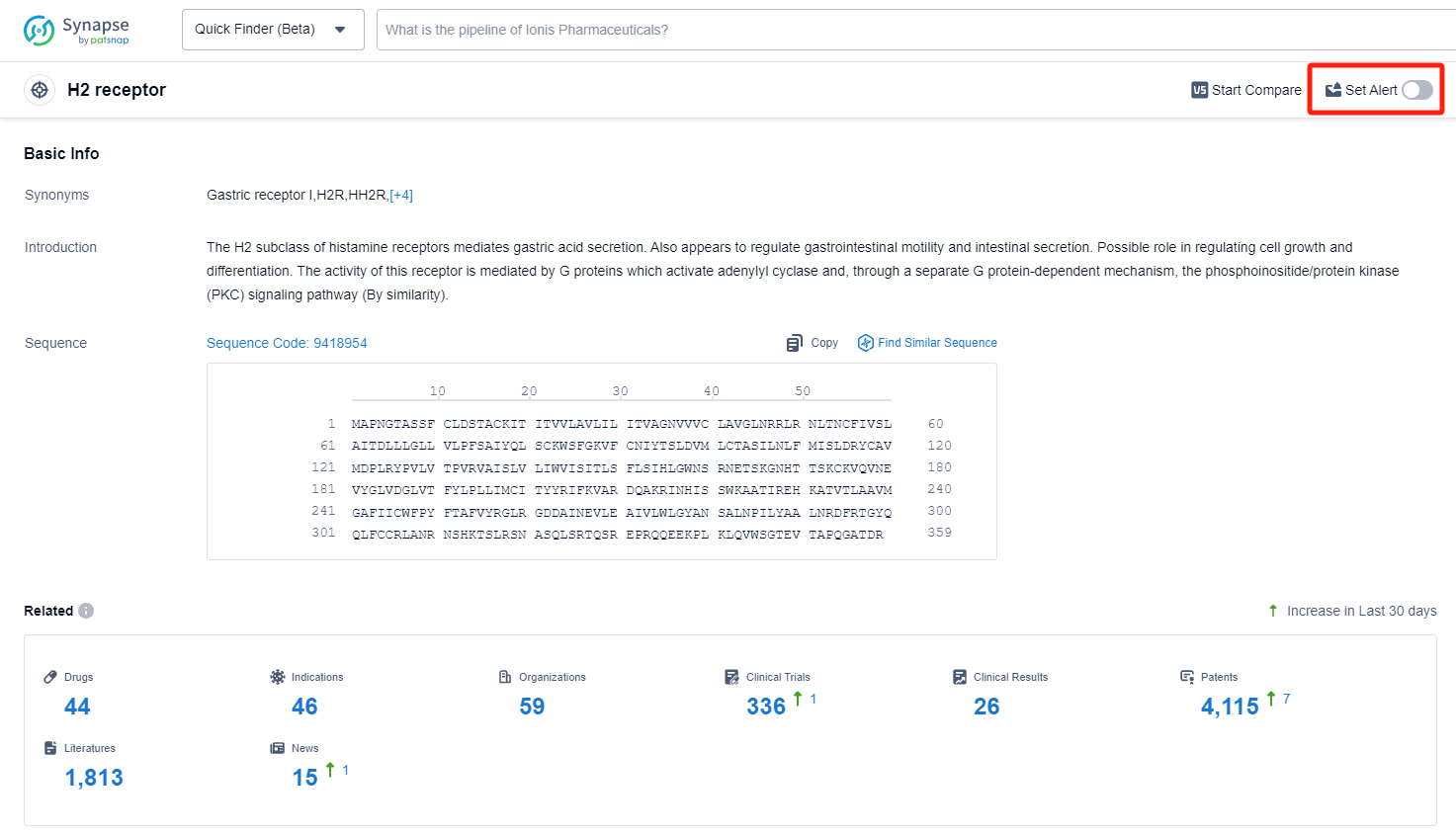
The analysis of the target H2 receptor reveals a competitive landscape with multiple companies focusing on the development of drugs for various indications related to gastrointestinal disorders. GSK Plc is leading in terms of the highest number of drugs in the approved stage. Small molecule drugs are the most common drug type, indicating intense competition. China, the United States, Japan, and South Korea are the countries/locations with the highest development progress. China, in particular, has made significant progress in the development of drugs for the target H2 receptor. The future development of the target H2 receptor is expected to continue with a focus on innovative small molecule drugs and biosimilars, particularly in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
How do they work?
H2 receptor antagonists, also known as H2 blockers, are a class of drugs that inhibit the action of histamine on the H2 receptors in the stomach. Histamine is a chemical released by cells in the stomach lining and stimulates the production of stomach acid. By blocking the H2 receptors, H2 receptor antagonists reduce the production of stomach acid, thereby decreasing acid-related symptoms and promoting healing of certain gastrointestinal conditions.
From a biomedical perspective, H2 receptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and gastritis. These drugs help alleviate symptoms like heartburn, acid reflux, and stomach pain by reducing the amount of acid produced in the stomach. They are often prescribed as a first-line treatment for these conditions and are available both over-the-counter and by prescription.
Examples of H2 receptor antagonists include famotidine, ranitidine, and cimetidine. These drugs work by binding to the H2 receptors on the surface of stomach cells, preventing histamine from binding and triggering acid production. By reducing gastric acid secretion, H2 receptor antagonists provide relief from acid-related symptoms and promote the healing of damaged stomach lining.
It's important to note that while H2 receptor antagonists are effective in managing certain gastrointestinal conditions, they may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications should consult with their healthcare provider before using H2 receptor antagonists. Additionally, prolonged use of these drugs may have some side effects, such as headaches, dizziness, and diarrhea. Therefore, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment as advised by a healthcare professional.
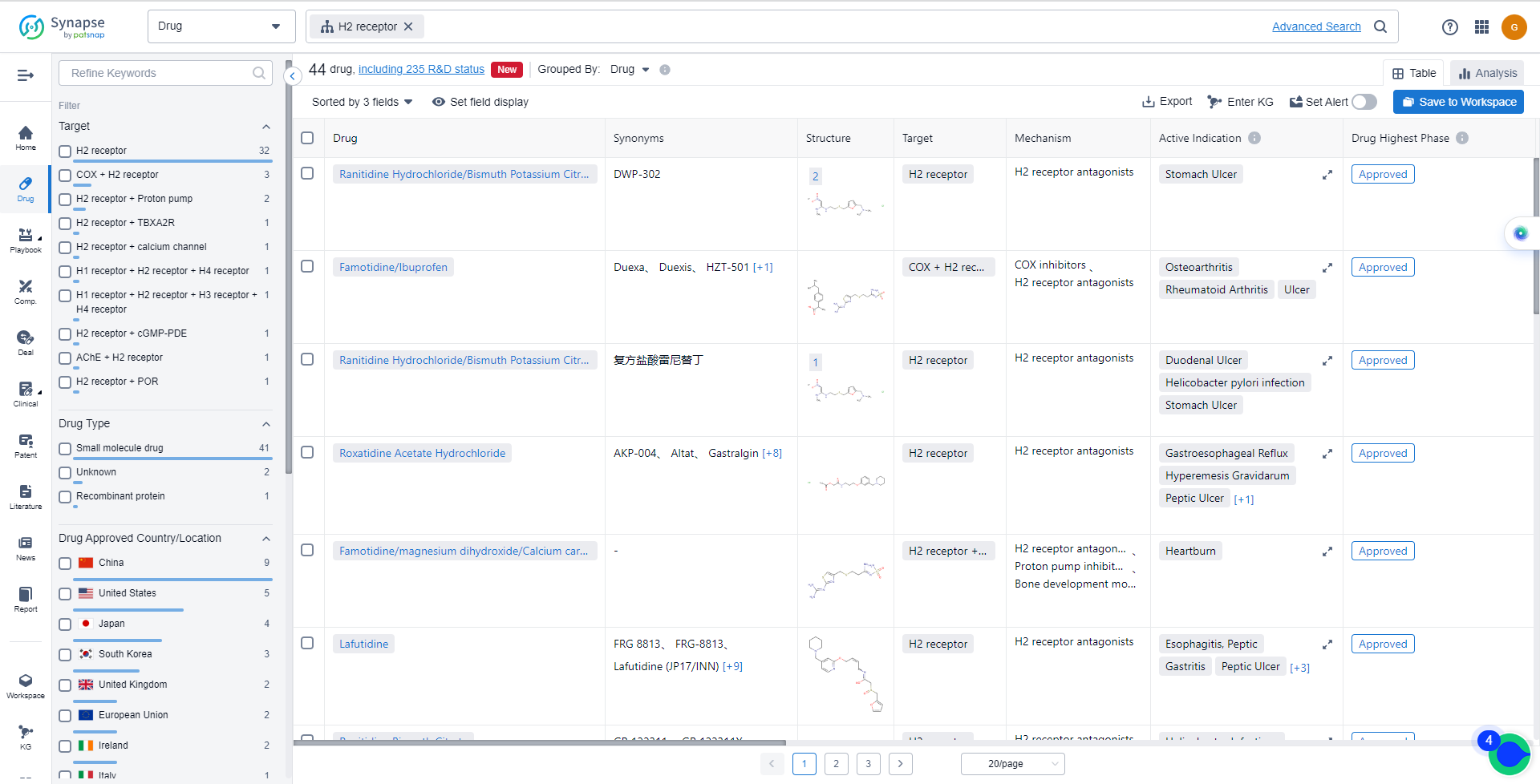
List of H2 receptor Antagonists
The currently marketed H2 receptor antagonists include:
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride/Bismuth Potassium Citrate/Sucralfate
- Famotidine/Ibuprofen
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride/Bismuth Potassium Citrate
- Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride
- Famotidine/magnesium dihydroxide/Calcium carbonate
- Lafutidine
- Ranitidine Bismuth Citrate
- Nizatidine
- Famotidine
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride
For more information, please click on the image below.
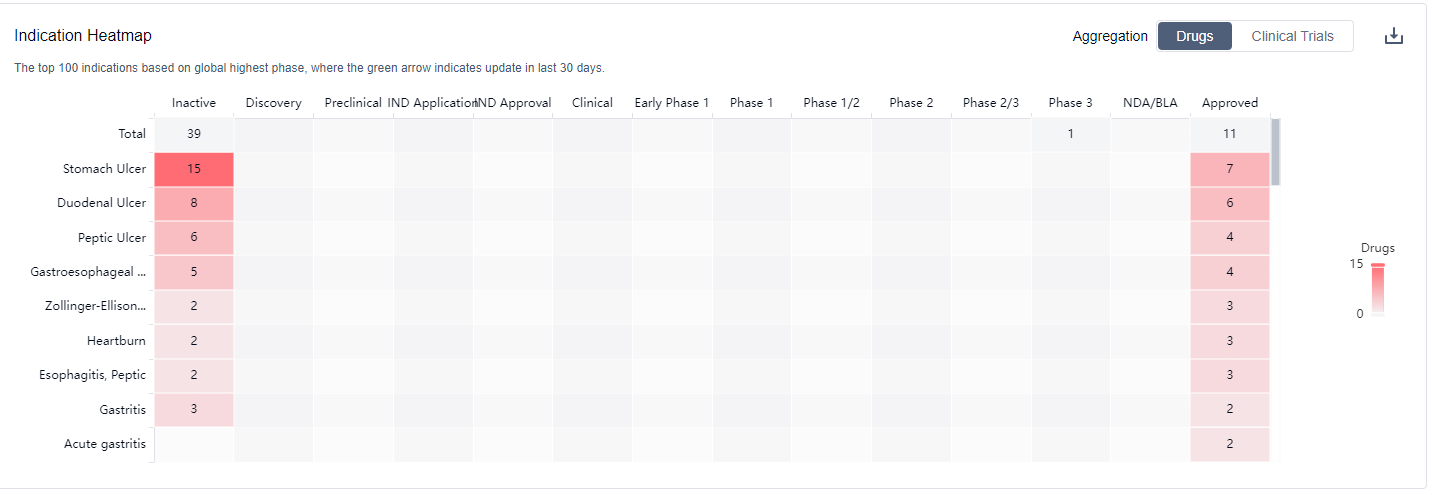
What are H2 receptor antagonists used for?
H2 receptor antagonists are commonly used in the treatment of conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and gastritis. For more information, please click on the image below to log in and search.
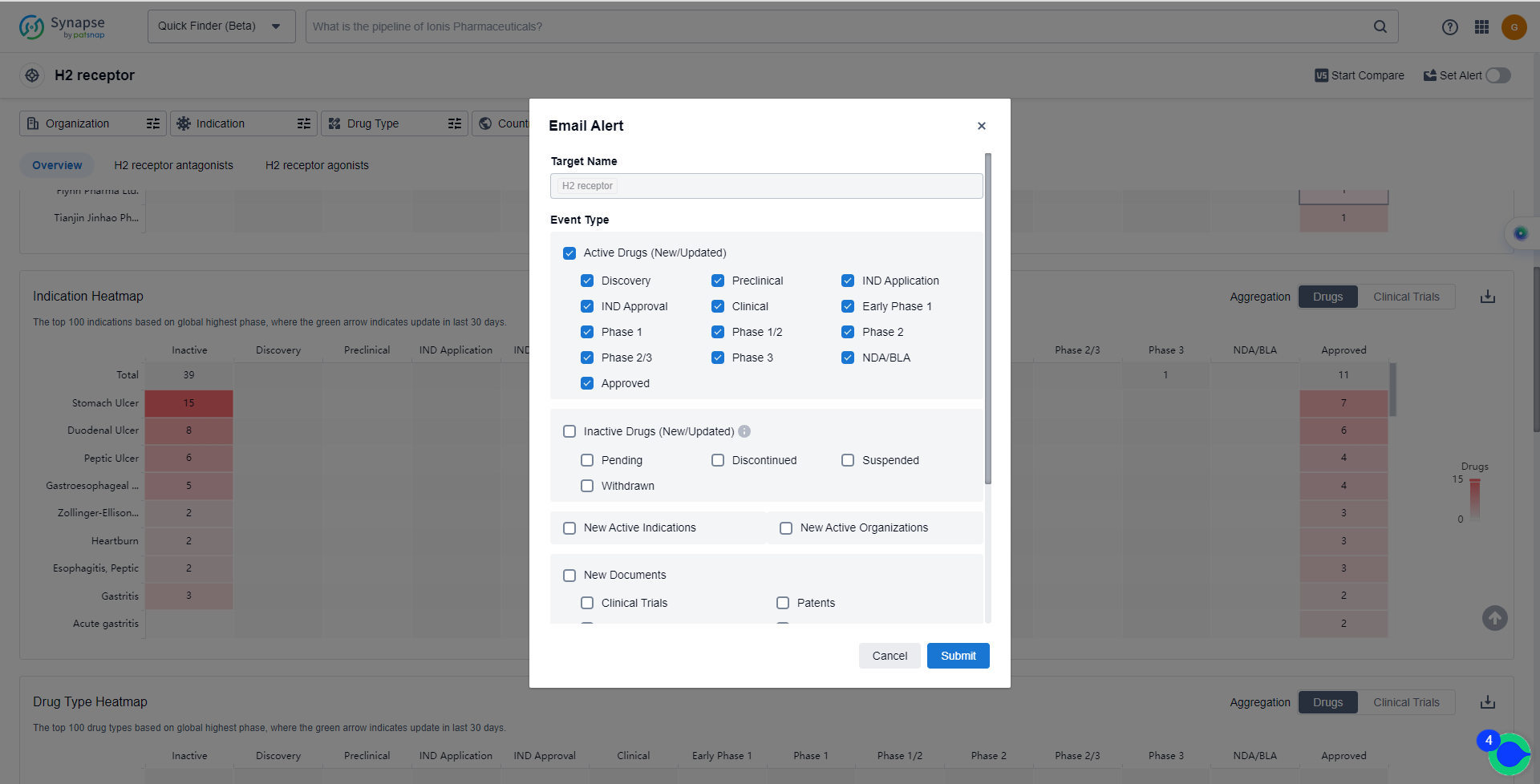
How to obtain the latest development progress of H2 receptor antagonists?
In the Synapse database, you can keep abreast of the latest research and development advances of H2 receptor antagonists anywhere and anytime, daily or weekly, through the "Set Alert" function. Click on the image below to embark on a brand new journey of drug discovery!